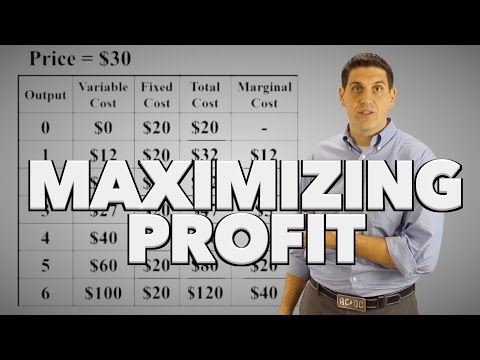
The profit maximizing level of output point is where the marginal revenue equals total cost. The revenue is greater than its variable costs ($900 > $800) so it should continue to produce! The profit maximizing level of output point is where the marginal revenue equals total cost.
Q. What is the profit maximizing level of output for the firm?
The profit-maximizing choice for a perfectly competitive firm will occur at the level of output where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost—that is, where MR = MC. This occurs at Q = 80 in the figure.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the profit maximizing level of output for the firm?
- Q. What is the profit maximizing level of output for this monopolist?
- Q. Which is the profit maximizing level of output for a monopoly quizlet?
- Q. Why would a perfectly competitive firm continue to operate if their economic profit is 0 in the long run?
- Q. What is long run profit?
- Q. What is the difference between the short run and the long run?
Q. What is the profit maximizing level of output for this monopolist?
The profit-maximizing choice for the monopoly will be to produce at the quantity where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost: that is, MR = MC. If the monopoly produces a lower quantity, then MR > MC at those levels of output, and the firm can make higher profits by expanding output.
Q. Which is the profit maximizing level of output for a monopoly quizlet?
A competitive firm maximizes profit at the point where average revenue equals marginal cost; a monopolist maximizes profit at the point where average revenue exceeds marginal cost. A monopoly firm maximizes its profit by producing 500 units output (so Q = 500).
Q. Why would a perfectly competitive firm continue to operate if their economic profit is 0 in the long run?
The existence of economic profits attracts entry, economic losses lead to exit, and in long-run equilibrium, firms in a perfectly competitive industry will earn zero economic profit. It will induce entry or exit in the long run so that price will change by enough to leave firms earning zero economic profit.
Q. What is long run profit?
Perfect Competition in the Long Run: In the long-run, economic profit cannot be sustained. In the long-run, the firm will make zero economic profit. Its horizontal demand curve will touch its average total cost curve at its lowest point.
Q. What is the difference between the short run and the long run?
Long Run. “The short run is a period of time in which the quantity of at least one input is fixed and the quantities of the other inputs can be varied. The long run is a period of time in which the quantities of all inputs can be varied.