In face-centred cubic, all directions are still equivalent, since all contain a sphere in the centre of the face. Thus, by turning it into a smaller body-centred tetragonal lattice we would be losing symmetry by making c unequal from a and b — this is not desirable.
Q. What is tetragonal unit cell?
The tetragonal unit cell is distinguished by an axis of fourfold symmetry, about which a rotation of the cell through an angle of 90° brings the atoms into coincidence with their initial positions. Crystals in a tetragonal system are characterized by three mutually perpendicular axes, two of which are equal in length.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is tetragonal unit cell?
- Q. How many atoms are in a tetragonal unit cell?
- Q. How many lattices are possible for the tetragonal structure?
- Q. Why are there only 14 Bravais lattices?
- Q. What are 14 Bravais lattices?
- Q. Which crystal system has maximum Bravais lattice?
- Q. What is called Bravais lattice?
- Q. What are the types of Bravais lattice?
- Q. How many Bravais lattice are there?
- Q. What is the difference between crystal system and Bravais lattice?
- Q. What are the 6 basic crystal systems?
- Q. What are the types of crystal structure?
- Q. What determines crystal structure?
- Q. What is the difference between a crystal structure and a crystal system?
- Q. Why is crystal structure important?
- Q. What is unit cell in crystal?
- Q. How does crystal structure affect mechanical properties?
- Q. What are the three types of crystalline structures?
- Q. How many types of crystal are found?
- Q. What are the four types of crystal?
- Q. What is the difference between crystal and gemstone?
- Q. Are Diamonds crystals?
- Q. How do you activate crystals?
- Q. Do crystals shine like diamonds?
- Q. Do diamonds have healing powers?
Q. How many atoms are in a tetragonal unit cell?
The simplest crystal structures are those in which there is only a single atom at each lattice point. In the fcc structures the spheres fill 74 % of the volume. The number of atoms in a unit cell is four (8×1/8 + 6×1/2 = 4). There are 26 metals that have the fcc lattice.
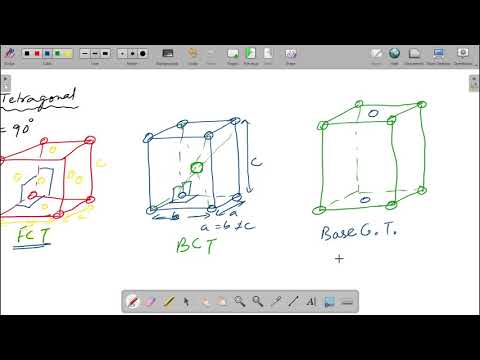
Q. How many lattices are possible for the tetragonal structure?
two
Q. Why are there only 14 Bravais lattices?
The Bravais lattices come from unit cells which have an internal symmetry. There are again not so many possibilities to have an internal symmetry, so this only makes 14 Bravais lattices out of the 7 crystal systems.
Q. What are 14 Bravais lattices?
The fourteen Bravais lattices
- Cubic (3 lattices) The cubic system contains those Bravias lattices whose point group is just the symmetry group of a cube.
- Tetragonal (2 lattices)
- Orthorhombic (4 lattices)
- Monoclinic (2 lattices)
- Triclinic (1 lattice)
- Trigonal (1 lattice)
- Hexagonal (1 lattice)
Q. Which crystal system has maximum Bravais lattice?
orthorhombic-type crystal
Q. What is called Bravais lattice?
Bravais Lattice refers to the 14 different 3-dimensional configurations into which atoms can be arranged in crystals. Thus, a Bravais lattice can refer to one of the 14 different types of unit cells that a crystal structure can be made up of. These lattices are named after the French physicist Auguste Bravais.
Q. What are the types of Bravais lattice?
In 3 dimensions
| Crystal family | Lattice system | 14 Bravais lattices |
|---|---|---|
| Primitive (P) | ||
| Orthorhombic | oP | |
| Tetragonal | tP | |
| Hexagonal | Rhombohedral | hR |
Q. How many Bravais lattice are there?
fourteen Bravais lattices
Q. What is the difference between crystal system and Bravais lattice?
Crystal system is a method of classifying crystalline substances on the basis of their unit cell. Bravais lattice is a set of points constructed by translating a single point in discrete steps by a set of basis vectors.
Q. What are the 6 basic crystal systems?
There are six basic crystal systems.
- Isometric system.
- Tetragonal system.
- Hexagonal system.
- Orthorhombic system.
- Monoclinic system.
- Triclinic system.
Q. What are the types of crystal structure?
The Seven Crystal Systems
- Triclinic System: All three axes are inclined towards each other, and they are of the same length.
- Monoclinic System:
- Orthorhombic System:
- Trigonal System:
- Hexagonal System:
- Tetragonal Systems:
- Cubic System:
Q. What determines crystal structure?
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the ordered arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystalline material. The unit cell completely reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal, which is built up by repetitive translation of the unit cell along its principal axes.
Q. What is the difference between a crystal structure and a crystal system?
Answer: A crystal structure is described by both the geometry of, and atomic arrangements within, the unit cell, whereas a crystal system is described only in terms of the unit cell geometry. For example, face-centered cubic and body-centered cubic are crystal structures that belong to the cubic crystal system.
Q. Why is crystal structure important?
A great example of the importance of crystal structure is the difference between two minerals; graphite and diamond. This shows us that it is not only important to know what elements are in the mineral, but it is also very important to know how those elements are stacked together.
Q. What is unit cell in crystal?
A unit cell is the smallest portion of a crystal lattice that shows the three-dimensional pattern of the entire crystal. A crystal can be thought of as the same unit cell repeated over and over in three dimensions. The Figure below illustrates the relationship of a unit cell to the entire crystal lattice.
Q. How does crystal structure affect mechanical properties?
The structure of the atoms affects the properties of the material, for example FCC metals and alloys have very good ductility. The crystal structure contains imperfections, such as point defects (for example solute atoms, vacancies) and dislocations, and these govern many of the properties of the material.
Q. What are the three types of crystalline structures?
Crystalline solids consist of repeating, three-dimensional patterns or lattices of molecules, ions or atoms. These particles tend to maximize the spaces they occupy, creating solid, nearly incompressible structures. There are three main types of crystalline solids: molecular, ionic and atomic.
Q. How many types of crystal are found?
four types
Q. What are the four types of crystal?
Crystalline substances can be described by the types of particles in them and the types of chemical bonding that takes place between the particles. There are four types of crystals: (1) ionic , (2)metallic , (3) covalent network, and (4) molecular .
Q. What is the difference between crystal and gemstone?
Gemstones – what are the differences? A gem is a rare mineral. This mineral is of the purest quality, so it is priced highly and considered “gem quality.” A crystal is a pure substance that has its molecules arranged in such a way that it creates a geometric pattern formation in some way.
Q. Are Diamonds crystals?
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond also has relatively high optical dispersion (ability to disperse light of different colors). Most natural diamonds have ages between 1 billion and 3.5 billion years.
Q. How do you activate crystals?
The trick with crystals is that you need to make them your own and “program” them with a specific intention before they can start working for you….The best times to clear your crystals & 5 ways to do it.
- Use sea salt.
- Use running water.
- Use other stones.
- Place them underneath the full moon.
- Bathe them in moon water.
Q. Do crystals shine like diamonds?
They are all human-made and contain lead glass, the component that makes the crystals sparkle as brilliantly as real diamonds.
Q. Do diamonds have healing powers?
Diamonds are very high frequency stones that can open all chakra channels, giving out positive healing properties. Diamonds hold a very powerful energy that many people take for granted. When one taps into its energy, they will find that it greatly enhances inner vision.