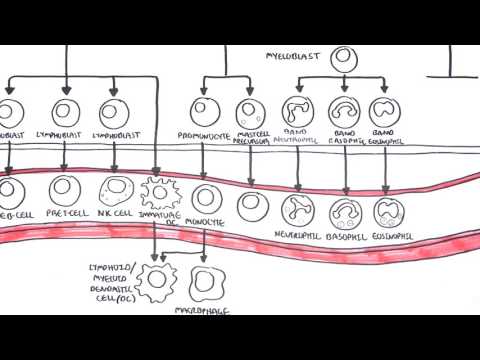
The identity and function of the major hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues: the bone marrow, spleen, thymus, and lymph nodes.
Q. What are hematopoietic tissues?
Listen to pronunciation. (hee-MA-toh-poy-EH-tik TIH-shoo) Tissue in which new blood cells are formed.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are hematopoietic tissues?
- Q. Which tissue is Haemopoietic?
- Q. Where is most hematopoietic tissue found in adults?
- Q. Where does hematopoiesis occur in adults?
- Q. What causes hematopoiesis?
- Q. What are the three stages of hematopoiesis?
- Q. Why does hematopoiesis happen?
- Q. What is the main function of stem cells in adults?
- Q. Which blood cell is known as scavenger?
- Q. What hormone stimulates hematopoiesis?
- Q. Which hormones require a second messenger?
- Q. What vitamins increase red blood cells?
- Q. What stimulates EPO production?
- Q. How can I increase my EPO naturally?
- Q. How fast does EPO work?
- Q. What does EPO do to your body?
- Q. How long does EPO stay in system?
- Q. What are the side effects of EPO injections?
Q. Which tissue is Haemopoietic?
The haemopoietic tissue of the embryo and fetal stage of vertebrates is the bone marrow, lymph nodes, yolk sac, liver, spleen, and thymus but after birth haemopoiesis occurs in the red bone marrow (see myeloid tissue).
Q. Where is most hematopoietic tissue found in adults?
Adult hematopoietic tissue is located in the flat bones and the ends of the long bones. Hematopoiesis occurs within the spongy trabeculae of the bone adjacent to vascular sinuses.
Q. Where does hematopoiesis occur in adults?
Prenatally, hematopoiesis occurs in the yolk sack, then in the liver, and lastly in the bone marrow. In the normal situation, hematopoiesis in adults occurs in the bone marrow and lymphatic tissues.
Q. What causes hematopoiesis?
When red blood cell (RBC) numbers are low, the body induces a homeostatic mechanism aimed to increase the synthesis of RBCs, typically via the production of erythropoietin. If the loss of RBCs becomes severe, hematopoiesis will occur in the extramedullary spaces outside the bone.
Q. What are the three stages of hematopoiesis?
During fetal development, hematopoiesis occurs in different areas of the developing fetus. This process has been divided into three phases: the mesoblastic phase, the hepatic phase, and the medullary phase.
Q. Why does hematopoiesis happen?
Hematopoiesis – the formation of blood cellular components – occurs during embryonic development and throughout adulthood to produce and replenish the blood system. Studying hematopoiesis can help scientists and clinicians to understand better the processes behind blood disorders and cancers.
Q. What is the main function of stem cells in adults?
The main functions of adult stem cells are to replace cells that are at risk of possibly dying as a result of disease or injury and to maintain a state of homeostasis within the cell.
Q. Which blood cell is known as scavenger?
Macrophages
Q. What hormone stimulates hematopoiesis?
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) stimulates hematopoietic cells through mechanisms of action that remain elusive. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is upregulated by PTH and stimulates hematopoiesis.
Q. Which hormones require a second messenger?
Second Messenger Systems
| Second Messenger | Examples of Hormones Which Utilize This System |
|---|---|
| Cyclic AMP | Epinephrine and norepinephrine, glucagon, luteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, calcitonin, parathyroid hormone, antidiuretic hormone |
Q. What vitamins increase red blood cells?
Your body needs vitamin B12 to make red blood cells. In order to provide vitamin B12 to your cells: You must eat foods that contain vitamin B12, such as meat, poultry, shellfish, eggs, fortified breakfast cereals, and dairy products.
Q. What stimulates EPO production?
Erythropoiesis is stimulated by eEpo, and under conditions of severe hypoxia (low O2 concentration) eEpo levels can increase up to 1000-fold (Erslev, 1997). Epo is initially synthesized as a 193 amino-acid precursor.
Q. How can I increase my EPO naturally?
Athletes tested at Northwestern State University scored a 65% increase in naturally occurring EPO after taking echinacea supplements for 14 days. Self-massaging the area around the kidneys stimulates the adrenal glands and encourages blood flow to produce more EPO.
Q. How fast does EPO work?
How soon after starting EPO medication will I feel better? It will take time for EPO medication to work in your body. Most people take 1 to 2 months to feel better.
Q. What does EPO do to your body?
EPO stimulates the production of red blood cells in bone marrow and regulates the concentration of red blood cells and haemoglobin in the blood. This is useful for athletes, since red blood cells shuttle oxygen to the cells, including muscle cells, enabling them to operate more effectively.
Q. How long does EPO stay in system?
In addition, EPO is short-lived, remaining in the body for as short a time as two days.
Q. What are the side effects of EPO injections?
Common side effects
- Allergic reaction. Rarely, some people have an allergic reaction to erythropoietin.
- Feeling sick or being sick. You may feel sick during treatment with erythropoietin.
- Diarrhoea.
- Blood clot risk.
- Headaches.
- High blood pressure.
- Muscle, joint or bone pain.
- Flu-like symptoms.