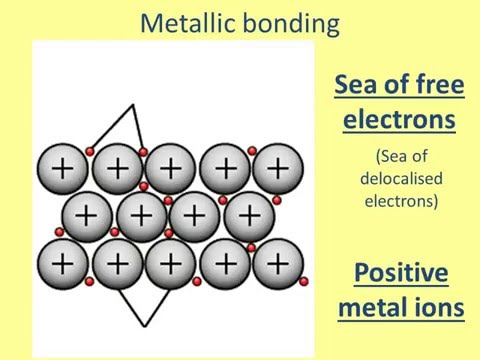
The valence electrons of metals move freely in this way because metals have relatively low electronegativity, or attraction to electrons. The positive metal ions form a lattice-like structure held together by all the metallic bonds. When nonmetals bond together, the atoms share valence electrons and do not become ions.
Q. What does the sea of electrons help explain?
That is to say, instead of orbiting their respective metal atoms, they form a “sea” of electrons that surrounds the positively charged atomic nuclei of the interacting metal ions. Metals are good conductors of electricity because the electrons in the electron sea are free to flow and carry electric current.
Table of Contents
- Q. What does the sea of electrons help explain?
- Q. What is the electron sea model *?
- Q. What does the electron sea model for metals suggest?
- Q. Which is a characteristic of the electron sea model?
- Q. Why do electrons become Delocalised in metals?
- Q. Are all electrons Delocalised in metals?
- Q. What does it mean when electrons are delocalized?
- Q. Can two metals bond?
- Q. What type of bond has 2 metals?
- Q. What is it called when you mix two metals together?
- Q. How do metals bond to one another?
- Q. What are the 5 metallic properties and explanation?
- Q. Which of the following bonds is the strongest?
- Q. Is a hydrogen bond?
- Q. How many types of hydrogen bond are there?
- Q. What is the difference between a covalent bond and a hydrogen bond?
- Q. Which hydrogen bond is strongest?
- Q. What is the weakest hydrogen bond?
- Q. Are covalent bonds strong or weak?
- Q. Why are hydrogen bonds so strong?
- Q. Which is stronger dipole or hydrogen?
- Q. Are hydrogen bonds strong in DNA?
- Q. Are hydrogen bonds strong or weak?
- Q. Why are hydrogen bonds weak in DNA?
- Q. Why does C and G have 3 hydrogen bonds?
- Q. Why does a pair with T and C with G?
Q. What is the electron sea model *?
(a) The model of metallic bonding where electrons float free in a sea of electrons around metal atoms.
Q. What does the electron sea model for metals suggest?
electron sea model for metals suggest that valence electrons drift freely around the metal cations. Explanation: These electrons are free to move within the metal atoms. Thus, we can conclude that the electron sea model for metals suggest that valence electrons drift freely around the metal cations.
Q. Which is a characteristic of the electron sea model?
-Electron sea model: Electrons all have approximately the same energy. -Band theory: Electrons move among orbitals of different energies. -Both models: Electrons move freely among atoms (delocalized). Copper (Cu) is often used for electrical wiring and cooking pans.
Q. Why do electrons become Delocalised in metals?
Metals tend to have high melting points and boiling points suggesting strong bonds between the atoms. The electrons can move freely within these molecular orbitals, and so each electron becomes detached from its parent atom. The electrons are said to be delocalized.
Q. Are all electrons Delocalised in metals?
Metallic bonding Metals consist of giant structures of atoms arranged in a regular pattern. The electrons from the outer shells of the metal atoms are delocalised , and are free to move through the whole structure. This sharing of delocalised electrons results in strong metallic bonding .
Q. What does it mean when electrons are delocalized?
In chemistry, delocalized electrons are electrons in a molecule, ion or solid metal that are not associated with a single atom or a covalent bond. In solid-state physics, this refers to free electrons that facilitate electrical conduction.
Q. Can two metals bond?
Metallic bonds occur among metal atoms. Whereas ionic bonds join metals to non-metals, metallic bonding joins a bulk of metal atoms. A sheet of aluminum foil and a copper wire are both places where you can see metallic bonding in action. A mixture of two or more metals is called an alloy.
