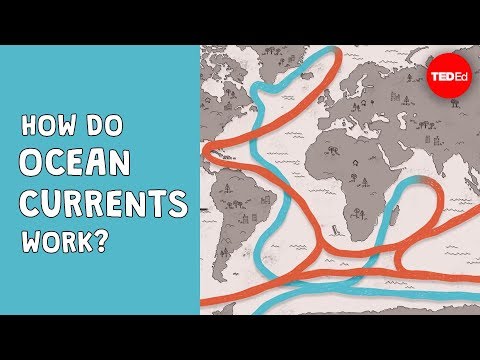
Surface ocean currents can occur on local and global scales and are typically wind-driven, resulting in both horizontal and vertical water movement. Deep ocean currents are density-driven and differ from surface currents in scale, speed, and energy.
Q. What is a poleward moving ocean current?
Longshore sand transport and longshore currents depend on waves impinging parallel to a shoreline. A poleward-moving ocean current is considered a warm current.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is a poleward moving ocean current?
- Q. What is the difference between ocean current wind-driven circulation and thermohaline circulation?
- Q. What is the fastest current in the world?
- Q. What happens if ocean currents stop?
- Q. What would cause the great ocean conveyor belt to stop?
- Q. What happens if the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation stops?
- Q. How does the temperature of ocean water affect its density?
- Q. Which two changes would increase the density of ocean water?
- Q. Why does cold air or water tend to sink?
- Q. What are 3 ways to increase water density?
- Q. Which solution has highest density?
- Q. Why does ice float in water but not rubbing?
- Q. Why does Diet Coke float in water and coke doesn t?
- Q. Does rubbing alcohol float water?
Q. What is the difference between ocean current wind-driven circulation and thermohaline circulation?
The wind-driven circulation is the more vigorous of the two and is configured as gyres that dominate an ocean region. The thermohaline circulation is more sluggish, with a typical speed of 1 cm (0.4 inch) per second, but this flow extends to the seafloor and forms circulation patterns that envelop the global ocean.
Q. What is the fastest current in the world?
the Gulf Stream
Q. What happens if ocean currents stop?
If ocean currents were to stop, climate could change quite significantly, particularly in Europe and countries in the North Atlantic. In these countries, temperatures would drop, affecting humans as well as plants and animals. In turn, economies could also be affected, particularly those that involve agriculture.
Q. What would cause the great ocean conveyor belt to stop?
Currents Tutorial Global climate change could disrupt the global conveyer belt, causing potentially drastic temperature changes in Europe and even worldwide. This sequence of events could slow or even stop the conveyor belt, which could result in potentially drastic temperature changes in Europe.
Q. What happens if the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation stops?
Further weakening of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) could result in more storms battering the UK, more intense winters and an increase in damaging heatwaves and droughts across Europe.
Q. How does the temperature of ocean water affect its density?
The density of water can also be affected by temperature. The warmer the water, the more space it takes up, and the lower its density. When comparing two samples of water with the same salinity, or mass, the water sample with the higher temperature will have a greater volume, and it will therefore be less dense.
Q. Which two changes would increase the density of ocean water?
Answer: The two main factors that affect density of ocean water are the temperature of the water and the salinity of the water. The density of ocean water continuously increases with decreasing temperature until the water freezes.
Q. Why does cold air or water tend to sink?
Explanation: When fluids (liquids and gases) are heated, they expand and therefore become less dense. When fluids are cooled, they contract and therefore become more dense. Any object or substance that is more dense than a fluid will sink in that fluid, so cold water sinks in warmer water.
Q. What are 3 ways to increase water density?
“1) Cold wind blowing on surface will bring down temperature of surface waers,increasing its density. 2) High rate of evaporation due to low relative humidity,wind action & sunlight will condense water bringing about increase in water density.
Q. Which solution has highest density?
Mercury has the highest density at standard temperature and pressure, Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more about other concepts such as the density of mercury.
Q. Why does ice float in water but not rubbing?
Alcohol is less dense than water, less even, than frozen water, so, since the ice cube is denser than the alcohol in the glass, it sinks.
Q. Why does Diet Coke float in water and coke doesn t?
Due to the difference in density, the can with the sugar in it sinks while the diet can floats. For a further refinement, mix in a bunch of salt–the density of the salt water increases enough that the sugared coke now floats.
Q. Does rubbing alcohol float water?
Expected results. Alcohol floats on oil and water sinks in oil. Water, alcohol, and oil layer well because of their densities, but also because the oil layer does not dissolve in either liquid. The oil keeps the water and alcohol separated so that they do not dissolve in one another.