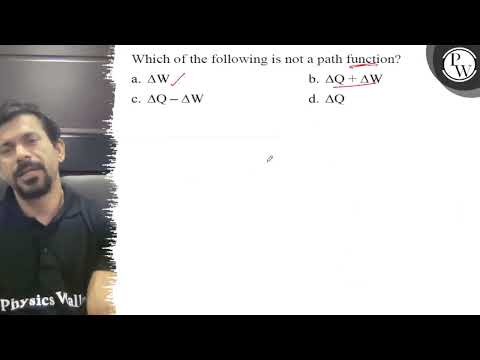Heat and work are path functions because they depend on how a sysem changes from initial to final state, hence they are state functions. Thermal conductivity is mainly a function of the motion of the free electrons therefore property of a material, not a path function.
Q. What is critical juncture?
In the analysis of path-dependent institutions, the concept of critical juncture refers to situations of uncertainty in which decisions of important actors are causally decisive for the selection of one path of institutional development over other possible paths.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is critical juncture?
- Q. Is QA a path function?
- Q. Is kinetic energy an intensive property?
- Q. Is potential energy a force?
- Q. Why is attractive force negative?
- Q. What is the difference between kinetic and potential energy?
- Q. At what point does the ball have the greatest kinetic energy?
- Q. What type of energy did the balls have just before they were released?
- Q. Which ball has the most kinetic energy?
- Q. Which ball has the least potential energy?
- Q. Which ball in Figure 4 1 has the least potential energy?
- Q. Which object has most potential energy?
- Q. Which letter shows the most energy?
- Q. What letter shows the lowest frequency?
- Q. What letter shows the EM wave with the highest energy?
- Q. Which point display the marble when it has the least kinetic energy?
- Q. What is the relationship between mass and kinetic energy?
- Q. What is the relationship between potential energy and height?
- Q. What energy conversion is taking place as the girl moves downwards?
- Q. What are the 4 types of energy transfer?
- Q. Why does the skateboarder eventually stop << read less?
- Q. What law states that energy Cannot be destroyed?
Q. Is QA a path function?
Path function: Their magnitudes depend on the path followed during a process as well as the end states. Work (W), heat (Q) are path functions. Point Function: They depend on the state only, and not on how a system reaches that state. All properties are point functions.
Q. Is kinetic energy an intensive property?
An intensive property, is a physical property of a system that does not depend on the system size or the amount of material in the system. Symbols for representing properties: Extensive properties are symbolized by upper case (capital) letter such as V (volume), KE (kinetic energy), PE (potential energy), etc.
Q. Is potential energy a force?
Negative Signs in Potential F in the definition of potential energy is the force exerted by the force field, e.g., gravity, spring force, etc. The potential energy U is equal to the work you must do against that force to move an object from the U=0 reference point to the position r.
Q. Why is attractive force negative?
Answers and Replies. In the usual radial coordinate system the positive r direction is outward. So a repulsive force is in the positive r direction and an attractive force is in the negative r direction .
Q. What is the difference between kinetic and potential energy?
Potential energy is the stored energy in any object or system by virtue of its position or arrangement of parts. However, it isn’t affected by the environment outside of the object or system, such as air or height. On the other hand, kinetic energy is the energy of an object or a system’s particles in motion.
Q. At what point does the ball have the greatest kinetic energy?
When the ball is held at its highest point, it has potential energy, specifically gravitational potential energy. 2. When the ball is falling towards the table, it has kinetic energy. It has the most kinetic energy at the very end of its descent when it is moving the fastest.
Q. What type of energy did the balls have just before they were released?
tational potential energy. As the ball falls towards the ground, its gravitational potential energy is transformed into kinetic energy. The kinetic energy of an object is the energy it possesses due to its motion.
Q. Which ball has the most kinetic energy?
As the ball falls from C to E, potential energy is converted to kinetic energy. The velocity of the ball increases as it falls, which means that the ball attains its greatest velocity, and thus its greatest kinetic energy, at E. 19.
Q. Which ball has the least potential energy?
Ball C
Q. Which ball in Figure 4 1 has the least potential energy?
3. Which ball in Figure 4-1 has the least potential energy? Car the will have the least.
Q. Which object has most potential energy?
The heavier the object and the higher it is above the ground, the more gravitational potential energy it holds. Gravitational potential energy increases as weight and height increases. Potential energy is energy that is stored in an object or substance.
Q. Which letter shows the most energy?
Gamma rays
Q. What letter shows the lowest frequency?
In modern Morse code, J, Y, and Q are least frequent.
Q. What letter shows the EM wave with the highest energy?
Q. Which point display the marble when it has the least kinetic energy?
Answer: it is in D. Explanation: More potential is to less kinetic that’s why it is on D.
Q. What is the relationship between mass and kinetic energy?
Kinetic energy is directly proportional to the mass of the object and to the square of its velocity: K.E. = 1/2 m v2. If the mass has units of kilograms and the velocity of meters per second, the kinetic energy has units of kilograms-meters squared per second squared.
Q. What is the relationship between potential energy and height?
Since the gravitational potential energy of an object is directly proportional to its height above the zero position, a doubling of the height will result in a doubling of the gravitational potential energy. A tripling of the height will result in a tripling of the gravitational potential energy.
Q. What energy conversion is taking place as the girl moves downwards?
kinetic energy
Q. What are the 4 types of energy transfer?
There are 4 ways energy can be transferred;
- Mechanically – By the action of a force.
- Electrically – By an electrical current.
- By radiation – By Light waves or Sound waves.
- By heating – By conduction, convection or radiation.
Q. Why does the skateboarder eventually stop << read less?
As the skateboad is riding down the hill and reaches the bottem it will slow down due to frictional force acting in the opposite direction. Here, the frictional force acts between the skateboard and the ground. This reduces the speed of the skateboard and it eventually comes to a stop.
Q. What law states that energy Cannot be destroyed?
The law of conservation of energy, also known as the first law of thermodynamics, states that the energy of a closed system must remain constant—it can neither increase nor decrease without interference from outside.