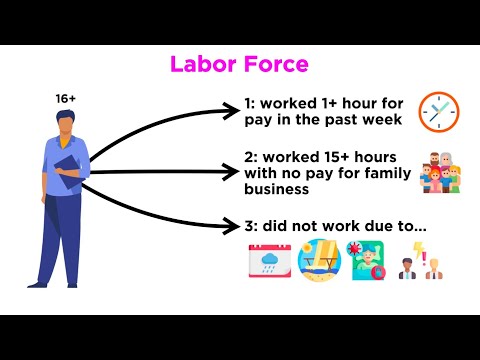
The labor force includes all people age 16 and older who are classified as either employed and unemployed, as defined below. Conceptually, the labor force level is the number of people who are either working or actively looking for work.
Q. What is meant by the Labour force supply?
The supply of labour is defined as the amount of labour, measured in person-hours, offered for hire during a given time-period. This amount can conveniently be expressed as a fraction or percentage of the total population, to give an activity or labour force participation rate.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is meant by the Labour force supply?
- Q. What are the two forms of labor?
- Q. What factors influence Labour supply?
- Q. How does supply and demand affect labor?
- Q. How is Labour a derived demand?
- Q. What is the demand for labor called?
- Q. What two things determine the demand for labor for every type of firm?
- Q. What shifts the labor demand curve?
- Q. What is the long run labor demand condition with respect to labor?
- Q. What is it called when the use of Labour is increased or decreased in the short run?
- Q. What is labor demand and supply?
- Q. What two factors affect the demand for labor?
- Q. What are the determinants of the labor demand and supply elasticities?
- Q. Which of the following does not affect labor demand?
- Q. What is the marginal product of labor MPN )?
- Q. Which statement best characterizes the impact education and training have on the demand for labor?
- Q. When we say that the demand for labor is a derived demand we mean that the demand is?
- Q. What is the meaning of Labour market?
- Q. Why do economists say labor is a derived demand?
- Q. What would be another example of a derived demand?
- Q. What is a derived demand in transport?
- Q. What is meant by fluctuations in demand?
- Q. What is autonomous and derived demand?
- Q. What are the 4 types of demand?
- Q. What are the three major types of demand?
- Q. What are the 6 factors that affect demand?
- Q. What factors affect demand and supply?
Q. What are the two forms of labor?
Kinds of Labour:
- Physical and Mental Labour.
- Skilled and Unskilled Labour. ADVERTISEMENTS:
- Productive and Unproductive Labour.
Q. What factors influence Labour supply?
The supply of labour is affected by numerous factors including the wage rate, migration patterns, changes in income tax, benefit reform, trade unions, government labour regulations, changes in the retirement age and female participation in the workforce.
Q. How does supply and demand affect labor?
When the supply of labor increases the equilibrium price falls, and when the demand for labor increases the equilibrium price rises. Therefore, firms will continue to add labor (hire workers) until the MRPL equals the wage rate. Thus, workers earn a wage equal to the marginal revenue product of their labor.
Q. How is Labour a derived demand?
Demand for labour is a derived demand. This means it depends on demand for the product the worker is producing. The demand for labour will also depend on labour productivity, the price of the good and their overall profitability to a firm.
Q. What is the demand for labor called?
Demand for labor is a concept that describes the amount of demand for labor that an economy or firm is willing to employ at a given point in time. This demand may not necessarily be in long-run equilibrium. This relationship is also called the marginal product of labor (MPL) in the economics community.
Q. What two things determine the demand for labor for every type of firm?
The wage and supply of labor determine the demand for labor for every firm type.
Q. What shifts the labor demand curve?
Factors that can shift the demand curve for labor include: a change in the quantity demanded of the product that the labor produces; a change in the production process that uses more or less labor; and a change in government policy that affects the quantity of labor that firms wish to hire at a given wage.
Q. What is the long run labor demand condition with respect to labor?
The long-run demand for labor is a schedule or curve indicating the amount of labor that firms will employ at each possible wage rate when both L and K are variable.
