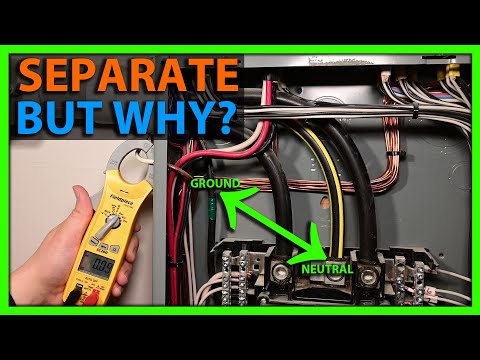
Grounds and neutrals were isolated to provide separate paths back to the panel. Another way to wire a subpanel was with a three-wire feed; two hots and a neutral, with grounds and neutrals connected together at the subpanel. In this case, the grounds and neutrals have to be connected together.
Q. What is difference between ground and neutral?
It can be stated that Neutral can be grounded, but Ground is not neutral. A Neutral represents a reference point within an electrical distribution system. A Ground represents an electrical path, normally designed to carry fault current when a insulation breakdown occurs within electrical equipment.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is difference between ground and neutral?
- Q. Can you touch the neutral bus bar?
- Q. What is the point of a neutral wire?
- Q. How much current is on the neutral?
- Q. Which wire is hot when both are black?
- Q. Why does neutral wire have voltage?
- Q. Why neutral current is high?
- Q. Why 3rd harmonics is dangerous?
- Q. Why is neutral current bad?
- Q. Is neutral current dangerous?
Q. Can you touch the neutral bus bar?
If the main breaker were on, all of the exposed stabs for the bus bar are all going to be carrying electricity. So you’re not going to want to touch any of that. The neutral is also a potential shock point if the power is on. Try to avoid touching any of the incoming service lines.
Q. What is the point of a neutral wire?
Neutral wire carries the circuit back to the original power source. More specifically, neutral wire brings the circuit to a ground or busbar usually connected at the electrical panel. This gives currents circulation through your electrical system, which allows electricity to be fully utilized.
Q. How much current is on the neutral?
In a perfectly balanced 3 phase system, the neutral current will be zero. This is because the neutral carries the vector sum the currents in the other 3 phases which when balanced sum to zero.
Q. Which wire is hot when both are black?
The black wire is the “hot” wire, which carries the electricity from the breaker panel into the switch or light source. The white wire is the “neutral” wire, which takes any unused electricity and current and sends them back to the breaker panel.
Q. Why does neutral wire have voltage?
All neutral wires of the same earthed (grounded) electrical system should have the same electrical potential, because they are all connected through the system ground. Neutral conductors are usually insulated for the same voltage as the line conductors, with interesting exceptions.
Q. Why neutral current is high?
High neutral currents can be caused by unbalanced and/or non-linear loads with high harmonics. K-rated transformers have a 200% rated neutral. Amperage should be measured with a meter capable of measuring true RMS currents.
Q. Why 3rd harmonics is dangerous?
The third harmonic causes a sharp increase in the current in the neutral conductor. Harmonics cause malfunctioning of electronic parts, transformer heating, and malfunctioning of power factor correction capacitors.
Q. Why is neutral current bad?
Whether because of load shifts and changes, or due to the diversity of loads being on or off at the same time, neutral current from unbalance may become high, but is seldom excessive. Problems happen when the neutral wire has been undersized and high currents still occur — possibly leading to a burnt neutral.
Q. Is neutral current dangerous?
The power wire that is grounded is called the “neutral” wire because it is not dangerous with respect to exposed metal parts or plumbing. The “hot” wire gets its name because it is dangerous. The grounding of the neutral wire is not related to the operation of electrical equipment but is required for reasons of safety.