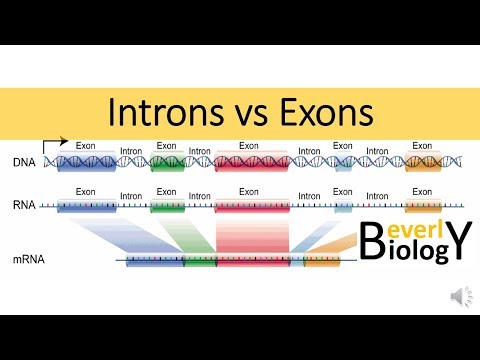
Exons are coding sections of an RNA transcript, or the DNA encoding it, that are translated into protein. Exons can be separated by intervening sections of DNA that do not code for proteins, known as introns.
Q. Are exons removed?
Introns and exons are nucleotide sequences within a gene. Introns are removed by RNA splicing as RNA matures, meaning that they are not expressed in the final messenger RNA (mRNA) product, while exons go on to be covalently bonded to one another in order to create mature mRNA.
Table of Contents
- Q. Are exons removed?
- Q. Why are exons called exons?
- Q. Where are introns removed?
- Q. Why do we need introns?
- Q. What are introns purpose?
- Q. What happens to introns after splicing?
- Q. What are the 3 steps of RNA processing?
- Q. Why are introns removed in splicing?
- Q. Does splicing occur before polyadenylation?
- Q. What is the process of splicing?
- Q. Why is RNA needed under splicing?
- Q. What is HnRNA?
- Q. What are splicing tools?
- Q. What is splicing a wire?
- Q. Is it OK to splice electrical wire?
- Q. How do I join wires?
- Q. How do you tap into a wire without cutting it?
Q. Why are exons called exons?
Exon. The parts of the gene sequence that are expressed in the protein are called exons, because they are expressed, while the parts of the gene sequence that are not expressed in the protein are called introns, because they come in between–or interfere with–the exons.
Q. Where are introns removed?
splice sites
Q. Why do we need introns?
Introns are crucial because the protein repertoire or variety is greatly enhanced by alternative splicing in which introns take partly important roles. Alternative splicing is a controlled molecular mechanism producing multiple variant proteins from a single gene in a eukaryotic cell.
Q. What are introns purpose?
Introns, from this perspective, have a profound purpose. They serve as hot spots for recombination in the formation of new combinations of exons. In other words, they are in our genes because they have been used during evolution as a faster pathway to assemble new genes.
Q. What happens to introns after splicing?
After transcription of a eukaryotic pre-mRNA, its introns are removed by the spliceosome, joining exons for translation. The intron products of splicing have long been considered ‘junk’ and destined only for destruction.
Q. What are the 3 steps of RNA processing?
The three most important steps of pre-mRNA processing are the addition of stabilizing and signaling factors at the 5′ and 3′ ends of the molecule, and the removal of intervening sequences that do not specify the appropriate amino acids. In rare cases, the mRNA transcript can be “edited” after it is transcribed.
Q. Why are introns removed in splicing?
During splicing, introns (non-coding regions) are removed and exons (coding regions) are joined together. For those eukaryotic genes that contain introns, splicing is usually required in order to create an mRNA molecule that can be translated into protein.
Q. Does splicing occur before polyadenylation?
For short transcription units, RNA splicing usually follows cleavage and polyadenylation of the 3′ end of the primary transcript. But for long transcription units containing multiple exons, splicing of exons in the nascent RNA usually begins before transcription of the gene is complete.
Q. What is the process of splicing?
During the process of splicing, introns are removed from the pre-mRNA by the spliceosome and exons are spliced back together. If the introns are not removed, the RNA would be translated into a nonfunctional protein. Splicing occurs in the nucleus before the RNA migrates to the cytoplasm.
Q. Why is RNA needed under splicing?
hnRNA is required to undergo splicing because of the presence of introns (the non-coding sequences) in it. These need to be removed and the exons (the coding sequences) have to be joined in a specific sequence for translation to take place.
Q. What is HnRNA?
HnRNA stands for heterogeneous nuclear RNA. As its name suggests, hnRNA is a term that encompasses various types and sizes of RNAs found in the eukaryotic cell nucleus. As you likely know, RNAs exist in many forms and carry out a wide range of functions.
Q. What are splicing tools?
Rope splicing tools are an essential part of any crafter or sailor’s toolkit. They’re uniquely designed to help you create smoother splices, whether you’re looking for a useful way to form a stopper at the end of a line or need to make a smaller opening in a rope for a smoother, fairer splice.
Q. What is splicing a wire?
Splicing is the process of combining 2 lengths of wires so they can carry a current. Before you splice your wires together, you need to prepare the wires by stripping them and turning off the power. There are many ways to splice wires together, from simply using wire caps to soldering them together.
Q. Is it OK to splice electrical wire?
Fortunately, no. Savvy electricians can splice wires together, safely adding the length they need to reach their destination.
Q. How do I join wires?
Twist the electrical wires together tightly starting at or near the first bit of exposed wire. Always twist the wires in a clockwise direction. That way when you screw on a twist-on connector (which also is tightened by turning it clockwise) you won’t be un-twisting your wires.
Q. How do you tap into a wire without cutting it?
You simply want to strip back the insulation on the wire you need WITHOUT cutting any of the copper wires themselves. Then use a pointed tool to poke through the copper strands and make an eye. Then simply thread your new wire through the eye. Then close up the eye and wrap your new wire around it.