Q. What is it called when the use of Labour is increased or decreased in the short run?
Marginal product is the change in output from increasing the number of workers used by one person, or by adding one more machine to the production process in the short run.
Q. What is labor demand and supply?
A labor supply curve shows the number of workers who are willing and able to work in an occupation at different wages. A labor demand curve shows the number of workers firms are willing and able to hire at different wages.
Q. What two factors affect the demand for labor?
Q. What are the determinants of the labor demand and supply elasticities?
Elasticity of Labour Demand: 4 Major Determinants
- Determinant # 1. The Availability of Good Substitutes:
- Determinant # 2. Elasticity of Demand for the Products of Unionized Firms:
- Determinant # 3. The Proportion of Labour Cost in Total Cost:
- Determinant # 4. The Elasticity of Supply of Substitute Inputs:
Q. Which of the following does not affect labor demand?
Which of the following does not affect labor demand? The supply of labor. According to the upward-sloping labor supply curve, at lower wages: Workers are less willing to supply labor.
Q. What is the marginal product of labor MPN )?
The MPN curve shows the marginal product of labor at each level of employment. It is related to the production function because the marginal product of labor is equal to the slope of the production function (where output is plotted against employment).
Q. Which statement best characterizes the impact education and training have on the demand for labor?
Which statement best characterizes the impact education and training have on the demand for labor? An educated and trained workforce shifts demand to the right because employers want workers with specialized training.
Q. When we say that the demand for labor is a derived demand we mean that the demand is?
We say that the demand for labor is a derived demand because: we demand the product that labor helps produce rather than labor service per se.
Q. What is the meaning of Labour market?
Definition: A labour market is the place where workers and employees interact with each other. In the labour market, employers compete to hire the best, and the workers compete for the best satisfying job. The supply and demand of labour in the market is influenced by changes in the bargaining power.
Q. Why do economists say labor is a derived demand?
When economists say that the demand for labor is a derived demand, they mean that it is: related to the demand for the product or service labor is producing. an increase in the price of one will increase the demand for the other.
Q. What would be another example of a derived demand?
Examples. Producers have a derived demand for employees. For another example, demand for steel leads to derived demand for steel workers, as steel workers are necessary for the production of steel. As the demand for steel increases, so does its price.
Q. What is a derived demand in transport?
The demand for transport is a derived demand, an economic term, which refers to demand for one good or service in one sector occurring as a result of demand from another. Users of transport are primarily consuming the service not because of its direct benefits, but because they wish to access other services.
Q. What is meant by fluctuations in demand?
demand in the industrial sector which rises and falls sharply in response to changing economic conditions and consumer spending patterns.
Q. What is autonomous and derived demand?
The autonomous demand arises due to the natural desire of an individual to consume the product. On the other hand, derived demand refers to the demand for a product that arises due to the demand for other products. For example, the demand for petrol, diesel, and other lubricants depends on the demand of vehicles.
Q. What are the 4 types of demand?
There are four types of demand namely Competitive Demand, Joint or Complementary Demand, Composite Demand and Derived Demand. Demand is the amount of a product buyers are willing and able to purchase at a given price over a particular period of time.
Q. What are the three major types of demand?
Types of demand
- Joint demand.
- Composite demand.
- Short-run and long-run demand.
- Price demand.
- Income demand.
- Competitive demand.
- Direct and derived demand.
Q. What are the 6 factors that affect demand?
6 Important Factors That Influence the Demand of Goods
- Tastes and Preferences of the Consumers: ADVERTISEMENTS:
- Income of the People:
- Changes in Prices of the Related Goods:
- Advertisement Expenditure:
- The Number of Consumers in the Market:
- Consumers’ Expectations with Regard to Future Prices:
Q. What factors affect demand and supply?
Factors That Affect Supply & Demand
- Price Fluctuations. Price fluctuations are a strong factor affecting supply and demand.
- Income and Credit. Changes in income level and credit availability can affect supply and demand in a major way.
- Availability of Alternatives or Competition.
- Trends.
- Commercial Advertising.
- Seasons.