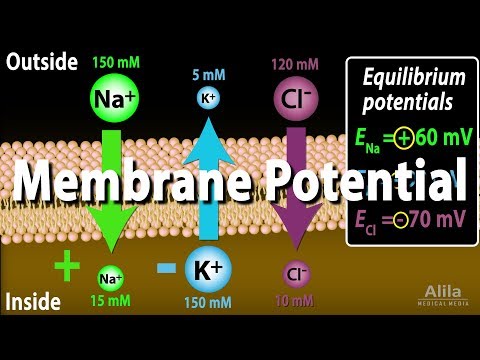
Because of this, the sodium equilibrium potential—the electrical potential difference across the cell membrane that exactly balances the Na+start text, N, a, end text, start superscript, plus, end superscript concentration gradient—will be positive. The channels open and Na+ can move through them.
Q. How is a resting potential maintained?
Resting membrane potentials are maintained by two different types of ion channels: the sodium-potassium pump and the sodium and potassium leak channels. The sodium-potassium pump moves three sodium ions out of the cell for every two potassium ions it moves into the cell continuously.
Table of Contents
- Q. How is a resting potential maintained?
- Q. Why is a resting potential important?
- Q. What happens during depolarization of the heart?
- Q. What happens during the depolarization phase of nerve cells quizlet?
- Q. What happens during the depolarization phase of nerve cells?
- Q. When the nerve signal reaches the axon terminal What happens next?
- Q. Which of the meninges provides the major protection for the brain and spinal cord?
Q. Why is a resting potential important?
Of primary importance, however, are neurons and the three types of muscle cells: smooth, skeletal, and cardiac. Hence, resting membrane potentials are crucial to the proper functioning of the nervous and muscular systems.
Q. What happens during depolarization of the heart?
Depolarization of the heart leads to the contraction of the heart muscles and therefore an EKG is an indirect indicator of heart muscle contraction. The cells of the heart will depolarize without an outside stimulus. This property of cardiac muscle tissue is called automaticity, or autorhythmicity.
Q. What happens during the depolarization phase of nerve cells quizlet?
What happens during the depolarization phase of nerve cells? It is an undisturbed period of the action potential during which the nerve is not transmitting impulses. The cell membrane decreases its permeability to sodium. The neurons are stimulated to fire.
Q. What happens during the depolarization phase of nerve cells?
Depolarization occurs when a stimulus reaches a resting neuron. During the depolarization phase, the gated sodium ion channels on the neuron’s membrane suddenly open and allow sodium ions (Na+) present outside the membrane to rush into the cell.
Q. When the nerve signal reaches the axon terminal What happens next?
Once at the axon terminal, neurotransmitters are released into the synapse that is formed between the axon terminal and a dendrite from another neuron (Figure 5.). The dendrites of the receiving cell send neurotansmitter information to the cell body and the process starts over again.
Q. Which of the meninges provides the major protection for the brain and spinal cord?
Immediately outside the arachnoid is a continuous sheath of strong connective tissue, the dura mater, which provides the major protection for the brain and spinal cord.