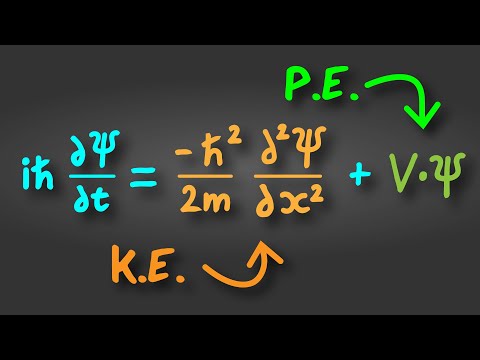Schrodinger equation gives us a detailed account of the form of the wave functions or probability waves that control the motion of some smaller particles. The equation also describes how these waves are influenced by external factors.
Q. What are the limitations of Schrodinger?
The disadvantage is that it is difficult to imagine a physical model of electrons as waves. The Schrödinger model assumes that the electron is a wave and tries to describe the regions in space, or orbitals, where electrons are most likely to be found.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the limitations of Schrodinger?
- Q. What are the limitations of wave function?
- Q. What does Schrodinger’s equation tell us?
- Q. Is everything made of waves?
- Q. Does light have mass?
- Q. What experiment proves light is a particle?
- Q. Does light interfere with itself?
- Q. Is light a particle or a wave quizlet?
- Q. What kind of waves are electromagnetic waves?
- Q. What are the 7 types of waves?
- Q. What is the most useful electromagnetic wave?
- Q. What are the 4 types of waves?
- Q. What are the 2 types of waves?
- Q. Which type of waves causes the most damage?
- Q. How do waves behave?
- Q. What type of waves Cannot be polarized?
- Q. What happens when two waves meet ks3?
- Q. What are the three types of sound waves?
- Q. Are sound waves sine waves?
Q. What are the limitations of wave function?
The function must be single valued. It must have a finite value or it must be normalized. It has continuous first derivative on the indicated interval. The wave function must be square integrable.
Q. What does Schrodinger’s equation tell us?
The Schrodinger equation plays the role of Newton’s laws and conservation of energy in classical mechanics – i.e., it predicts the future behavior of a dynamic system. The Schrodinger equation gives the quantized energies of the system and gives the form of the wavefunction so that other properties may be calculated.
Q. Is everything made of waves?
Everything in the universe has both particle and wave nature, at the same time. They’re really just different language describing the same mathematical object.
Q. Does light have mass?
Light is composed of photons, so we could ask if the photon has mass. The answer is then definitely “no”: the photon is a massless particle. According to theory it has energy and momentum but no mass, and this is confirmed by experiment to within strict limits.
Q. What experiment proves light is a particle?
the double-slit experiment
Q. Does light interfere with itself?
Since light itself does not have electric charge, one photon cannot directly interact with another photon. Instead, they just pass right through each other without being affected. In contrast, if you shine one light beam such that it crosses another light beam, they will just pass through each other unaffected.
Q. Is light a particle or a wave quizlet?
Visible light is carried by photons, and so are all the other kinds of electromagnetic radiation like X-rays, microwaves and radio waves. In other words, light is a particle.
Q. What kind of waves are electromagnetic waves?
When you listen to the radio, watch TV, or cook dinner in a microwave oven, you are using electromagnetic waves. Radio waves, television waves, and microwaves are all types of electromagnetic waves. They only differ from each other in wavelength. Wavelength is the distance between one wave crest to the next.
Q. What are the 7 types of waves?
The EM spectrum is generally divided into seven regions, in order of decreasing wavelength and increasing energy and frequency. The common designations are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared (IR), visible light, ultraviolet (UV), X-rays and gamma rays.
Q. What is the most useful electromagnetic wave?
The different types of waves have different uses and functions in our everyday lives. The most important of these is visible light, which enables us to see. Radio waves have the longest wavelengths of all the electromagnetic waves. They range from around a foot long to several miles long.
Q. What are the 4 types of waves?
Types of Waves in Physics
- Mechanical waves.
- Electromagnetic waves.
- Matter waves.
Q. What are the 2 types of waves?
Waves come in two kinds, longitudinal and transverse. Transverse waves are like those on water, with the surface going up and down, and longitudinal waves are like of those of sound, consisting of alternating compressions and rarefactions in a medium.
Q. Which type of waves causes the most damage?
S waves are more dangerous than P waves because they have greater amplitude and produce vertical and horizontal motion of the ground surface. The slowest waves, surface waves, arrive last. They travel only along the surface of the Earth. There are two types of surface waves: Love and Rayleigh waves.
Q. How do waves behave?
Light waves across the electromagnetic spectrum behave in similar ways. When a light wave encounters an object, they are either transmitted, reflected, absorbed, refracted, polarized, diffracted, or scattered depending on the composition of the object and the wavelength of the light.
Q. What type of waves Cannot be polarized?
Longitudinal waves such as sound waves cannot be polarized because the motion of the particles is in one-dimension. Thus, ultrasonic waves being a sound wave cannot be polarized.
Q. What happens when two waves meet ks3?
If two waves meet each other in step, they add together and reinforce each other. They produce a much higher wave, a wave with a greater amplitude .
Q. What are the three types of sound waves?
Sound waves fall into three categories: longitudinal waves, mechanical waves, and pressure waves.
Q. Are sound waves sine waves?
Single-frequency sound waves are sinusoidal waves. The graph of a sound wave is repeated Figure 2.4 with some of its parts labeled. The amplitude of a wave is its y value at some moment in time given by x. If we’re talking about a pure sine wave, then the wave’s amplitude, A, is the highest y value of the wave.