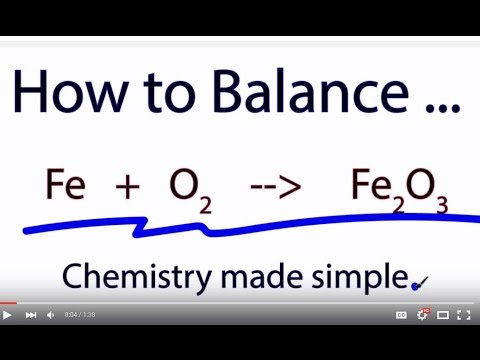
Iron(III) oxide is a neutral compound, which implies the net charge of the compound equals 0 ; i.e. the charges of all the atoms must add up to 0 . Oxygen in nearly all cases has a charge of 2− (except for a few compounds such as potassium superoxide, KO2 ), so the total ionic charge the O atoms exhibit is 3(−2)=−6 .
Q. Do transition metals have a positive or negative charge?
Transitions metals are uniformly positively charged.
Table of Contents
- Q. Do transition metals have a positive or negative charge?
- Q. Do transition metals only have one charge?
- Q. Are transition metals charges always positive?
- Q. Do all transition metals have a 2 charge?
- Q. Why do transition metals have different charges?
- Q. Why are transition metals positively charged?
- Q. What transition metal has only one ion?
- Q. Why can transition metals form multiple charges?
- Q. Which transition metals have a fixed charge?
- Q. How do you determine the charge of transition metals?
- Q. What are the charges of transition metals on periodic table?
- Q. How are the charges of some transition metal ions determined?
- Q. How do transition metals differ from other metals?
Q. Do transition metals only have one charge?
Many of the elements on the periodic table will always form ions that have the same charge. The alkali metals (shown in yellow) always form +1 ions. Many of the transition metals (orange) can have more than one charge. The notable exceptions are zinc (always +2), silver (always +1) and cadmium (always +2).
Q. Are transition metals charges always positive?
Transition metal atoms are quite good at giving up electrons, and so they can form positively charged cations. But in the atomic state they are always neutral.
Q. Do all transition metals have a 2 charge?
Many transition metals cannot lose enough electrons to attain a noble-gas electron configuration. In addition, the majority of transition metals are capable of adopting ions with different charges. Because most transition metals have two valence electrons, the charge of 2+ is a very common one for their ions.
Q. Why do transition metals have different charges?
Q. Why are transition metals positively charged?
In the chemistry of the transition elements, the 4s orbital behaves as the outermost, highest energy orbital. When these metals form ions, the 4s electrons are always lost first, leading to a positive charge on ion.
Q. What transition metal has only one ion?
Transition Metal Ions
| 1+ | 2+ | 3+ |
|---|---|---|
| copper(I), Cu+ | cadmium, Cd2+ | chromium(III), Cr3+ |
| gold(I), Au+ | chromium(II), Cr2+ | cobalt(III), Co3+ |
| mercury(I), Hg22+ | cobalt(II), Co2+ | gold(III), Au3+ |
| silver, Ag+ | copper(II), Cu2+ | iron(III), Fe3+ |
Q. Why can transition metals form multiple charges?
Q. Which transition metals have a fixed charge?
Fixed Charge – The charge is always the same value – based on electron configuration. Exceptions: The transition metals Ag+1, Zn2+, and Cd2+ have fixed charges.
Q. How do you determine the charge of transition metals?
To determine the charge on a given transition metal atom, you have to consider what element it is, the charges on the other atoms in the molecule, and the net charge on the molecule itself. The charges are always whole numbers, and the sum of all the atomic charges equals the charge on the molecule.
Q. What are the charges of transition metals on periodic table?
Transition Metals of the Periodic Table. Transition metals tend to have varying positive charges. The most common charges for the first row of transition metals are provided as: Transition Metal Ion Charges. The checkmarks in red represent the most common charge for the given transition metal. The multiple charges of transition metals can be further explained when examining concepts such as electronegativity, valence electrons, valence charge, oxidation number and electron configurations
Q. How are the charges of some transition metal ions determined?
The electric charge on a transition metal ion is all about the number of electrons it has lost to other atoms in a chemical reaction. To determine the charge on a given transition metal atom, you have to consider what element it is, the charges on the other atoms in the molecule, and the net charge on the molecule itself.
Q. How do transition metals differ from other metals?
• Transition metals are less reactive compared to other metals. • Transition metals can form colored compounds. • Transition metals can have various oxidation states within compounds, but other metals can have limited number of oxidation states (most of the time one state).