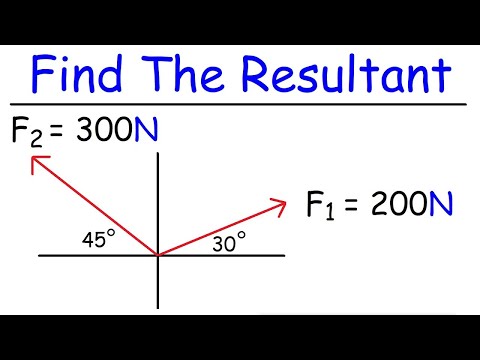
The resultant is the vector sum of two or more vectors. It is the result of adding two or more vectors together. If two or more velocity vectors are added, then the result is a resultant velocity. If two or more force vectors are added, then the result is a resultant force.
Q. What happens if 2 vectors are perpendicular?
If two vectors are perpendicular to each other, then their dot product is equal to zero.
Table of Contents
- Q. What happens if 2 vectors are perpendicular?
- Q. What is a vector diagram?
- Q. What is space diagram and vector diagram?
- Q. How do you solve a vector diagram?
- Q. How do you solve a vector problem?
- Q. What is the formula of position vector?
- Q. What is the formula for the magnitude of a vector?
- Q. Why is small angular displacement a vector?
Q. What is a vector diagram?
Vector diagrams are diagrams that depict the direction and relative magnitude of a vector quantity by a vector arrow. Vector diagrams can be used to describe the velocity of a moving object during its motion. In a vector diagram, the magnitude of a vector quantity is represented by the size of the vector arrow.
Q. What is space diagram and vector diagram?
The space diagram takes care of the point of application of forces and the geometry of the truss. The above shown figure is only to get the reactions. Applied force is ab and force is bc in the vector diagram. Reaction is equal to da and Reaction is equal to cd in the vector diagram.
Q. How do you solve a vector diagram?
Starting from where the head of the first vector ends, draw the second vector to scale in the indicated direction. Label the magnitude and direction of this vector on the diagram. Draw the resultant from the tail of the first vector to the head of the last vector. Label this vector as Resultant or simply R.
Q. How do you solve a vector problem?
Let’s work through it.
- Step 1) Draw the vector.
- Step 2) Add in the triangle legs.
- Step 3) Math. y-direction = magnitude * sin(angle) = 5 meters * sin (37) = 3 meters. x-direction = magnitude * cos(angle) = 5 meters * cos (37) = 4 meters.
- Step 4) Plug the solutions into the definition of a vector. Vector = 3 +4ŷ
Q. What is the formula of position vector?
The position function →r(t) r → ( t ) gives the position as a function of time of a particle moving in two or three dimensions. Graphically, it is a vector from the origin of a chosen coordinate system to the point where the particle is located at a specific time.
Q. What is the formula for the magnitude of a vector?
The formula for the magnitude of a vector can be generalized to arbitrary dimensions. For example, if a=(a1,a2,a3,a4) is a four-dimensional vector, the formula for its magnitude is ∥a∥=√a21+a22+a23+a24.
Q. Why is small angular displacement a vector?
Angular displacement is a vector quantity, which means that angular displacement has a size and a direction associated with it. As the object rotates from point “0” to point “1”, it rotates about an axis, so the direction of the angular displacement is measured along the axis.