Schist is a still higher degree of metamorphism, characterized by coarse grained foliation and/or lineation, with mica crystals large enough to be easily identified with the unaided eye. Gneiss is a medium to coarse-grained, irregularly banded rock with only poorly developed cleavage.
Q. Which metamorphic rock consists mostly parallel aligned coarse grained mica flakes?
marble
Table of Contents
- Q. Which metamorphic rock consists mostly parallel aligned coarse grained mica flakes?
- Q. Which type of foliated metamorphic rock is coarse grained and weakly foliated?
- Q. Which metamorphic rock will be composed predominantly of mica?
- Q. What are the 3 main types of metamorphic rocks?
- Q. How are metamorphic rocks classified?
- Q. What are the two main classifications of metamorphic rocks?
- Q. What are three examples of foliated metamorphic rocks?
- Q. What are the major types of metamorphic rocks?
- Q. What are 5 examples of metamorphic rocks?
- Q. What is the texture of metamorphic rocks?
- Q. What type of rock is shale?
- Q. Is shale a strong rock?
- Q. Where can I find shale rock?
- Q. How do you identify a shale rock?
- Q. Is there gold in shale rock?
- Q. What happens when shale is metamorphosed?
- Q. Why does shale often crumble easily?
- Q. Can you build a house on shale?
- Q. How is black shale formed?
- Q. Where is black shale found?
- Q. What environment is likely to produce a black shale?
- Q. Does shale have oil?
- Q. What are the disadvantages of using oil shale?
- Q. Is shale oil better than crude oil?
- Q. What is the difference between oil shale and shale oil?
- Q. Who is the richest oil tycoon?
- Q. Who is the richest oil company?
- Q. What country has the most oil shale?
Q. Which type of foliated metamorphic rock is coarse grained and weakly foliated?
Metamorphic Rocks
| Metamorphic rock | Texture | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Migmatite | Weakly foliated | Composed of contorted layers |
| Mylonite | Weakly foliated | Hard, fine-grained rock |
| Metaconglomerate | Weakly foliated | Strongly stretched pebbles |
| Amphibolite | Weakly foliated | Coarse-grained |
Q. Which metamorphic rock will be composed predominantly of mica?
Phyllite
Q. What are the 3 main types of metamorphic rocks?
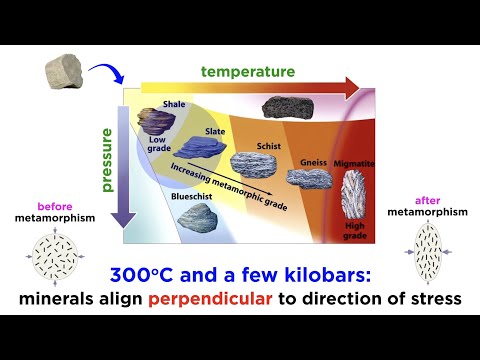
There are three ways that metamorphic rocks can form. The three types of metamorphism are Contact, Regional, and Dynamic metamorphism. Contact Metamorphism occurs when magma comes in contact with an already existing body of rock.
Q. How are metamorphic rocks classified?
Metamorphic rocks are broadly classified as foliated or non-foliated. Non-foliated metamorphic rocks do not have aligned mineral crystals. Non-foliated rocks form when pressure is uniform, or near the surface where pressure is very low. The other minerals have been crushed and deformed into a fine-grained matrix (Mtx).
Q. What are the two main classifications of metamorphic rocks?
There are two main types of metamorphic rocks: those that are foliated because they have formed in an environment with either directed pressure or shear stress, and those that are not foliated because they have formed in an environment without directed pressure or relatively near the surface with very little pressure …
Q. What are three examples of foliated metamorphic rocks?
Foliated Compostion Examples of foliated rocks are slate, phyllite and schist
Q. What are the major types of metamorphic rocks?
Common metamorphic rocks include phyllite, schist, gneiss, quartzite and marble.
Q. What are 5 examples of metamorphic rocks?
Some examples of metamorphic rocks are gneiss, slate, marble, schist, and quartzite. Slate and quartzite tiles are used in building construction. Marble is also prized for building construction and as a medium for sculpture.
