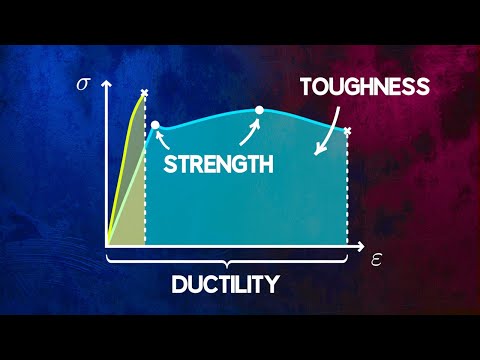
In contrast, ductility is the ability of a solid material to deform under tensile stress. Practically, a ductile material is a material that can easily be stretched into a wire when pulled as shown in the figure below.
Q. What is ductility with example?
Ductility is the physical property of a material associated with the ability to be hammered thin or stretched into wire without breaking. Examples: Most metals are good examples of ductile materials, including gold, silver, copper, erbium, terbium, and samarium.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is ductility with example?
- Q. What is ductility in science for kids?
- Q. What is ductility in science for Class 8?
- Q. What is ductility physics?
- Q. What is Millie ability?
- Q. What is meant by ductility class 10?
- Q. What is ductility in science Brainly?
- Q. What is ductility in 8th standard?
- Q. What is ductility in Wikipedia?
- Q. What is short ductility?
- Q. What is meant by Meliability?
- Q. What is the scientific definition of ductility?
- Q. What is the definition of ductility in chemistry?
- Q. What is ductile in chemistry?
- Q. What is ductility index?
Q. What is ductility in science for kids?
Ductility is when a solid material stretches under tensile strain. If ductile, a material may be stretched into a wire. Malleability, a similar property, is a material’s ability to deform under pressure (compressive stress). If malleable, a material may be flattened by hammering or rolling.
Q. What is ductility in science for Class 8?
Ductility :- The property of metal by which metals can be drawn into wires. Ductility is the physical property of a material associated with the ability to be hammered thin or stretched into wire without breaking. A ductile substance can be drawn into a wire.
Q. What is ductility physics?
ductility, Capacity of a material to deform permanently (e.g., stretch, bend, or spread) in response to stress. When a material specimen is stressed, it deforms elastically (see elasticity) at first; above a certain deformation, called the elastic limit, deformation becomes permanent.
Q. What is Millie ability?
Millie was a former member of the Ghouls, a villain gang that prevailed during the Age of Anarchy. She has the power of psychometry.
Q. What is meant by ductility class 10?
Property of metals by which they can be drawn into thin wires is called as ductility. The ductility of different metals is different.
Q. What is ductility in science Brainly?
Ductility is the physical property of a material associated with the ability to be hammered thin or stretched into wire without breaking.
Q. What is ductility in 8th standard?
The property of metals, which makes the metals to be drawn into thin wires is called ductility.
Q. What is ductility in Wikipedia?
Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material’s amenability to drawing (e.g. into wire). In materials science, ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stress before failure.
Q. What is short ductility?
: the quality or state of being ductile especially : the ability of a material to have its shape changed (as by being drawn out into wire or thread) without losing strength or breaking When certain alloys are added to metal, hardness and strength can be improved without decreasing the ductility. —
Q. What is meant by Meliability?
: the quality or state of being malleable: such as. a : capability of being shaped or extended by hammering, forging, etc. the malleability of tin. b : capability of being influenced or altered by external forces The malleability of memory …
Q. What is the scientific definition of ductility?
Freebase (0.00 / 0 votes)Rate this definition: Ductility. In materials science, ductility is a solid material’s ability to deform under tensile stress; this is often characterized by the material’s ability to be stretched into a wire.
Q. What is the definition of ductility in chemistry?
Ductility is a measure of a material’s ability to undergo appreciable plastic deformation before fracture; it may be expressed as percent elongation or percent area reduction from a tensile test. Generalic, Eni . “Ductility.”. Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary.
Q. What is ductile in chemistry?
Ductility is the plastic deformation that occurs in metal as a result of such types of strain. The term “ductile” literally means that a metal substance is capable of being stretched into a thin wire without becoming weaker or more brittle in the process.
Q. What is ductility index?
ductility index. The ratio of the total deformation at maximum load to the elastic limit deformation.