If oxygen is available, glycolysis is followed by two processes in the mitochondria — the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, respectively — that further increase ATP yield.
Q. Does photosynthesis release energy from glucose?
Most life on Earth depends on photosynthesis. The process is carried out by plants, algae, and some types of bacteria, which capture energy from sunlight to produce oxygen (O2) and chemical energy stored in glucose (a sugar).
Table of Contents
- Q. Does photosynthesis release energy from glucose?
- Q. Does glycolysis release energy from glucose?
- Q. What happens after glycolysis if oxygen is present?
- Q. Does the presence of oxygen in the environment stop glycolysis?
- Q. What process releases energy from food in the presence of oxygen?
- Q. What is the first step in releasing energy of glucose?
- Q. What process stores energy?
- Q. What is the source of energy for ATP?
- Q. How is glycogen used to make ATP?
- Q. What foods produce ATP?
- Q. What supplements increase ATP?
- Q. What causes low ATP?
- Q. Does caffeine increase ATP production?
- Q. Does exercise increase ATP production?
- Q. How do you restore ATP?
- Q. Can you take ATP supplements?
- Q. What is the best ATP supplement?
- Q. Can you isolate ATP?
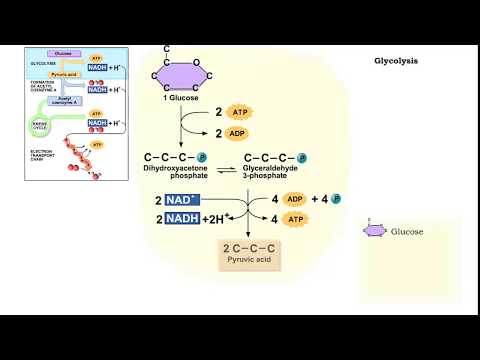
Q. Does glycolysis release energy from glucose?
Glycolysis produces 2 ATP, 2 NADH, and 2 pyruvate molecules: Glycolysis, or the aerobic catabolic breakdown of glucose, produces energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and pyruvate, which itself enters the citric acid cycle to produce more energy. Instead, glycolysis is their sole source of ATP.
Q. What happens after glycolysis if oxygen is present?
In the presence of oxygen, the next stage after glycolysis is oxidative phosphorylation, which feeds pyruvate to the Krebs Cycle and feeds the hydrogen released from glycolysis to the electron transport chain to produce more ATP (up to 38 molecules of ATP are produced in this process).
Q. Does the presence of oxygen in the environment stop glycolysis?
Glycolysis requires no oxygen. It is an anaerobic type of respiration performed by all cells, including anaerobic cells that are killed by oxygen. For these reasons, glycolysis is believed to be one of the first types of cell respiration and a very ancient process, billions of years old.
Q. What process releases energy from food in the presence of oxygen?
cellular respiration
Q. What is the first step in releasing energy of glucose?
Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism. Glycolysis consists of an energy-requiring phase followed by an energy-releasing phase.
Q. What process stores energy?
By breaking the chemical bonds in glucose, cells release the stored energy and make the ATP they need. The process in which glucose is broken down and ATP is made is called cellular respiration. Together, the two processes store and release energy in living organisms.
Q. What is the source of energy for ATP?
Together ATP and phosphocreatine are called ‘high-energy’ phosphates as large amounts of energy are released quickly during their breakdown. Carbohydrates are the bodies preferred source of food energy for the synthesis of ATP, with one gram of CHO providing four calories of energy.
Q. How is glycogen used to make ATP?
During intense, intermittent exercise and throughout prolonged physical activity, muscle glycogen particles are broken down, freeing glucose molecules that muscle cells then oxidize through anaerobic and aerobic processes to produce the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules required for muscle contraction.
Q. What foods produce ATP?
The ATP your body produces and stores comes from the oxygen you breathe and the food you eat. Boost your ATP with fatty acids and protein from lean meats like chicken and turkey, fatty fish like salmon and tuna, and nuts.
Q. What supplements increase ATP?
For example, creatine is a widely used nutritional supplement that has been proven in multiple studies to increase skeletal muscle phosphocreatine and free creatine concentrations, which may enhance the ability to sustain high adenosine triphosphate (ATP) turnover rates during strenuous exercise [1].
Q. What causes low ATP?
Complex changes in mitochondrial structure and function, including disorganization of mitochondrial structure, decline in the activity of enzymes involved in mitochondrial ATP synthesis, accumulation of mtDNA mutations, increased damage of mitochondrial proteins and lipids by reactive oxygen species are considered to …
Q. Does caffeine increase ATP production?
In the human body, caffeine acts as a stimulant for the central nervous system. It keeps us awake by blocking one of the body’s key sleep-inducing molecules, a substance called adenosine. Your body needs a constant supply of energy, which it gets by breaking down a high-energy molecule called ATP.
Q. Does exercise increase ATP production?
High-intensity exercise can result in up to a 1,000-fold increase in the rate of ATP demand compared to that at rest (Newsholme et al., 1983). To sustain muscle contraction, ATP needs to be regenerated at a rate complementary to ATP demand.
Q. How do you restore ATP?
ATP that is already present in the muscle is used and recycled by breaking down creatine phosphate. Once we have depleted our ATP (through a 1 rep max attempt, for example), it takes at least 3 minutes of rest for muscles to recover the maximum amount possible of ATP and creatine phosphate.
Q. Can you take ATP supplements?
ATP is the primary source of energy for the cells, and supplementation may enhance the ability to maintain high ATP turnover during high-intensity exercise. Oral ATP supplements have beneficial effects in some but not all studies examining physical performance.
Q. What is the best ATP supplement?
creatine monohydrate
Q. Can you isolate ATP?
Yes, ATP can be synthesised, isolated and you can even eat it. However, ATP is rarely shuffled into or out of cells.