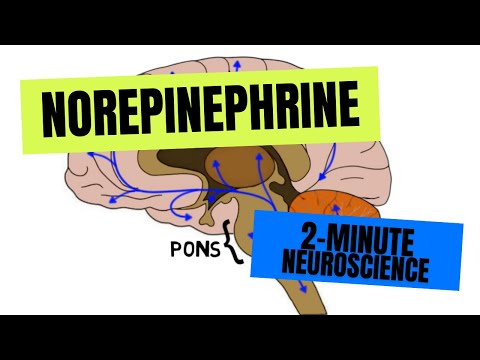
In the brainstem, the locus coeruleus is the primary site of norepinephrine synthesis. Noradrenergic neurons are projected bilaterally from this nucleus to several brain areas, including the cerebral cortex, limbic system, and spinal cord.
Q. Where does norepinephrine come from?
Norepinephrine is produced in the inner part of the adrenal glands, also called the adrenal medulla. The adrenal medulla also makes adrenaline (also known as epinephrine). Norepinephrine, adrenaline and dopamine belong are part of the catecholamine family.
Table of Contents
- Q. Where does norepinephrine come from?
- Q. What causes release of norepinephrine?
- Q. What stimulates norepinephrine production?
- Q. How is too much norepinephrine treated?
- Q. Does norepinephrine burn fat?
- Q. Is there a leptin supplement?
- Q. What are the symptoms of low norepinephrine?
- Q. How does low norepinephrine cause depression?
- Q. How does norepinephrine affect behavior?
- Q. What disease is associated with norepinephrine?
- Q. Does norepinephrine cause anger?
- Q. How does norepinephrine cause anxiety?
- Q. Does norepinephrine help anxiety?
Q. What causes release of norepinephrine?
Norepinephrine is released when a host of physiological changes are activated by a stressful event. In the brain, this is caused in part by activation of an area of the brain stem called the locus ceruleus. This nucleus is the origin of most norepinephrine pathways in the brain.
Q. What stimulates norepinephrine production?
Elevated levels of tyrosine in the central nervous system (CNS) triggers the production of norepinephrine and other catecholamines.
Q. How is too much norepinephrine treated?
Treatment. Several kinds of treatments can help you boost your NE activity. Common medications that raise norepinephrine levels are: Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), such as Cymbalta (duloxetine) and Savella (milnacipran)6
Q. Does norepinephrine burn fat?
The higher levels of norepinephrine in the body enhance the overall rate of fat loss by stimulating the release of fatty acids from fat cells into the bloodstream for burning as fuel (Johnson et al. 2012).
Q. Is there a leptin supplement?
Because leptin is a digestible protein that doesn’t enter the bloodstream, it can’t be taken in supplement form, Atkinson says. “If you were to take it as a pill, it’s just like eating chicken or beef. It’s a protein and your body would just break it up, so you wouldn’t absorb it from a pill.”
Q. What are the symptoms of low norepinephrine?
Low levels of epinephrine and norepinephrine can result in physical and mental symptoms, such as:
- anxiety.
- depression.
- changes in blood pressure.
- changes in heart rate.
- low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia.
- migraine headaches.
- problems sleeping.
Q. How does low norepinephrine cause depression?
The monoamine hypothesis suggests that the basis of depression is a reduction in the levels of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine in the body. Norepinephrine plays a role in a number of functions including memory, attention, stress reactions, energy levels, and the regulation of emotions.
Q. How does norepinephrine affect behavior?
Norepinephrine is involved in the sympathetic “flight-or-fight” response and thus is sensitive to environmental challenges and can modulate behavior accordingly. The noradrenergic system has been shown to mediate behavior, particularly aggression, in animals as well as in psychiatric illnesses.
Q. What disease is associated with norepinephrine?
Norepinephrine has been shown to play a role in a person’s mood and ability to concentrate. Low levels of norepinephrine may lead to conditions such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), depression, and hypotension (very low blood pressure).
Q. Does norepinephrine cause anger?
Elevating brain levels of norepinephrine increases an individual’s heart rate and primes the body for a fight-or-flight response. Overactivity of this neurotransmitter can interfere with cognitive functioning within the prefrontal cortex and lead to impulsive and aggressive behavior (Birnbaum et al.
Q. How does norepinephrine cause anxiety?
Norepinephrine is responsible for how the person reacts to stress and anxiety and is associated with the fight-or-flight response. SNRIs work to influence both serotonin and norepinephrine by preventing a person’s brain cells from rapidly absorbing these neurotransmitters.
Q. Does norepinephrine help anxiety?
By inhibiting the reuptake of these two neurotransmitters, SNRIs essentially increase the levels of norepinephrine and serotonin in the brain. 2 Serotonin helps regulate mood, anxiety, and other functions and norepinephrine helps mobilize the brain for action and can improve energy and attentiveness.