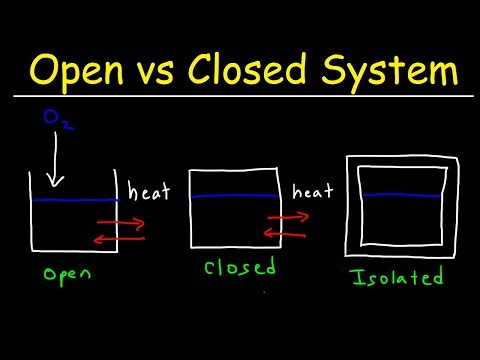
An open system is a system that has external interactions. Such interactions can take the form of information, energy, or material transfers into or out of the system boundary, depending on the discipline which defines the concept.
Q. What is an example of a closed system in thermodynamics?
A closed system allows only energy transfer but no transfer of mass. Example: a cup of coffee with a lid on it, or a simple water bottle. Isolated systems allow neither mass nor energy to flow through their boundaries. Example: a thermos flask.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is an example of a closed system in thermodynamics?
- Q. Which of the following is true for a closed system 2 points?
- Q. Which of the following quantities is not the property of the system?
- Q. Which of the following is an extensive property of the system?
- Q. What is intensive property of a system?
- Q. Which of the following is intensive property of the system?
- Q. Which of the following is an example of intensive properties?
- Q. Which of the following is an intensive variable?
- Q. Is pH an intensive property?
- Q. Is force an intensive property?
- Q. Is internal energy an intensive property?
- Q. Is heat intensive or extensive?
- Q. Is heat an intensive variable?
- Q. What do you mean by extensive and intensive properties?
- Q. What is the difference between extensive and intensive property?
- Q. What is the difference between intensive and extensive properties explain with example?
- Q. What is the difference between intensive and extensive reading?
- Q. Is buoyancy an intensive or extensive property?
- Q. Is smell a chemical or physical property?
Q. Which of the following is true for a closed system 2 points?
7. Which of the following is true for a closed system? Explanation: For a closed system mass does not change.
Q. Which of the following quantities is not the property of the system?
Out of the given quantities, heat doesn’t describe the state of a system so it is not a thermodynamic property because a system doesn’t contain heat but only can transfer heat.
Q. Which of the following is an extensive property of the system?
Mass, volume and pressure are extensive properties.
Q. What is intensive property of a system?
An intensive property does not depend on the system size or the amount of material in the system. Examples of intensive properties include temperature, T; refractive index, n; density, ρ; and hardness of an object, η.
Q. Which of the following is intensive property of the system?
Intensive properties: Properties which are independent of the amount of substance (or substances) present in the system are called intensive properties, e.g. pressure, density, temperature, viscosity, surface tension, refractive index, emf, chemical potential, sp. heat etc, These are intensive properties.
Q. Which of the following is an example of intensive properties?
Mass and volume are examples of extensive properties. An intensive property is a property of matter that depends only on the type of matter in a sample and not on the amount. Color, temperature, and solubility are examples of intensive properties.
Q. Which of the following is an intensive variable?
Temperature is independent of the quantity of matter, hence it is an intensive variable. So the correct option is (D).
Q. Is pH an intensive property?
As the pH is the measure of concentration of H+ ions and as concentration is an intensive property so pH is also an intensive property. It’s intensive as it is mass independent. pH means negative log of concentration of hydroniun ions in the solution.
Q. Is force an intensive property?
The ratio of two extensive properties is an intensive property. Force is an extensive property because F = m*a, and mass is extensive (as it depends on the number of particles). The product of an intensive and an extensive property is extensive.
Q. Is internal energy an intensive property?
An intensive property, is a physical property of a system that does not depend on the system size or the amount of material in the system. According to the definitions, density, pressure and temperature are intensive porperties and volume, internal energy are extensive properties.
Q. Is heat intensive or extensive?
Heat is an extensive property, and is proportional to the total energy of all atoms in an object. Temperature, on the other hand, is an intensive property, as it is proportional to the average energy per atom.
Q. Is heat an intensive variable?
The heat capacity is therefore an extensive variable since a large quantity of matter will have a proportionally large heat capacity. Specific heat is therefore an intensive variable and has units of energy per mass per degree.
Q. What do you mean by extensive and intensive properties?
An extensive property is a property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample. Mass and volume are examples of extensive properties. An intensive property is a property of matter that depends only on the type of matter in a sample and not on the amount.
Q. What is the difference between extensive and intensive property?
All properties of matter are either extensive or intensive and either physical or chemical. Extensive properties, such as mass and volume, depend on the amount of matter that is being measured. Intensive properties, such as density and color, do not depend on the amount of matter.
Q. What is the difference between intensive and extensive properties explain with example?
Also, it can be noted that the ratio of any two extensive properties will yield an intensive property. For Example: the ratio of mass and volume is equal to the density….Extensive Properties.
| Difference between Intensive and Extensive properties | |
|---|---|
| INTENSIVE | EXTENSIVE |
| Independent property | Dependent property |
| Size does not change | Size changes |
Q. What is the difference between intensive and extensive reading?
The first difference is that Extensive Reading covers large area, while Intensive Reading covers narrower area. According to Graham Stanley, Extensive Reading involves students reading long texts or large quantities for general understanding, with the intention of enjoying the texts.
Q. Is buoyancy an intensive or extensive property?
Matter Test
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Is buoyancy a physical or chemical property? Intensive or extensive? | Physical; Intensive |
| Is viscosity a physical or chemical property? Intensive or extensive? | Physical; Intensive |
| Is phase a physical or chemical property? Intensive or extensive? | Physical; Intensive |
Q. Is smell a chemical or physical property?
Properties that can be determined without changing the composition of a substance are referred to as physical properties. Characteristics such as melting point, boiling point, density, solubility, color, odor, etc. are physical properties.