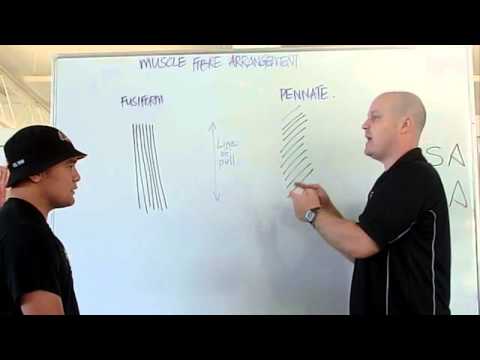
A pennate or pinnate muscle (also called a penniform muscle) is a muscle with fascicles that attach obliquely (in a slanting position) to its tendon. These types of muscles generally allow higher force production but smaller range of motion When a muscle contracts and shortens, the pennation angle increases.
Q. What is the main function of muscle fascicle?
Fascicle arrangements determine what type of movement a muscle can make. For instance, circular muscles act as sphincters, closing orifices. Muscles work in pairs to facilitate movement of the bones around the joints.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the main function of muscle fascicle?
- Q. What is meant by Multipennate muscle?
- Q. What is an example of a Bipennate muscle?
- Q. How many Multipennate muscles are there?
- Q. What is the strongest muscle shape?
- Q. How many fascicles does a muscle have?
- Q. Why does a Pennate muscle generate more tension?
- Q. Do Pennate or fusiform muscles generate more power?
- Q. Is bicep fusiform?
- Q. Where is fusiform muscle found?
- Q. Is cardiac muscle fusiform?
- Q. What are the 4 muscle categories?
- Q. Is cardiac muscle Multinucleated?
- Q. Is histological a muscle?
- Q. What is difference between muscle and cartilage?
- Q. Which muscle type can be controlled?
Q. What is meant by Multipennate muscle?
Definition. noun. A type of pennate muscle wherein the diagonal muscle fibers are in multiple rows with the central tendon branching into two or more tendons.
Q. What is an example of a Bipennate muscle?
A type of pennate muscle wherein the muscle fibers or fascicles are in opposite sides of the central tendon. Example of bipennate muscle is rectus femoris.
Q. How many Multipennate muscles are there?
These are the skeletal muscles that enable the body to move, and there are more than 600 of them in the human body. Their fibers are grouped together in sheaths of muscle cells.
Q. What is the strongest muscle shape?
The strongest muscle based on its weight is the masseter. With all muscles of the jaw working together it can close the teeth with a force as great as 55 pounds (25 kilograms) on the incisors or 200 pounds (90.7 kilograms) on the molars. The uterus sits in the lower pelvic region.
Q. How many fascicles does a muscle have?
The number of fascicles in a muscle ranged from 61 to 101 fascicles per whole muscle. During dissection it was observed that the fascicles did not always run from distal to proximal tendon, that some fascicles were in series, and that they were not the same length as the whole muscle.
Q. Why does a Pennate muscle generate more tension?
Why can a pennate muscle generate more tension than can a parallel muscle of the same size? A pennate muscle contains more muscle fibers, and thus more myofibrils and sarcomeres, than does a parallel muscle of the same size, resulting in a contraction that generates more tension.
Q. Do Pennate or fusiform muscles generate more power?
Fusiform muscles typically can produce greater force than similarly sized pennate muscles.
Q. Is bicep fusiform?
A muscle that has a shape of spindle, which is being wider in the middle and narrowing towards both ends. Example of fusiform muscle is the biceps brachii. However, compared with penniform muscle, they are not a very powerful type of muscle. …
Q. Where is fusiform muscle found?
digastricus of the head and the m. rectus abdominis, respectively. Fusiform muscles are those in which all the muscle belly fibers are arranged parallel to each other. An example of the fusiform muscle is m.
Q. Is cardiac muscle fusiform?
Cardiac muscle also has cross-striations and is composed of elongated, often branched cells bound to one another at structures called intercalated discs which are unique to cardiac muscle. Smooth muscle consists of collections of fusiform cells which lack striations and have slow, involuntary contractions.
Q. What are the 4 muscle categories?
Different types of muscle
- Skeletal muscle – the specialised tissue that is attached to bones and allows movement.
- Smooth muscle – located in various internal structures including the digestive tract, uterus and blood vessels such as arteries.
- Cardiac muscle – the muscle specific to the heart.
Q. Is cardiac muscle Multinucleated?
Skeletal muscle cells are multinucleated from the fusion of muscle cells. Smooth muscle cells are strictly mononucleated, and cardiac muscle cells are mononucleated in humans. Therefore, cardiac muscle is functionally multinucleated and skeletal (voluntary) muscle are true multinucleated.
Q. Is histological a muscle?
Fascicles are actually bundles of individual muscle cells (myofibers or myocytes). These bundles are surrounded by a connective tissue sheath called the perimysium. Each fascicle is made up of several muscle cells known as myocytes. They may also be called myofibers or muscle fibers.
Q. What is difference between muscle and cartilage?
Cartilage allows the body to move freely by protecting the joints from rubbing against each other, and is harder and not as flexible as tendons and ligaments, but not as rigid as bone. It is made up of elastic fibres and, like ligaments, collagen. What’s the difference between muscles, tendons and ligaments?
Q. Which muscle type can be controlled?
Skeletal Muscle The peripheral portion of the central nervous system (CNS) controls the skeletal muscles. Thus, these muscles are under conscious, or voluntary, control.