Q. What is the texture of metamorphic rocks?
TEXTURES Textures of metamorphic rocks fall into two broad groups, FOLIATED and NON-FOLIATED. Foliation is produced in a rock by the parallel alignment of platy minerals (e.g., muscovite, biotite, chlorite), needle-like minerals (e.g., hornblende), or tabular minerals (e.g., feldspars).
Q. What type of rock is shale?
sedimentary rocks
Q. Is shale a strong rock?
Shale is a hardened, compacted clay or silty clay that commonly breaks along bedding planes some of which are no thicker than paper. The best exposures are found beneath ledges of harder more resistant rocks such as limestone and sandstones. Most shales are soft enough to be cut with a knife and can be very brittle.
Q. Where can I find shale rock?
Shales are often found with layers of sandstone or limestone. They typically form in environments where muds, silts, and other sediments were deposited by gentle transporting currents and became compacted, as, for example, the deep-ocean floor, basins of shallow seas, river floodplains, and playas.
Q. How do you identify a shale rock?
Shale is a fine-grained rock made from compacted mud and clay. The defining characteristic of shale is its ability to break into layers or fissility. Black and gray shale are common, but the rock can occur in any color
Q. Is there gold in shale rock?
The principal gold-bearing stratum is supposed to be the Benton group, including the Ostrea shales and the Blue Hill shales. It is stated that these rocks over practically the whole of the areas in which they occur contain more or less gold and silver, though the metals may be rather irregularly distributed.
Q. What happens when shale is metamorphosed?
Shales that are subject to heat and pressure of metamorphism alter into a hard, fissile, metamorphic rock known as slate. With continued increase in metamorphic grade the sequence is phyllite, then schist and finally gneiss.
Q. Why does shale often crumble easily?
Why does shale often crumble quite easily? better sorted than deposits sorted by wave activity. commonly better sorted than materials deposited by streams. Materials were transported a short distance before they were deposited and some other medium may have transported them.
Q. Can you build a house on shale?
In the construction business, shale is an excellent rock to build a foundation on because it’s so strong. Plus, it’s compact enough to endure a structural piling without cracking, unlike clay.
Q. How is black shale formed?
Just one or two percent organic materials can impart a dark gray or black color to the rock. In addition, this black color almost always implies that the shale formed from sediment deposited in an oxygen-deficient environment. Any oxygen that entered the environment quickly reacted with the decaying organic debris.
Q. Where is black shale found?
marine sediments
Q. What environment is likely to produce a black shale?
Black shales are dark-colored, usually thinly laminated mudstones containing appreciable organic matter (>0.5 wt% C), authigenic iron sulfides and, silt- and clay-sized detrital particles that in most cases have been accumulated under anoxic bottom water and/or bottom sediment conditions in marine or continental …
Q. Does shale have oil?
Oil shale is a sedimentary rock. As it reaches its oil window, oil shale releases a liquid known as shale oil. Oil shale is the rock from which shale oil is extracted. Shale oil is similar to petroleum, and can be refined into many different substances, including diesel fuel, gasoline, and liquid petroleum gas (LPG)
Q. What are the disadvantages of using oil shale?
Surface mining of oil shale deposits causes the usual environmental impacts of open-pit mining. In addition, the combustion and thermal processing generate waste material, which must be disposed of, and harmful atmospheric emissions, including carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas.
Q. Is shale oil better than crude oil?
The shale oil derived from oil shale does not directly substitute for crude oil in all applications. It may contain higher concentrations of olefins, oxygen, and nitrogen than conventional crude oil. Some shale oils may have higher sulfur or arsenic content.
Q. What is the difference between oil shale and shale oil?
Shale oil refers to hydrocarbons that are trapped in formations of shale rock. Oil shale is different than shale oil in that oil shale is essentially rock that contains a compound called kerogen, which is used to make oil.
Q. Who is the richest oil tycoon?
Mukesh Ambani
Q. Who is the richest oil company?
China’s Sinopec Group ranks first on the list of the world’s leading oil and gas companies of 2019 with revenues of more than US$430 billion, ahead of Shell and Saudi Aramco. According to company filings, U.S. oil and gas company Exxon Mobil ranked sixth that year, with a total 2019 revenue of some US$275 billion
Q. What country has the most oil shale?
The United States