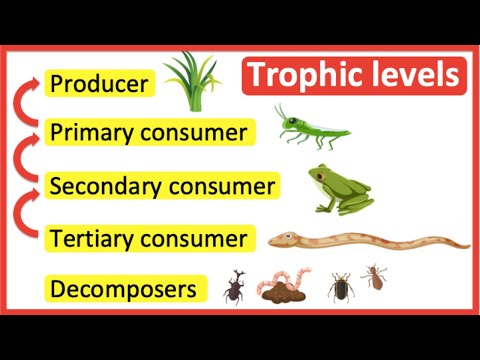
carbon dioxide: a type of gas found in Earth’s atmosphere • Producers: Producers are organisms that get their energy directly from the Sun. Their cells are able to turn sunlight into food through a process called photosynthesis.
Q. Which of the following groups gets energy from decaying organisms?
Decomposers (Figure below) get nutrients and energy by breaking down dead organisms and animal wastes. Through this process, decomposers release nutrients, such as carbon and nitrogen, back into the environment.
Table of Contents
- Q. Which of the following groups gets energy from decaying organisms?
- Q. Which of the following organisms get energy both from producers and consumers?
- Q. Which type of organism can obtain energy directly from any of the other organisms in an ecosystem?
- Q. Which organisms are considered Heterotrophs?
- Q. What are the 5 types of Heterotrophs?
- Q. What are 4 types of Heterotrophs?
- Q. What are 3 types of Heterotrophs?
- Q. Why animals are called heterotrophs?
- Q. Why humans are called heterotrophs?
- Q. Is algae a Heterotroph?
- Q. Why are humans called Heterotrophs *?
- Q. Are humans Organotrophs?
- Q. Is Grass a Heterotroph?
- Q. Is a cow an Autotroph or Heterotroph?
- Q. Is Grass a decomposer?
- Q. Is a zebra Autotroph or Heterotroph?
- Q. Is a slug a Heterotroph?
- Q. Is a frog a Heterotroph?
- Q. Is a zebra a herbivore?
- Q. Is an elephant a herbivore?
- Q. Can horses mate with zebras?
- Q. Which is faster a zebra or horse?
- Q. Can a zebra and a giraffe mate?
- Q. Are zebras faster than lions?
- Q. Why do we ride horses but not zebras?
Q. Which of the following organisms get energy both from producers and consumers?
Answer. Answer: Animals that eat both producers and consumers are called omnivores. When animals die, decomposers can break them down so that plants can use the nutrients again and the cycle can start over.
Q. Which type of organism can obtain energy directly from any of the other organisms in an ecosystem?
Autotrophs are the foundation of every ecosystem on the planet. That may sound dramatic, but it’s no exaggeration! Autotrophs form the base of food chains and food webs, and the energy they capture from light or chemicals sustains all the other organisms in the community.
Q. Which organisms are considered Heterotrophs?
Heterotrophs are known as consumers because they consume producers or other consumers. Dogs, birds, fish, and humans are all examples of heterotrophs. Heterotrophs occupy the second and third levels in a food chain, a sequence of organisms that provide energy and nutrients for other organisms.
Q. What are the 5 types of Heterotrophs?
What Types Are There?
- Carnivores eat the meat of other animals.
- Herbivores eat plants.
- Omnivores can eat both meat and plants.
- Scavengers eat things left behind by carnivores and herbivores.
- Decomposers break down dead plant or animal matter into soil.
- Detritivores eat soil and other very small bits of organic matter.
Q. What are 4 types of Heterotrophs?
There are four different types of heterotrophs which include herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and decomposers.
Q. What are 3 types of Heterotrophs?
There are three types of heterotrophs: are herbivores, carnivores and omnivores.
Q. Why animals are called heterotrophs?
Animals depend on other organisms for getting their food. They cannot make their own food, so they are heterotrophs. Animals need readymade food and therefore they depend on either plants or other animals which they eat.
