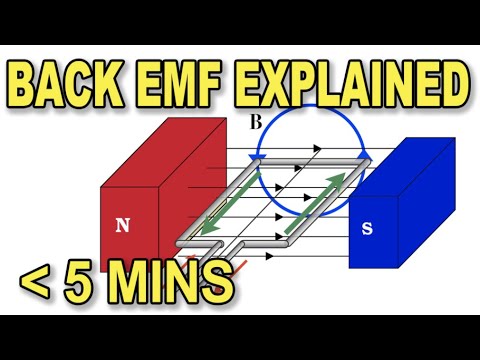
Counter-electromotive force (counter EMF, CEMF), also known as back electromotive force (back EMF), is the electromotive force (voltage) that opposes the change in current which induced it. CEMF is the EMF caused by magnetic induction (see Faraday’s law of induction, electromagnetic induction, Lenz’s law).
Q. What happens when a magnet is moved alongside a wire?
Because the magnetic field created by the electric current in the wire is changing directions around the wire, it will repel both poles of the magnet by bending away from the wire.
Table of Contents
- Q. What happens when a magnet is moved alongside a wire?
- Q. What happens when a magnet is moved back and forth inside a wire coil apex?
- Q. What is induced emf?
- Q. Can you have negative EMF?
- Q. Is back EMF good or bad?
- Q. What happens if there is no back EMF?
- Q. What will happen if the back EMF?
- Q. How do you overcome back EMF?
- Q. How is back EMF generated?
- Q. What does back EMF depend on?
- Q. Do generators have back EMF?
- Q. What factors limit the size of the back EMF?
- Q. What is back EMF in battery?
- Q. What is the difference between EMF and back EMF?
- Q. What is back emf in dc motor?
- Q. How do you reduce the back EMF of a dc motor?
- Q. Under which condition is the back EMF in an electric motor at its maximum value?
- Q. Does DC have EMF?
- Q. Can DC current produce flux?
- Q. What is in a DC motor?
Q. What happens when a magnet is moved back and forth inside a wire coil apex?
If the magnet or coil is moved back and forth repeatedly, alternating current is produced. Electric generators and electric transformers use electromagnetic induction to generate electricity or change the voltage of electric current.
Q. What is induced emf?
Induced EMF, also known as electromagnetic induction or EMF Induction is the production of voltage in a coil because of the change in a magnetic flux through a coil. Many electrical components such as motors, galvanometer, generators, transformers, etc., work based on the principle of induced EMF.
Q. Can you have negative EMF?
The negative sign in Faraday’s law comes from the fact that the emf induced in the coil acts to oppose any change in the magnetic flux. Lenz’s law: The induced emf generates a current that sets up a magnetic field which acts to oppose the change in magnetic flux.
Q. Is back EMF good or bad?
Back EMF is important for DC motors . During starting , the back emf is zero and very large current flows through the motor (limited by armature resistance which itself is very small) , however as the motor picks up speed , the back emf opposes and limit the current to safe value.
Q. What happens if there is no back EMF?
If there is no back end then large current flows in starting of motors because initial speed is zero and back emf is zero thus winding gets damaged for this purpose only we use starters for all motors. motor will not start. when the motor runs,there has to be back emf.
Q. What will happen if the back EMF?
What will happen if the back emf of a DC motor vanishes suddenly? Explanation: If back emf vanishes suddenly, motor circuit will try to retain back emf by drawing more current from supply. If supplying unit didn’t trip down by this time, excess current in armature may heat up the armature. 3.
Q. How do you overcome back EMF?
Back EMF cannot be prevented but it can be controlled. In suppressing the back EMF the objective is to prevent the very high voltages and dissipate the stored energy in a controlled way.
Q. How is back EMF generated?
When the coil of a motor is turned, magnetic flux changes, and an emf (consistent with Faraday’s law of induction) is induced. Lenz’s law tells us the emf opposes any change, so that the input emf that powers the motor will be opposed by the motor’s self-generated emf, called the back emf of the motor.
Q. What does back EMF depend on?
The back EMF depends, of course, on the speed of the motor — the change in magnetic flux that generates it increases with motor speed — so that as the motor begins to turn, the back EMF grows until the motor has reached its maximum speed, at which point the back EMF stays at its maximum value.
Q. Do generators have back EMF?
Explain how an electric generator works. Determine the induced emf in a loop at any time interval, rotating at a constant rate in a magnetic field. Show that rotating coils have an induced emf; in motors this is called back emf because it opposes the emf input to the motor.
Q. What factors limit the size of the back EMF?
The magnitude of the back emf induced in a coil is directly proportional to the rate of change of flux. As the rate of change of flux depend upon the speed of the motor, therefore by increasing the speed of the motor will increase the back emf and decreasing its speed will decrease the back emf.
Q. What is back EMF in battery?
The counter-electromotive force (abbreviated counter EMF, or CEMF), also known as the back electromotive force, is the voltage, or electromotive force, that pushes against the current which induces it. For example, the voltage drop across an inductor is due to the induced magnetic field inside the coil.
Q. What is the difference between EMF and back EMF?
If an open coil is subjected to a variable magnetic field, at the ends of the coil a potential difference is induced which is called induced emf. If a coil is connected to an emf source and switched on, the rising current will produced an variable magnetic field which in turn produces an emf. It is called back emf.
Q. What is back emf in dc motor?
When the armature of the DC motor rotates under the influence of driving torque, the armature of the conductors moves through a magnetic field inducing an emf in them. The induced emf is in the opposite direction to the applied voltage and is known as the back emf.
Q. How do you reduce the back EMF of a dc motor?
To avoid this problem, take the effect of back-EMF into consideration in system design. Motors do have a blowback voltage, a back-EMF that is usually addressed by adding a reverse-biased fast diode, sometimes in addition to a capacitor, across the motor’s supply wires.
Q. Under which condition is the back EMF in an electric motor at its maximum value?
Under which condition is the back emf in an electric motor at its maximum value? Motor speed is at maximum.
Q. Does DC have EMF?
Most power systems operate with alternating current (AC). But there are some direct current (DC) power lines, which produce DC or static EMFs. Not many studies have been done of the health of people living near DC power lines.
Q. Can DC current produce flux?
DC current does product magnetic flux. In fact any charge motion will produce magnetic flux. But with DC, since the current is constant, the flux also remains constant.
Q. What is in a DC motor?
A DC motor consists of an stator, an armature, a rotor and a commutator with brushes. Opposite polarity between the two magnetic fields inside the motor cause it to turn. DC motors are the simplest type of motor and are used in household appliances, such as electric razors, and in electric windows in cars.