plutonic
Q. What is an igneous rock with large crystals?
Igneous rocks that have crystals large enough to be seen by the naked eye are called phaneritic; those with crystals too small to be seen are called aphanitic. Generally speaking, phaneritic implies an intrusive origin; aphanitic an extrusive one.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is an igneous rock with large crystals?
- Q. What does the presence of large and small crystals in igneous rock indicate?
- Q. What are the five characteristics of igneous rocks?
- Q. What characteristics are used to identify igneous rocks?
- Q. What are the characteristics of intrusive igneous rocks?
- Q. How will you know if they are igneous rocks?
- Q. How can you tell the difference between igneous and metamorphic rocks?
- Q. What are the characteristics of metamorphic rocks?
- Q. What affects the crystal size in igneous rocks?
- Q. What is the difference between plutonic and volcanic igneous rocks?
- Q. Is granite a plutonic rock?
- Q. Is granite a plutonic or volcanic rock?
- Q. What do you mean by plutonic rock?
- Q. What is the example of plutonic rock?
- Q. What is the most common plutonic rock?
- Q. What is the characteristics of plutonic rocks?
Q. What does the presence of large and small crystals in igneous rock indicate?
Summary. Intrusive igneous rocks cool from magma slowly because they are buried beneath the surface, so they have large crystals. Extrusive igneous rocks cool from lava rapidly because they form at the surface, so they have small crystals. Texture reflects how an igneous rock formed.
Q. What are the five characteristics of igneous rocks?
Igneous rocks can be easily identified with their texture, density, colour, and mineral composition. Its texture depends on the shape, size, time period to cool down and solidify, and the arrangement of crystals in the rock.
Q. What characteristics are used to identify igneous rocks?
Two main characteristics are used to classify igneous rocks: 1) texture (the size of the mineral grains in the rock; and 2) composition (often determined by what the actual minerals are).
Q. What are the characteristics of intrusive igneous rocks?
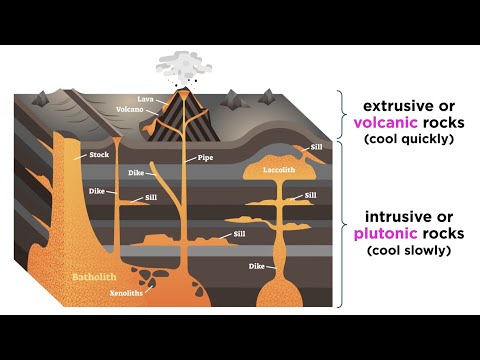
When magma cools and solidifies in these spaces, Intrusive or plutonic igneous rocks are formed deep beneath the Earth’s surface. Intrusive features like stocks, laccoliths, sills, and dikes are formed.
Q. How will you know if they are igneous rocks?
Look for crystals in igneous rocks. Examples of igneous rocks are gabbro, granite, pumice and obsidian. Metamorphic rocks are rocks that have become changed by intense heat or pressure while forming. One way to tell if a rock sample is metamorphic is to see if the crystals within it are arranged in bands.
Q. How can you tell the difference between igneous and metamorphic rocks?
Summary: 1. Igneous rocks are formed when magma (or molten rocks) have cooled down and solidified. Sedimentary rocks are formed by the accumulation of other eroded substances, while Metamorphic rocks are formed when rocks change their original shape and form due to intense heat or pressure.
Q. What are the characteristics of metamorphic rocks?
Metamorphic rocks were once igneous or sedimentary rocks, but have been changed (metamorphosed) as a result of intense heat and/or pressure within the Earth’s crust. They are crystalline and often have a “squashed” (foliated or banded) texture.
Q. What affects the crystal size in igneous rocks?
The size of the crystals depends on how quickly the molten magma solidified: magma that cools slowly will form an igneous rock with large crystals. lava that cools quickly will form an igneous rock with small crystals.
Q. What is the difference between plutonic and volcanic igneous rocks?
Plutonic rocks are formed when magma cools and solidifies underground. Volcanic rocks are formed from lava that flows on the surface of the Earth and other planets and then cools and solidifies. The texture of an igneous rock depends on the size of the crystals in the rock.
Q. Is granite a plutonic rock?
Granite, coarse- or medium-grained intrusive igneous rock that is rich in quartz and feldspar; it is the most common plutonic rock of the Earth’s crust, forming by the cooling of magma (silicate melt) at depth.
Q. Is granite a plutonic or volcanic rock?
Basalt and obsidian are volcanic rocks; granite is plutonic. Ask students how they can determine this. The answer is: plutonic rocks (such as granite) cool slowly in a relatively undisturbed environment permitting the growth of large mineral crystals which can easily be seen by the unaided eye.
Q. What do you mean by plutonic rock?
In geology, a pluton is a body of intrusive igneous rock (also called plutonic rock) that is crystallized from magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. The most common rock types in plutons are granite, granodiorite, tonalite, monzonite, and quartz diorite.
Q. What is the example of plutonic rock?
Igneous rocks which cool and solidify deep in the earths crust are called plutonic rocks. Examples of plutonic rocks are granite, gabbro, and granodiorite.
Q. What is the most common plutonic rock?
When magma never reaches the surface and cools to form intrusions (dykes, sills etc) the resulting rocks are called plutonic. Depending on their silica content, they are called (in ascending order of silica content) gabbro, diorite, granite and pegmatite. By quantity, these are the by far most common rock types.
Q. What is the characteristics of plutonic rocks?
The characteristic textures of plutonic rocks distinguish them from the rapidly-cooled volcanic rocks. Plutonic rocks are holocrystalline (without glass) and their average grain size is 1–5 mm. Porphyritic textures are shown by many granites. The grain-to-grain relationships reflect the history of crystallization.