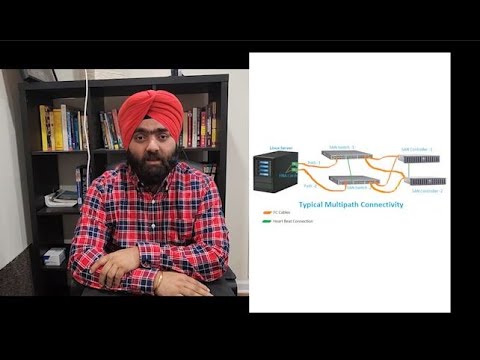
Multipathing is the technique of creating more than one physical path between the server and its storage devices. It results in better fault tolerance and performance enhancement. Oracle VM Servers are installed with multipathing enabled because it is a requirement for SAN disks to be discovered by Oracle VM Manager.
Q. What is multipathing in redhat?
Multipathing allows the combination of multiple physical connections between a server and a storage array into one virtual device. Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 supports multipathing using the dm-multipath subsystem.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is multipathing in redhat?
- Q. What is Device Mapper multipathing?
- Q. How do I enable multipathing in RHEL 7?
- Q. What exactly does Red Hat do?
- Q. What is multipathing in VMware?
- Q. How do I disable device mapper?
- Q. What is multipathing software?
- Q. How do I find multipathing software in Linux?
- Q. What is iSCSI multipath?
- Q. Is Red Hat free to use?
- Q. What is the name of a multipath device in Red Hat?
- Q. Where to find multipath bindings in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6?
- Q. What are the I / O paths in Red Hat?
- Q. Are there any San multipathing solutions in Linux?
Q. What is Device Mapper multipathing?
Device Mapper Multipathing (or DM-multipathing) is a Linux native multipath tool, which allows you to configure multiple I/O paths between server nodes and storage arrays into a single device. These I/O paths are physical SAN connections that can include separate cables, switches, and controllers.
Q. How do I enable multipathing in RHEL 7?
use the following procedure to set up DM Multipath for a basic failover configuration.
- Enter the mpathconf command with the –enable option specified: # mpathconf –enable.
- Edit the /etc/multipath. conf file if necessary.
- Save the configuration file and exit the editor, if necessary.
- Execute the following command:
Q. What exactly does Red Hat do?
Red Hat provides storage, operating system platforms, middleware, applications, management products, and support, training, and consulting services. Red Hat creates, maintains, and contributes to many free software projects.
Q. What is multipathing in VMware?
Multipathing modules manage physical paths that connect your host with storage. The modules include VMware native NMP and HPP, and any third-party MPPs. Use the esxcli command to list all storage devices controlled by the VMware NMP and display SATP and PSP information associated with each device.
Q. How do I disable device mapper?
1. To disable device-mapper-multipath, turn it off with the chkconfig command. chkconfig command makes sure that dm-multipath is not started after reboot or service restart.
Q. What is multipathing software?
Multipathing Software Overview Multipathing software enables you to define and control redundant physical paths to I/O devices such as storage devices and network interfaces. If the active path to a device becomes unavailable, the software can automatically switch to an alternate path to maintain availability.
Q. How do I find multipathing software in Linux?
Steps
- Enter the following command on the Linux host: multipath -v3 -d -ll.
- Verify that the multipathd is running by entering the following command:
- To view a list of the multipath devices, including which /dev/sd x devices are used, enter the following command: multipath -ll.
Q. What is iSCSI multipath?
Multipath I/O is a technique called to increase fault tolerance and performance by establishing multiple paths to the same iSCSI target. In case one of the network connections fails, the iSCSI targets will still be accessible via the other one.
Q. Is Red Hat free to use?
Since Red Hat Enterprise Linux is based completely on free and open source software, Red Hat makes available the complete source code to its enterprise distribution through its FTP site to anybody who wants it.
Q. What is the name of a multipath device in Red Hat?
When the user_friendly_names option in the multipath configuration file is set to yes, the name of a multipath device is of the form mpath n. For the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 release, n is an alphabetic character, so that the name of a multipath device might be mpatha or mpathb.
Q. Where to find multipath bindings in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6?
In the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 release, the location of the multipath bindings file is /etc/multipath/bindings . The Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 release provides three new defaults parameters in the multipath.conf file: checker_timeout, fast_io_fail_tmo, and dev_loss_tmo.
Q. What are the I / O paths in Red Hat?
These I/O paths are physical SAN connections that can include separate cables, switches, and controllers. Multipathing aggregates the I/O paths, creating a new device that consists of the aggregated paths. This chapter provides a summary of the features of DM-Multipath that were added subsequent to the initial release of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.
Q. Are there any San multipathing solutions in Linux?
There are a lot of SAN multipathing solutions on Linux at the moment. Two of them are discussesed in this blog. The first one is device mapper multipathing that is a failover and load balancing solution with a lot of configuration options. The second one ( mdadm multipathing) is just a failover solution with manuel re-anable of a failed path.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-aGmEB-iYX0