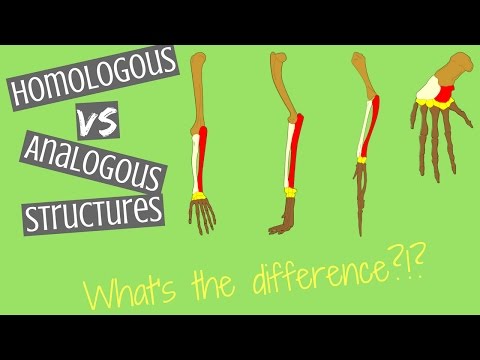
Answer: Homologous organs: These are organs having a similar structural plan, but different functions. Analogous organs: These are organs having different structural plans, but common functions. For example, the wing of a bird and the wing of an insect.
Q. What is homologous and analogous organs?
Homologous structures share a similar embryonic origin; analogous organs have a similar function. For example, the bones in the front flipper of a whale are homologous to the bones in the human arm. The wings of a butterfly and the wings of a bird are analogous but not homologous.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is homologous and analogous organs?
- Q. What are the differences between homologous organs & analogous organs?
- Q. What is homologous and analogous organs give example?
- Q. What is an analogous organ?
- Q. What is analogy and homology?
- Q. What is the difference between analogy and homology?
- Q. What is analogous organs give example?
- Q. What is homology organ?
- Q. What are homologous and analogous organs Class 10?
- Q. What are homologous organs 12th?
- Q. What is the difference between analogous and homologous organs?
- Q. Why are homologous organs known as divergent evolution?
- Q. Which is an example of a homologous structure?
- Q. Which is an example of an analogous structure?
Q. What are the differences between homologous organs & analogous organs?
Homologous structures share an identical embryonic origin; analogous organs have an identical function. For instance, the bones within the front flipper of a whale are homologous to the bones within the human arm. The wings of a butterfly and therefore the wings of a bird are analogous but not homologous.
Q. What is homologous and analogous organs give example?
(a) Analogous Organs: Organs which performs similar function but are different in structure and origin. Example – wings of a bird and wings of an insect. Homologous Organ: Organs which have different functions but similar structure and origin. Example – fore arm of frog, lizard, bird and human.
Q. What is an analogous organ?
An analogous organ pertains to an organ that functions similarly to the organ from another yet evolutionary disparate species. The smelling organs of the terrestrial coconut crab are similar to the sensilla of insects.
Q. What is analogy and homology?
In biology, homology is the resemblance of the arrangement, physiology, or growth of various species of organisms. In biology, an analogy is a functional similarity of structure, based on the similarity of use and not upon common evolutionary origins. Due to a similar structure, they do have similar functions.
Q. What is the difference between analogy and homology?
In biology, homology is the resemblance of the arrangement, physiology, or growth of various species of organisms. In biology, an analogy is a functional similarity of structure, based on the similarity of use and not upon common evolutionary origins. Due to different structures, they do not have similar functions.
Q. What is analogous organs give example?
Analogous organs are the opposite of homologous organs, which have similar functions but different origins. An example of an analogous trait would be the wings of insects, bats and birds that evolved independently in each lineage separately after diverging from an ancestor without wings.
Q. What is homology organ?
Homologous organs are referred to the organs/traits that are inherited by two different organisms but from the same ancestry. They are similar in the morphology but do different works. That means their functions are different. Example of homologous organs- forelimb of god and flipper of whales.
Q. What are homologous and analogous organs Class 10?
Q. What are homologous organs 12th?
An organ is known as a homologous organ if they have the same ancestor but the function differs. Example: The arm of whales, humans and birds has been derived from the same ancestor but they perform different function. Analogous structures.
Q. What is the difference between analogous and homologous organs?
Namely homologous organs and analogous organs. Let us learn about these organs. Homologous organs are defined as the organs of different animals that are having a similar structure but differ in their functions. The structure of the two different animals resemble but the functions of their organs vary.
Q. Why are homologous organs known as divergent evolution?
1) homologous organ is also known as divergent evolution because of same structure have become different in different organism due to different adaptation 2) these structures have different in appearance and different function 3) these structure have similar basic structure and developmental origin
Q. Which is an example of a homologous structure?
Q. Structures that are inherited from a common ancestor are homologous. Q. When would convergent evolution occur? Q. Humans, birds, whales, and lizards all have similar arm bones. What is the reason for this? Q. Shark fins and dolphin fins are examples of analogous structures. Q. Analogous structures show common ancestry. Q.
Q. Which is an example of an analogous structure?
Q. Humans, birds, whales, and lizards all have similar arm bones. What is the reason for this? Q. Shark fins and dolphin fins are examples of analogous structures. Q. Analogous structures show common ancestry. Q. When did life on Earth begin? Q. Which of the following places the geologic time eras in order from oldest to most recent? Q.