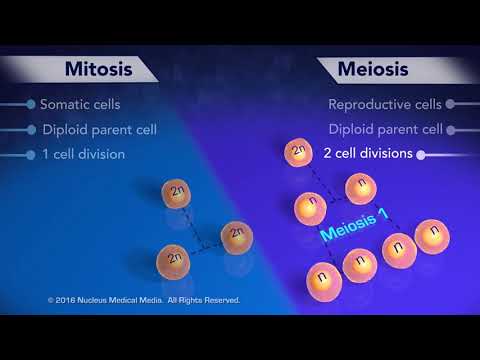
Cell division by mitosis occurs in all human body cells except the gonads (sex cells). During mitosis, the DNA is exactly copied and a new daughter cell created with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, ie 46.
Q. How many daughter cells are there in mitosis?
two daughter cells
Table of Contents
- Q. How many daughter cells are there in mitosis?
- Q. Does mitosis produce 2 or 4 daughter cells?
- Q. How many daughter cells are there in meiosis?
- Q. Why is it called the daughter cell?
- Q. Are two daughter cells genetically identical?
- Q. Does mitosis have daughter cells?
- Q. Are daughter cells smaller than parent cells?
- Q. What is the structure of daughter cells?
- Q. Why are daughter cells smaller?
- Q. How are mutated genes passed to daughter cells?
- Q. What do you notice about the size of the cell?
- Q. Whats the largest cell in the world?
- Q. Which is the largest cell in plants?
- Q. Is acetabularia the largest plant cell?
Q. Does mitosis produce 2 or 4 daughter cells?
Mitosis creates two identical daughter cells that each contain the same number of chromosomes as their parent cell. In contrast, meiosis gives rise to four unique daughter cells, each of which has half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Q. How many daughter cells are there in meiosis?
four daughter cells
Q. Why is it called the daughter cell?
Answer: So naturally organisms/cells capable of producing offspring are also given a feminine trait. The parent cell is often called the mother cell, and the daughter cells are so named because they eventually become mother cell themselves.
Q. Are two daughter cells genetically identical?
In terms of DNA content, or the amount of DNA, the daughter cells are identical to the parent. In organisms, mitosis is a way to produce two daughter cells that will have different functions or become different cell types. In either case, the daughter cells still have the same amount of DNA as the parent cell.
Q. Does mitosis have daughter cells?
Mitosis produces new cells, and replaces cells that are old, lost or damaged. In mitosis a cell divides to form two identical daughter cells.
Q. Are daughter cells smaller than parent cells?
Daughter cells are normally smaller than mother cells and can be easily distinguished and removed from their progenitors by micromanipulation (Mortimer, 1959).
Q. What is the structure of daughter cells?
The cytoplasm of the mother cell divides to form two daughter cells, each containing the same number and kind of chromosomes as the mother cell. The stage, or phase, after the completion of mitosis is called interphase.
Q. Why are daughter cells smaller?
More evidence comes from the observation that daughter cells complete mitosis at a significantly smaller size in poor nutrients than in rich nutrients (Johnston et al., 1977). This suggests the existence of a checkpoint that operates after G1, during bud growth, to control the size at which daughter cells are born.
Q. How are mutated genes passed to daughter cells?
Mutations are irreversible and are passed on to the daughter cells during mitosis. Mutations in suppressor genes can result in cells dividing uncontrollably. For example most human tumour cells have a defective p53 gene – one of the most important tumour suppressor genes.
Q. What do you notice about the size of the cell?
Cell size is limited by a cell’s surface area to volume ratio. A smaller cell is more effective and transporting materials, including waste products, than a larger cell. Cells come in many different shapes. A cell’s function is determined, in part, by its shape.
Q. Whats the largest cell in the world?
The largest cell is an ostrich egg, it is about 15cm to 18 cm long and wide.
Q. Which is the largest cell in plants?
xylem cells
Q. Is acetabularia the largest plant cell?
When it comes to Acetabularia, it is one of the largest plant cells. It is significant to know that it is the genus of extremely green algae mostly found in the subwaters. Acetabularia is also called mermaid wine glass. It also resembles the completely round leaves of the nasturtium and it 0.5 to 10 cm tall.