What is Nernst potential for K+ in the “depolarization” medium at 37°C? In this case, we have T = 37°C = 310K, and thus RT/F = 26.7 mV.
Q. What would happen to the membrane potential if there was an increase in the permeability of the membrane to K+ ions?
If the membrane permeability to K+ ions is increased, then over the short term (a few minutes) a. the K+ equilibrium potential will become more positive.
Table of Contents
- Q. What would happen to the membrane potential if there was an increase in the permeability of the membrane to K+ ions?
- Q. Why is the resting membrane potential negative 70?
- Q. Why do you think there are no changes in current with the membrane clamped?
- Q. What direction does current flow in a membrane?
- Q. How does a voltage clamp isolate current flow?
- Q. What is the difference between voltage clamp and current clamp?
- Q. What does a current clamp do?
- Q. What does a voltage clamp do?
- Q. Can record cell activity in voltage and current clamp mode?
- Q. What does current-clamp mode measure?
- Q. What is the difference between an extracellular and intracellular recording?
- Q. What is whole-cell voltage clamp recording?
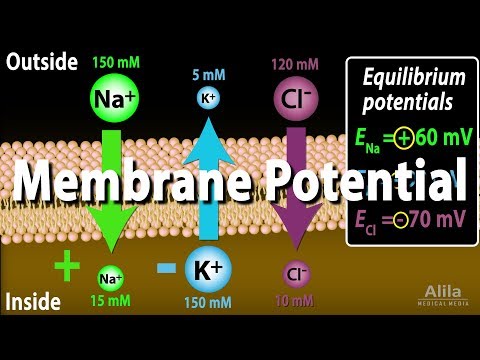
Q. Why is the resting membrane potential negative 70?
The resting membrane potential of a neuron is about -70 mV (mV=millivolt) – this means that the inside of the neuron is 70 mV less than the outside. At rest, there are relatively more sodium ions outside the neuron and more potassium ions inside that neuron.
Q. Why do you think there are no changes in current with the membrane clamped?
When the membrane potential is clamped at a voltage below the equilibrium potential for Na+, Na+ will flow into the cell. As the membrane potential approaches the equilibrium potential of Na+, no current will flow.
Q. What direction does current flow in a membrane?
Depending on the direction of the flow, currents can be inward (current flows from outside to inside the cell) or outward (current flows from inside to outside of the cell).
Q. How does a voltage clamp isolate current flow?
The voltage clamp is a classic electrophysiological technique to measure ion currents across the cell membrane. Under voltage clamp conditions, voltage-gated ion channels open and close as normal, but the voltage clamp apparatus compensates for the changes in the ion current to maintain a constant membrane potential.
Q. What is the difference between voltage clamp and current clamp?
Unlike in the voltage clamp mode, where the membrane potential is held at a level determined by the experimenter, in “current clamp” mode the membrane potential is free to vary, and the amplifier records whatever voltage the cell generates on its own or as a result of stimulation.
Q. What does a current clamp do?
Current clamps are typically used to read the magnitude of alternating current (AC) and, with additional instrumentation, the phase and waveform can also be measured. Some clamp meters can measure currents of 1000 A and more. Hall effect and vane type clamps can also measure direct current (DC).
Q. What does a voltage clamp do?
Voltage-clamp allows the investigator to control the transmembrane voltage and subsequently measure current flow through an ion channel after activation. An ion channel can be activated by either a change in transmembrane voltage or a selective ligand, acting as a switching mechanism.
Q. Can record cell activity in voltage and current clamp mode?
Cell-attached voltage-clamp recording can be used to record the firing activity of the cell without changing that activity. Cell firing activity is recorded in the form of action potential currents, with the amplifier in voltage-clamp mode (Fig. 5).
Q. What does current-clamp mode measure?
In a current-clamp experiment, one applies a known current and measures the change in membrane potential (Vm) caused by the applied current. This type of experiment mimics the current produced by a synaptic input.
Q. What is the difference between an extracellular and intracellular recording?
Intracellular recordings can provide information on ionic reversal potentials, resting membrane potentials, single-channel conductance, second messenger roles in receptor function, and synaptic plasticity in neurons. However, unlike extracellular recordings, intracellular recordings are invasive to the neuron.
Q. What is whole-cell voltage clamp recording?
Patch-Clamp Techniques Whole-cell recording allows the measurement of the overall electrical properties of a cell membrane and, specifically, either the total current through all the channels on the membrane or the membrane potential.