The equator
Q. Where does most of the heat in the ocean water come from?
sunlight
Table of Contents
- Q. Where does most of the heat in the ocean water come from?
- Q. At which locations are solar energy most concentrated?
- Q. Which planet receives the least amount of solar energy?
- Q. How much solar radiation does Earth’s surface absorb?
- Q. How do you calculate solar radiation?
- Q. What is meant by solar constant?
- Q. What can change the solar constant?
- Q. What is solar constant formula?
- Q. What is solar constant used for?
- Q. Is solar radiation constant?
- Q. What is the value of solar constant Mcq?
- Q. What is the average value for solar irradiance?
- Q. What is the relationship between solar intensity and latitude?
- Q. How many solar panels do I need for 1000 kWh per month?
- Q. What time of day is solar radiation at a maximum?
- Q. In which month solar radiation is maximum?
- Q. Which air does not absorb solar radiation?
- Q. Is there solar radiation at night?
- Q. Which is the most dangerous radiation?
- Q. What are the 4 main effects of solar radiation on Earth?
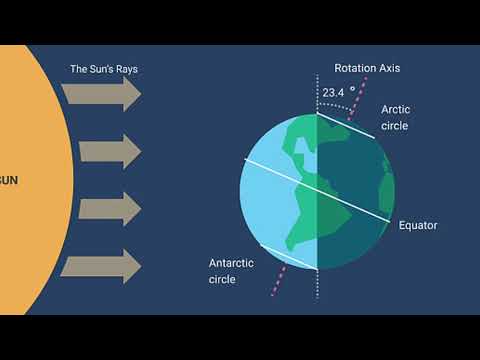
Q. At which locations are solar energy most concentrated?
Earth receives different amounts of solar energy at different latitudes, with the most at the equator and the least at the poles.
Q. Which planet receives the least amount of solar energy?
Neptune
Q. How much solar radiation does Earth’s surface absorb?
The Earth absorbs most of the energy reaching its surface, a small fraction is reflected. In total approximately 70% of incoming radiation is absorbed by the atmosphere and the Earth’s surface while around 30% is reflected back to space and does not heat the surface.
Q. How do you calculate solar radiation?
Be aware that this nominal ratio is given for standard test conditions (STC) : radiation=1000 W/m2, cell temperature=25 celcius degree, Wind speed=1 m/s, AM=1.5. The unit of the nominal power of the photovoltaic panel in these conditions is called “Watt-peak” (Wp or kWp=1000 Wp or MWp=1000000 Wp).
Q. What is meant by solar constant?
Solar constant, the total radiation energy received from the Sun per unit of time per unit of area on a theoretical surface perpendicular to the Sun’s rays and at Earth’s mean distance from the Sun. The value of the constant is approximately 1.366 kilowatts per square metre.
Q. What can change the solar constant?
The solar constant actually varies by +/-3% because of the Earth’s slightly elliptical orbit around the Sun. The Sun-Earth distance is smaller when the Earth is at perihelion (first week in January) and larger when the Earth is at aphelion (first week in July).
Q. What is solar constant formula?
The specific value at Earth of 1,361 W/m2 is called the “solar constant”. In order to calculate the total amount of energy arriving at Earth, we need to know how much area is being lit. KS = solar insolation (“solar constant”) = 1,361 watts per square meter. RE = radius of Earth = 6,371 km = 6,371,000 meters.
Q. What is solar constant used for?
The solar constant is used to quantify the rate at which energy is received upon a unit surface such as a solar panel. In this context, the solar constant provides a total measurement of the sun’s radiant energy as it is absorbed at a given point. Solar constants are used in various atmospheric and geological sciences.
Q. Is solar radiation constant?
Above the earth’s atmosphere, solar radiation has an intensity of approximately 1380 watts per square meter (W/m2). This value is known as the Solar Constant.
Q. What is the value of solar constant Mcq?
ANS :The intensity of solar radiation incident on unit cross-sectional area of earth exposed perpendicularly to the rays of sun at an average distance is called solar constant. Its value is 1.353 kW/m2.
Q. What is the average value for solar irradiance?
Average annual solar radiation arriving at the top of the Earth’s atmosphere is roughly 1361 W/m2. The Sun’s rays are attenuated as they pass through the atmosphere, leaving maximum normal surface irradiance at approximately 1000 W/m2 at sea level on a clear day.
Q. What is the relationship between solar intensity and latitude?
Therefore, the solar radiation is concentrated over a smaller surface area, causing warmer temperatures. At higher latitudes, the angle of solar radiation is smaller, causing energy to be spread over a larger area of the surface and cooler temperatures.
Q. How many solar panels do I need for 1000 kWh per month?
forty panels
Q. What time of day is solar radiation at a maximum?
noon
Q. In which month solar radiation is maximum?
July
Q. Which air does not absorb solar radiation?
Earth’s Energy Balance 3. Most of the atmosphere is relatively transparent to solar radiation, with the most notable exception being clouds. At the surface, snow and ice have a high albedo and consequently absorb little incoming radiation.
Q. Is there solar radiation at night?
So not only are there the obvious intensity changes in ground solar radiation level during the day, going to zero at night, but the spectrum of the radiation changes through each day because of the changing absorption and scattering path length.
Q. Which is the most dangerous radiation?
Gamma rays
Q. What are the 4 main effects of solar radiation on Earth?
Solar Radiation at the Earth’s Surface
- atmospheric effects, including absorption and scattering;
- local variations in the atmosphere, such as water vapour, clouds, and pollution;
- latitude of the location; and.
- the season of the year and the time of day.