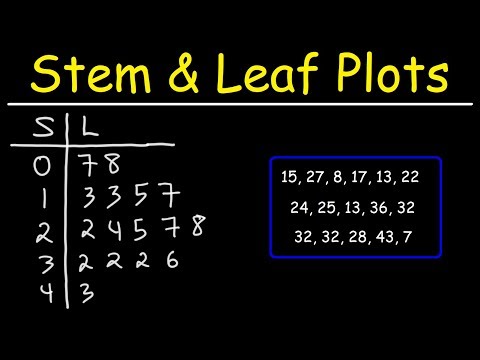
The smallest number in the stem-and-leaf plot is 22. You can see that by looking at the first stem and the first leaf. The greatest number is the last stem and the last leaf on the chart. In this case, the largest number is 55.
Q. What is the count of a stem and leaf plot?
In a stem and leaf plot, the stem is like the first digit and the stem would be the number following it. For example, in number 24, the 2 is the stem and 4 would be the leaf.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the count of a stem and leaf plot?
- Q. What are the 7 steps for constructing a stem and leaf plot?
- Q. Do you repeat numbers in a stem and leaf plot?
- Q. Do you put a 0 in a stem and leaf plot?
- Q. How do you know if a stem and leaf plot is skewed?
- Q. How do you read a Stemplot?
- Q. Do stem and leaf plots have to be in order?
- Q. What is an ordered stem and leaf diagram?
- Q. How do you calculate stem and leaf?
- Q. How do stem plots work?
- Q. What is the key for stem and leaf plot?
- Q. What is the difference between a histogram and a stem leaf plot?
- Q. How are stem and leaf like dot plots?
- Q. What is the advantage of a stem and leaf plot over a histogram?
- Q. How are histograms and dot plots similar?
- Q. What is an disadvantage of using a stem and leaf plot instead of a histogram?
- Q. What is an advantage of using a histogram?
- Q. When describing a distribution What three things should you always mention?
- Q. Why is stem-and-leaf plot useful?
- Q. Where are stem and leaf plots used?
- Q. What is a double stem and leaf plot?
- Q. How do you do a stem and leaf plot in Excel?
- Q. What is a stretched stem and leaf display?
- Q. Can Excel make box and whisker plots?
- Q. What are the lowest and highest salaries at law firm A?
Q. What are the 7 steps for constructing a stem and leaf plot?
Steps for Making Stem-and-Leaf Plots
- Step 1: Determine the smallest and largest number in the data. The game stats are as follows:
- Step 2: Identify the stems.
- Step 3: Draw a vertical line and list the stems to the left of the line.
- Step 4: Fill in the leaves.
- Step 5: Sort the leaf data.
Q. Do you repeat numbers in a stem and leaf plot?
Say what the stem and leaf mean (Stem “2” Leaf “3” means 2.3) In this case each leaf is a decimal. It is OK to repeat a leaf value. 5.0 has a leaf of “0”…2.3, 2.5, 2.5, 2.7, 2.8 3.2, 3.6, 3.6, 4.5, 5.0.
| Stem | Leaf |
|---|---|
| 5 | 0 |
Q. Do you put a 0 in a stem and leaf plot?
The leaf is the digit in the place farthest to the right in the number, and the stem is the digit, or digits, in the number that remain when the leaf is dropped. To show a one-digit number (such as 9) using a stem-and-leaf plot, use a stem of 0 and a leaf of 9.
Q. How do you know if a stem and leaf plot is skewed?
Skewed: As with the horizontal skewing of a histogram, stem plots with a obvious skew toward one end or the other tend to indicate an increased number of outliers either lesser than the mode (skewed down – correlating to a left-skew in a histogram) or greater than the mode (skewed up – correlating to a right-skewed …
Q. How do you read a Stemplot?
This stemplot is read as follows: the stem is the tens digit and each digit in the “leaves” section is a ones digit. Put them together to have a data point. In the particular case there are 15 data points therefore the median is 79. Thus the first quartile is 69 and the third quartile is 87.
Q. Do stem and leaf plots have to be in order?
Usually, a stem and leaf plot is ordered, which simply means that the leaves are arranged in ascending order from left to right. Also, there is no need to separate the leaves (digits) with punctuation marks (commas or periods) since each leaf is always a single digit.
Q. What is an ordered stem and leaf diagram?
In such a diagram, the “stem” is a column of the unique elements of data after removing the last digit. The final digits (“leaves”) of each column are then placed in a row next to the appropriate column and sorted in numerical order. This diagram was invented by John Tukey.