Q. Why humans are called heterotrophs?
Humans do not possess the physiological mechanism to produce their own food from the raw materials in their surroundings like the plants. Hence, humans consume plants and other animals to fulfill their energy needs. As they derive food or energy from other sources they are referred to as heterotrophs.
Q. Is algae a Heterotroph?
In other words, most algae are autotrophs or more specifically, photoautotrophs (reflecting their use of light energy to generate nutrients). However, there exist certain algal species that need to obtain their nutrition solely from outside sources; that is, they are heterotrophic.
Q. Why are humans called Heterotrophs *?
1 Answer. Humans are heterotrophs or omnivores because Humans eat both animal proteins and plant for food.
Q. Are humans Organotrophs?
Organotrophs, including humans, fungi, and many prokaryotes, are chemotrophs that obtain energy from organic compounds. Lithotrophs (“litho” means “rock”) are chemotrophs that get energy from inorganic compounds, including hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and reduced iron. Lithotrophy is unique to the microbial world.
Q. Is Grass a Heterotroph?
Grass is an autotroph.
Q. Is a cow an Autotroph or Heterotroph?
Animals are heterotrophic. Heterotrophs must eat food. Some hetertrophs, like cows, eat autotrophic organisms (grass), and other heterotrophs, like lions, eat other heterotrophs, say a cow, to get their food. It does matter where the food comes from the energy all comes from the same place; the Sun.
Q. Is Grass a decomposer?
Producer: organism on the food chain that can produce its own energy and nutrients. Examples: grasses, Jackalberry tree, Acacia tree. Decomposer/detritivores: organisms that break down dead plant and animal material and waste and release it as energy and nutrients in the ecosystem.
Q. Is a zebra Autotroph or Heterotroph?
Heterotrophic or Autotrophic: The zebra is Heterotrophic, and this is because the zebra does not have the ability to go through photosynthesis, meaning that it does not make its own food using energy (sunlight).
Q. Is a slug a Heterotroph?
Meet the sea slugs who double up as plants (well kind of) by creating their own energy via photosynthesis. It is perhaps one of the greatest evolutionary adaptations to be both heterotrophic like animals and autotrophic like plants. Organisms that can do this are known as mixotrophic.
Q. Is a frog a Heterotroph?
Frogs are heterotrophic organisms that means that they do not produce any form of sustenance, meaning they will not create their own food.
Q. Is a zebra a herbivore?
Zebras are herbivores and feed mostly by grazing on grasses, although they also might browse a bit on the leaves and stems of bushes. They graze for many hours each day, using their strong front teeth to clip off the tips of the grass.
Q. Is an elephant a herbivore?
All elephant species are herbivores, consuming only plant material. The elephants of Africa are browsers, and eat mostly grasses, turning to leaves, twigs, bark, flowers, and fruits when the grasses are not available.
Q. Can horses mate with zebras?
A zorse is the offspring of a zebra stallion and a horse mare. This cross is also called a zebrose, zebrula, zebrule, or zebra mule. The rarer reverse pairing is sometimes called a hebra, horsebra, zebret, zebrinny, or zebra hinny. Like most other animal hybrids, the zorse is sterile.
Q. Which is faster a zebra or horse?
A horse is much faster than a zebra clocking in at a max of just about 55 miles per hour where zebras max out at 40 miles per hour.
Q. Can a zebra and a giraffe mate?
is a hybrid between a giraffe and a zebra still appears to be current. Apart from the fact that hybrids between such widely different animals do not occur in nature, the okapi is essentially a giraffe in structure and fully a dozen specimens are known.
Q. Are zebras faster than lions?
With a top speed of 64 km/h, zebra are far from the fastest animals on the savannah. A zebra’s main nemesis is the lion, an animal that can sprint at 81 km/h!
Q. Why do we ride horses but not zebras?
So, the answer: We don’t ride zebras because they are wild animals not wild about being ridden. We don’t ride them because we are for the most part happier admiring them from afar doing what zebras do best: being bad-tempered and eating grass!