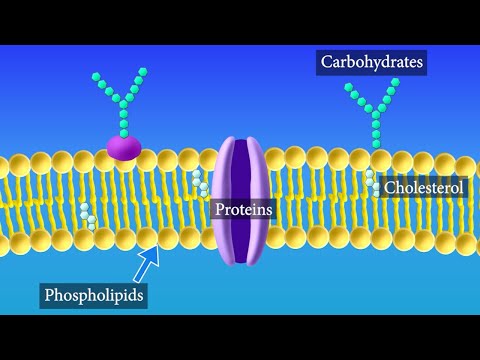
Key Concept: What is the basic structure of a cell membrane? The core of nearly all cell membranes is a double-layered sheet called a lipid bilayer. Most cell membranes contain protein molecules that run through the lipid bilayer, and carbohydrate molecules are attached to these proteins.
Q. What is the structure of membranes?
The plasma membrane is composed of a bilayer of phospholipids, with their hydrophobic, fatty acid tails in contact with each other. The landscape of the membrane is studded with proteins, some of which span the membrane. Some of these proteins serve to transport materials into or out of the cell.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the structure of membranes?
- Q. Which lipid is the main component of cell membranes?
- Q. What is the main molecule that makes up the cell membrane quizlet?
- Q. What are the major component of the plasma membrane?
- Q. Which of these are basic functions of membranes quizlet?
- Q. Which of these are basic functions of membranes?
- Q. What are 6 functions of membranes?
- Q. What is unit membrane concept?
- Q. Why is the unit membrane model rejected?
- Q. Who discovered the unit membrane?
- Q. Why it is called unit membrane model?
- Q. How many models of cell membranes are there?
- Q. What is the cell membrane model?
Q. Which lipid is the main component of cell membranes?
Cholesterol
Q. What is the main molecule that makes up the cell membrane quizlet?
Phospholipids
Q. What are the major component of the plasma membrane?
The principal components of the plasma membrane are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrate groups that are attached to some of the lipids and proteins. A phospholipid is a lipid made of glycerol, two fatty acid tails, and a phosphate-linked head group.
Q. Which of these are basic functions of membranes quizlet?
Terms in this set (23)
- Define boundaries for the cell and organelles.
- serve as sites for enzymes and receptor proteins.
- Provide for and regulate transport processes.
- contain protein receptors to detect external signals.
Q. Which of these are basic functions of membranes?
Biological membranes have three primary functions: (1) they keep toxic substances out of the cell; (2) they contain receptors and channels that allow specific molecules, such as ions, nutrients, wastes, and metabolic products, that mediate cellular and extracellular activities to pass between organelles and between the …
Q. What are 6 functions of membranes?
- Attachment to cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix. Maintains cell shape and stabilizes cytoskeleton.
- Intercellular joining. Proteins on adjacent cells hook together, briefly, for cell interaction/sharing.
- Signal transduction.
- Enzymatic activity.
- Cell-cell recognition.
- Transport.
Q. What is unit membrane concept?
: the limiting membrane of cells and various organelles viewed formerly as a 3-layered structure with an inner lipid layer and two outer protein layers and currently as a fluid phospholipid bilayer with intercalating proteins.
Q. Why is the unit membrane model rejected?
The nonpolar protein portions would separate the polar portions of the phospholipids from water, causing the bilayer to dissolve. Meaning, the Davson-Danielli model is not only incorrect, but it is also impossible. Because of this, the phospholipid bilayer sandwiched on the inside would remain isolated from the water.
Q. Who discovered the unit membrane?
Robert Hooke
Q. Why it is called unit membrane model?
Robertson proposed unit membrane concept for biological membranes. According to this concept, the biological membrane is a lipid bilayer surrounded on either side by proteins with a difference in their type for the outer and inner side.
Q. How many models of cell membranes are there?
The following points highlight the top four historical models of Plasma Membrane. The models are: 1. Lipid and Lipid Bilayer Models 2. Unit Membrane Model (Protein-Lipid Bilayer-Protein) 3.
Q. What is the cell membrane model?
The fluid mosaic model describes the cell membrane as a tapestry of several types of molecules (phospholipids, cholesterols, and proteins) that are constantly moving. This movement helps the cell membrane maintain its role as a barrier between the inside and outside of the cell environments.