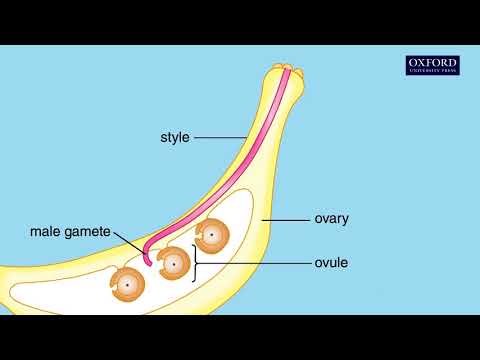
When the pollen grain germinates on the stigma it creates a burrow called the pollen tube as it travels toward the ovary. When the sperm cell from the pollen grain reaches the ovary or ovule the sperm joins with the egg. This is called fertilization. The fertilized zygote will become a tiny new plant inside the seed.
Q. What is the function of a pollen tube?
In compatible pollination, pollen tubes carrying two sperm cells grow through the pistil transmitting tract and are precisely guided to the ovules, discharging the sperm cells to the embryo sac for fertilization.
Q. What is the function of the pollen tube quizlet?
A tube that forms after germination of the pollen grain and that functions in the delivery of sperm to the ovule.
Q. What is the importance of pollen tube and why does it grow?
Q. What does the pollen tube contain?
In most plant species, the pollen tube cell wall consists of two layers, the inner sheath of callose and outer coating containing mainly pectin with cellulose and hemicellulose. The pollen tube grows exclusively at its tip, where the newly synthesized cell wall is continually forming (Taylor and Hepler, 1997).
The male reproductive organ of the flower, the stamen, produces pollen. Once a pollen grain settles on a compatible pistil, it may germinate in response to a sugary fluid secreted by the mature stigma. Lipids at the surface of the stigma may also stimulate pollen tube growth for compatible pollen.
Q. What happens when a pollen grain germinates?
Q. What are the specific terms used for inner and outer walls of pollen grain?
In general, pollen grains have a double wall consisting of a thin inner wall composed of cellulose, termed the endospore, and a thick outer wall comprised of sporopollenin, termed the exospore.
Q. What term is applied for inner wall of the pollen grain?
intine
Q. How many walls are in a pollen grain?
Instead, the proximal part of the central pollen body (the corpus) has four walls: exine, a thin intine layer, a callosic wall and another thick intine wall, continuous with the intine surrounding the tube cell (Pacini et al.
Q. What is pollen grain and its function?
Pollen grains are microscopic structures that carry the male reproductive cell of plants. The inside of the grain contains cytoplasm along with the tube cell (which becomes the pollen tube) and the generative cell (which releases the sperm nuclei).
Q. What is pollen grain in easy words?
: one of the granular microspores that occur in pollen and give rise to the male gametophyte of a seed plant.
Q. What is pollen grain simple definition?
Each pollen grain is a minute body, of varying shape and structure, formed in the male structures of seed-bearing plants and transported by various means (wind, water, insects, etc.) to the female structures, where fertilization occurs. In angiosperms, pollen is produced by the anthers of the stamens in flowers.
Q. How is pollen grain formed?
Development of pollen grains (male gametophytes) takes place in the anther. Pollen development begins when specialized cells (microsporocytes) differentiate in young anthers. There are generally hundreds or thousands of microsporocytes per anther and each passes through meiosis to produce four haploid microspores.
Q. Where is pollen grains are found?
anthers
Q. What is Colporate?
The term colporate is used to describe a pollen grain that has compound aperture consisting ectoaperture and endoaperture where ectoaperture is colpus and the endoaperture is os. Colpus is formed on sexine and os is formed on nexine. Colpus with os forms the colporate pollen grain.
Q. What is meant by Pollinium?
: a coherent mass of pollen grains often with a stalk bearing an adhesive disk that clings to insects.
Q. What are different types of aperture?
An aperture is a thin or missing part of the exine, which is independent of the patterning of the exine. Two different types of apertures can be distinguished: pores and fissures (colpi). The latter are more primitive, they are elongated with pointed ends. Pores are usually isodiametric.
Q. What is the difference between spore and pollen?
Spore is a haploid cell derived from sporangium via meiosis, whereas pollen is an immature, endosporic male gametophyte derived from male spores (microspores) in seed plants.
Q. Can a plant have spores and pollen?
Both spores and pollen are reproductive products that are generally single cells. The fungi, mosses, liverworts, hornworts, and seedless vascular plants produce spores, but only seed-bearing plants produce pollen.
Q. Is pollen a diploid?
A pollen grain is a male gametophyte, and pollen grains are formed in anthers, the male parts of flowers. Meiosis occurs in the anthers. Cells called pollen mother cells undergo meiosis. Of course, in the case that the plant is tetraploid, then the pollen grains will be diploid.
Q. What is the difference between a sperm a spore and a pollen grain?
A spore is the different male and female parts (megaspore and microspore), whereas sperm is what is released after pollination and the pollen grain has grown a pollen tube.