Which of the following statements comparing osmoregulation in marine and freshwater bony fishes is incorrect? Freshwater fishes drink seawater to obtain water and salt ions, while marine fishes drink almost none. This process rids the body of nitrogenous metabolites and other waste products.
Q. Which feature of Osmoregulation is common in both marine and freshwater bony fish?
5) Which feature of osmoregulation is found in both marine and freshwater bony fish? A) using their gills and kidneys to rid themselves of sea salts.
Table of Contents
- Q. Which feature of Osmoregulation is common in both marine and freshwater bony fish?
- Q. How do saltwater fish and freshwater fish Osmoregulation?
- Q. How does Osmoregulation take place in freshwater fish?
- Q. What is Osmoregulation with example?
- Q. What is the process of Osmoregulation?
- Q. What is the importance of Osmoregulation?
- Q. What do you mean by Osmoregulation?
- Q. What organ is responsible for Osmoregulation?
- Q. What happens if Osmoregulation fails?
- Q. How is Osmoregulation maintained in humans?
- Q. What is Osmoregulation how it is maintained in human body?
- Q. Are humans Osmoconformers?
- Q. What animals are Osmoconformers?
- Q. What is Stenohaline example?
- Q. What animals can live in both fresh and saltwater?
Q. How do saltwater fish and freshwater fish Osmoregulation?
The process of osmosis makes the blood of freshwater (FW) fishes have a higher osmotic pressure than the water in which they swim. Saltwater fish are hypoosmotic to the sea, their blood has a lower solute content and, therefore, a lower osmotic pressure (about 400 mOsmol) than sea water (about 1000 mOsmol).
Q. How does Osmoregulation take place in freshwater fish?
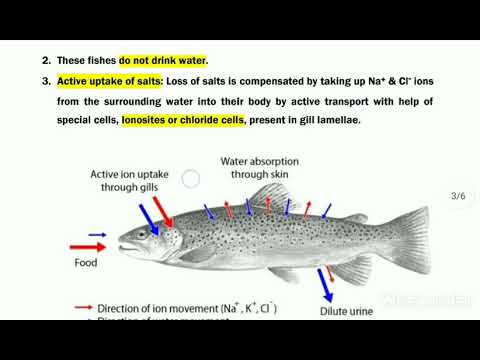
To combat this, freshwater fish have very efficient kidneys that excrete water quickly. They also reabsorb salt from their urine before it is ejected to minimize losses and actively take salt from their environment using special cells in the gills.
Q. What is Osmoregulation with example?
It is the way by which an organism maintains suitable concentration of solutes and amount of water in the body fluids. An example employed by organisms is excretion (such as getting rid of metabolic wastes and other substances toxic to the body when they are in large amounts). See also: osmosis, solute.
Q. What is the process of Osmoregulation?
Osmoregulation is the process of maintenance of salt and water balance (osmotic balance) across membranes within the body’s fluids, which are composed of water plus electrolytes and non-electrolytes. An electrolyte is a solute that dissociates into ions when dissolved in water.
Q. What is the importance of Osmoregulation?
Osmoregulation is an important process in both plants and animals as it allows organisms to maintain a balance between water and minerals at the cellular level despite changes in the external environment.
Q. What do you mean by Osmoregulation?
Osmoregulation, in biology, maintenance by an organism of an internal balance between water and dissolved materials regardless of environmental conditions. Other organisms, however, must actively take on, conserve, or excrete water or salts in order to maintain their internal water-mineral content.
Q. What organ is responsible for Osmoregulation?
Kidneys
Q. What happens if Osmoregulation fails?
Without a mechanism to regulate osmotic pressure, or when a disease damages this mechanism, there is a tendency to accumulate toxic waste and water, which can have dire consequences.
Q. How is Osmoregulation maintained in humans?
Humans. Kidneys play a very large role in human osmoregulation by regulating the amount of water reabsorbed from glomerular filtrate in kidney tubules, which is controlled by hormones such as antidiuretic hormone (ADH), aldosterone, and angiotensin II.
Q. What is Osmoregulation how it is maintained in human body?
Osmoregulation is the process in which the concentration of water and salt or the osmotic pressure is regulated to keep the body in homeostasis. In the body of human beings, it is controlled by the Kidneys. It regulates the amount of water that should go along with the urine.
Q. Are humans Osmoconformers?
Humans are osmoregulators. Other animals which exhibit osmoregulation includes freshwater fish such as rohu. …
Q. What animals are Osmoconformers?
Most osmoconformers are marine invertebrates such as echinoderms (such as starfish), mussels, marine crabs, lobsters, jellyfish, ascidians (sea squirts – primitive chordates), and scallops. Some insects are also osmoconformers.
Q. What is Stenohaline example?
They cannot tolerate the rapid changes in salinity that occur during each tidal cycle in an estuary. Examples include Goldfish and many other marine fishes….Additional Information:
| Euryhaline | Stenohaline |
|---|---|
| Examples include Molly, the green crab, salmon, eels, herring etc. | Examples include Goldfish, haddock etc. |
Q. What animals can live in both fresh and saltwater?
Euryhaline organisms are able to adapt to a wide range of salinities. An example of a euryhaline fish is the molly (Poecilia sphenops) which can live in fresh water, brackish water, or salt water. The green crab (Carcinus maenas) is an example of a euryhaline invertebrate that can live in salt and brackish water.