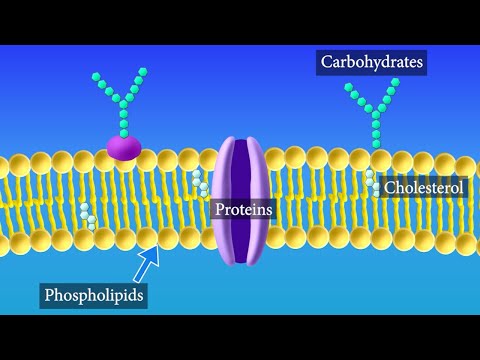
What is the location and main component of cell wall? Cell wall is a rigid structure found outside the plasma membrane of the plant cells. It is composed of cellulose – a fibrous polysaccharide.
Q. Are cell walls located inside the plant cell?
Besides the presence of chloroplasts, another major difference between plant and animal cells is the presence of a cell wall. The cell wall surrounds the plasma membrane of plant cells and provides tensile strength and protection against mechanical and osmotic stress. The cell wall is assembled in place.
Table of Contents
- Q. Are cell walls located inside the plant cell?
- Q. What is the location of cell?
- Q. Is cell wall found in plants or animals?
- Q. What are 5 similarities between plant and animal cells?
- Q. What are 4 similarities between plant and animal cells?
- Q. What are similarities between plant and animal?
- Q. What are 3 main differences between plant and animal cells?
- Q. What is difference between plant and animal?
- Q. What are the 5 differences between plant and animal cells Class 8?
- Q. What do animal cells have that plant cells do not?
- Q. What kind of transport does require energy?
- Q. What type of transport is osmosis?
- Q. What process does not require ATP?
- Q. Which process requires ATP?
- Q. Does Calvin cycle require ATP?
- Q. Where is ATP used in Calvin cycle?
- Q. How are ATP and glucose similar?
Q. What is the location of cell?
Nucleus Location The cell’s nucleus is in the middle of the cell’s cytoplasm, the liquid that fills the cell. The nucleus may not, however, be right in the middle of the cell itself. Taking up about 10 percent of the cell’s volume, the nucleus is usually around the center of the cell itself.
Q. Is cell wall found in plants or animals?
Plant cells have a cell wall, as well as a cell membrane. In plants, the cell wall surrounds the cell membrane. This gives the plant cell its unique rectangular shape. Animal cells simply have a cell membrane, but no cell wall.
Q. What are 5 similarities between plant and animal cells?
Both animal and plant cells are eukaryotic cells and have several similarities. The similarities include common organelles like cell membrane, cell nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes and golgi apparatus.
Q. What are 4 similarities between plant and animal cells?
Structurally, plant and animal cells are very similar because they are both eukaryotic cells. They both contain membrane-bound organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and peroxisomes. Both also contain similar membranes, cytosol, and cytoskeletal elements.
Q. What are similarities between plant and animal?
1) They both are living organisms. 2) They make/catch their own food. 3) They both have charecters of living things. 4) They are made up of cells.
Q. What are 3 main differences between plant and animal cells?
Major structural differences between a plant and an animal cell include:
- Plant cells have a cell wall, but animals cells do not.
- Plant cells have chloroplasts, but animal cells do not.
- Plant cells usually have one or more large vacuole(s), while animal cells have smaller vacuoles, if any are present.
Q. What is difference between plant and animal?
Animal: Animals are eukaryotic organisms with many cells. They do not use light to get energy and grow, as plants do. Differences between plants and animals: Locomotion: Plants generally are rooted in one place and do not move on their own (locomotion), whereas most animals have the ability to move fairly freely.
Q. What are the 5 differences between plant and animal cells Class 8?
Plant cells are larger than animal cells. Plant cells have plastids whereas animal cells do not have plastids. Centrosomes are absent in plant cell whereas animal cell have centrosomes. Plant cells are without cilia whereas animal cells are with cilia.
Q. What do animal cells have that plant cells do not?
Animal cells have centrosomes (or a pair of centrioles), and lysosomes, whereas plant cells do not. Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts, plasmodesmata, and plastids used for storage, and a large central vacuole, whereas animal cells do not.
Q. What kind of transport does require energy?
Active transport
Q. What type of transport is osmosis?
Osmosis is a type of simple diffusion in which water molecules diffuse through a selectively permeable membrane from areas of high water concentration to areas of lower water concentration.
Q. What process does not require ATP?
Three transport processes that do not require energy are; diffusion, osmosis and facilitated diffusion.
Q. Which process requires ATP?
ATP is consumed for energy in processes including ion transport, muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, substrate phosphorylation, and chemical synthesis. These processes, as well as others, create a high demand for ATP.
Q. Does Calvin cycle require ATP?
The Calvin cycle is not totally independent of light since it relies on ATP and NADH, which are products of the light-dependent reactions. The light-independent reactions of the Calvin cycle can be organized into three basic stages: fixation, reduction, and regeneration.
Q. Where is ATP used in Calvin cycle?
Unlike the light reactions, which take place in the thylakoid membrane, the reactions of the Calvin cycle take place in the stroma (the inner space of chloroplasts). This illustration shows that ATP and NADPH produced in the light reactions are used in the Calvin cycle to make sugar.
Q. How are ATP and glucose similar?
ATP and glucose are similar because they are both chemical sources of energy used by cells. Glucose is made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen only. ATP has phosphorus and nitrogen Also, ATP is the only form of energy your body can use.