Q. What type of bond has 2 metals?
Ionic Bonds An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond formed through an electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions. Ionic bonds are formed between a cation, which is usually a metal, and an anion, which is usually a nonmetal.
Q. What is it called when you mix two metals together?
An alloy is an admixture of metals, or a metal combined with one or more other elements. Combining iron with non-metallic carbon or silicon produces alloys called steel or silicon steel.
Q. How do metals bond to one another?
Metallic bond, force that holds atoms together in a metallic substance. The atoms that the electrons leave behind become positive ions, and the interaction between such ions and valence electrons gives rise to the cohesive or binding force that holds the metallic crystal together. …
Q. What are the 5 metallic properties and explanation?
Metals are lustrous, malleable, ductile, good conductors of heat and electricity. Other properties include: State: Metals are solids at room temperature with the exception of mercury, which is liquid at room temperature (Gallium is liquid on hot days).
Q. Which of the following bonds is the strongest?
Electronic repulsions are absent in hydrogen molecule as an atom of hydrogen has only one electron. Also the bond length is least in Hydrogen molecule. Smaller the bond length, more is the bond energy. So, H−H bond is the strongest bond among the given options.
Q. Is a hydrogen bond?
Hydrogen bonding, interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity for electrons; such a bond is weaker than an ionic bond or covalent bond but stronger than van der Waals forces.
Q. How many types of hydrogen bond are there?
Hydrogen bondings are of two types, and it is classified as the following: The Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding. The Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonding.
Q. What is the difference between a covalent bond and a hydrogen bond?
Covalent bonds are intramolecular bonds whereas hydrogen bonds are intermolecular bonds. Water is held together with covalent bonds. In covalent bonds, electrons are shared between the atoms. Due to these partial charges, the hydrogen is also attracted to the oxygen atom of a second water molecule.
Q. Which hydrogen bond is strongest?
As fluorine has small size and high electronegativity, it has high tendency to attract partial positive charge accumulated on H-atom. So, fluorine forms strongest H-bond.
Q. What is the weakest hydrogen bond?
Weakest hydrogen bond will be formed when the electronegativity difference between the atom and H is the least. Hence, S−H−−−−−H form the weakest hydrogen bond.
Q. Are covalent bonds strong or weak?
Covalent bonds are strong – a lot of energy is needed to break them. Substances with covalent bonds often form molecules with low melting and boiling points, such as hydrogen and water.
Q. Why are hydrogen bonds so strong?
Hydrogen bonding is so strong among dipole-dipole interactions because it itself is a dipole-dipole interaction with one of the strongest possible electrostatic attractions. Remember that hydrogen bonding cannot occur unless hydrogen is covalently bonded to either oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine.
Q. Which is stronger dipole or hydrogen?
Although a hydrogen bond is much stronger than an ordinary dipole-dipole force, it is roughly one-tenth as strong as a covalent bond between atoms of the same two elements. Hydrogen bonding in alcohol is stronger than dipole-dipole interactions in alkyl halides.
Q. Are hydrogen bonds strong in DNA?
Hydrogen bonds are weak, noncovalent interactions, but the large number of hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs in a DNA double helix combine to provide great stability for the structure.
Q. Are hydrogen bonds strong or weak?
The hydrogen bond is one of the strongest intermolecular attractions, but weaker than a covalent or an ionic bond. Hydrogen bonds are responsible for holding together DNA, proteins, and other macromolecules.
Q. Why are hydrogen bonds weak in DNA?
Hydrogen bonds do not involve the exchange or sharing of electrons like covalent and ionic bonds. The weak attraction is like that between the opposite poles of a magnet. Hydrogen bonds occur over short distances and can be easily formed and broken. They can also stabilize a molecule.
Q. Why does C and G have 3 hydrogen bonds?
Guanine pairs with cytosine with 3 hydrogen bonds. This creates a difference in strength between the two sets of Watson and Crick bases. Guanine and cytosine bonded base pairs are stronger then thymine and adenine bonded base pairs in DNA.
Q. Why does a pair with T and C with G?
The only pairs that can create hydrogen bonds in that space are adenine with thymine and cytosine with guanine. A and T form two hydrogen bonds while C and G form three. It’s these hydrogen bonds that join the two strands and stabilize the molecule, which allows it to form the ladder-like double helix.