Q. How do you calculate stem and leaf?
The mode is the number that occurs the most in a set of data. You can use a stem-and-leaf plot to find the mean, median and mode of a set of data. To find the mean, add up all of the numbers in the set and divide by the number of values that you added. Then, divide by the number of values, which is 16.
Q. How do stem plots work?
A plot where each data value is split into a “leaf” (usually the last digit) and a “stem” (the other digits). For example “32” is split into “3” (stem) and “2” (leaf). The “stem” values are listed down, and the “leaf” values are listed next to them.
Q. What is the key for stem and leaf plot?
Part 1: Reading a Stem and Leaf Plot It will guide you on how to read the other values. The key on this plot shows that the stem is the tens place and the leaf is the ones place.
Q. What is the difference between a histogram and a stem leaf plot?
A stem and leaf plot is a way to plot data where the data is split into stems (the largest digit) and leaves (the smallest digits). The stem and leaf plot is used like a histogram; it allows you to compare data. While a histogram uses bars to represent amounts, the leaves of the stemplot represent amounts.
Q. How are stem and leaf like dot plots?
In terms of displaying data, how is a stem-and-leaf plot similar to a dot plot? Both plots can be used to identify unusual data values. Both plots can be used to determine specific data entries. Both plots show how data are distributed.
Q. What is the advantage of a stem and leaf plot over a histogram?
The stem and leaf plot essentially provides the same information as a histogram, with the following added benefits: The plot can be constructed quickly using pencil and paper. The values of each individual data point can be recovered from the plot.
Q. How are histograms and dot plots similar?
Histograms subdivide data into intervals (bins), and use rectangles (usually columns) to show the frequency (count) of observations in each interval. Dot plots include ALL values from the data set, with one dot for each occurrence of an observed value from the set.
Q. What is an disadvantage of using a stem and leaf plot instead of a histogram?
What is a disadvantage of using a stem-and-leaf plot instead of a histogram? Histograms easily organize data of all sizes where stem-and-leaf plots do not. The mean is the measure of central tendency most likely to be affected by. an extreme value (outlier) because the outlier will affect the sum of the data values.
Q. What is an advantage of using a histogram?
The main advantages of a histogram are its simplicity and versatility. It can be used in many different situations to offer an insightful look at frequency distribution.
Q. When describing a distribution What three things should you always mention?
When describing a distribution, make sure to always tell about three things: shape, center, and spread… What is the Shape of the Distribution?
Q. Why is stem-and-leaf plot useful?
A stem-and-leaf display or stem-and-leaf plot is a device for presenting quantitative data in a graphical format, similar to a histogram, to assist in visualizing the shape of a distribution. They evolved from Arthur Bowley’s work in the early 1900s, and are useful tools in exploratory data analysis.
Q. Where are stem and leaf plots used?
A stem-and-leaf plot is used most when the number of data values is large, and it allows you to easily calculate the mode and the median of a data set.
Q. What is a double stem and leaf plot?
Double stem and leaf plots are used to compare two distributions side-by-side. This type of double stem and leaf plot contains three columns, each separated by a vertical line. The center column contains the stems. The first and third columns each contain the leaves of a different distribution.
Q. How do you do a stem and leaf plot in Excel?
How to Create a Stem-and-Leaf Plot in Excel
- Step 1: Enter the data. Enter the data values in a single column:
- Step 2: Identify the minimum and maximum values.
- Step 3: Manually enter the “stems” based on the minimum and maximum values.
- Step 4: Calculate the “leaves” for the first row.
- Step 5: Repeat the calculation for each row.
Q. What is a stretched stem and leaf display?
Stretched Stem-and-Leaf Display Whenever a stem value is stated twice, the first value corresponds to leaf values of 0 – 4 , and the second value corresponds to leaf values of 5 – 9 . In the preceding example, the leaf unit was 1. • A single digit is used to define each leaf.
Q. Can Excel make box and whisker plots?
Excel doesn’t offer a box-and-whisker chart. Instead, you can cajole a type of Excel chart into boxes and whiskers. Instead of showing the mean and the standard error, the box-and-whisker plot shows the minimum, first quartile, median, third quartile, and maximum of a set of data. The median divides the box.
Q. What are the lowest and highest salaries at law firm A?
At law firm A, the lowest salary was $90,000 and the highest salary was $203,000.