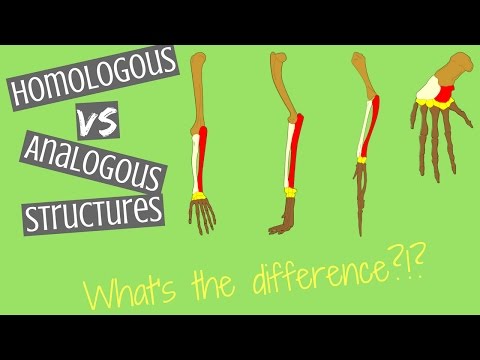
A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the wings of bats and birds, the arms of primates, the front flippers of whales and the forelegs of four-legged vertebrates like dogs and crocodiles are all derived from the same ancestral tetrapod structure.
Q. When can it be said that two species possess common ancestor?
If two or more species share a unique physical trait they may all have inherited this trait from a common ancestor. Traits that are shared due to common ancestry are homologous structures.
Table of Contents
- Q. When can it be said that two species possess common ancestor?
- Q. Why do some species have similar body structures and developmental patterns?
- Q. How are analogous structures evidence of evolution?
- Q. What is a analogous structure?
- Q. What are two homologous structures?
- Q. What is an example of vestigial structures?
- Q. How can you tell the difference between homologous and analogous structures?
- Q. What explains the existence of analogous structures?
- Q. What is a homologous trait?
- Q. Is DNA a homologous trait?
- Q. What are homologous structures give an example is it necessary?
- Q. What are home ologist structure?
- Q. What are homologous and analogous organs Class 10?
- Q. What is the homologous structure found in humans cats whales and bats?
- Q. Are bat and bird wings homologous?
- Q. Are humans and apes analogous or homologous?
- Q. What is homologous to the wing of a bat?
- Q. Are bat wings and human arms homologous structures?
- Q. Are bats and birds related?
- Q. How do bats fly differently than birds?
Q. Why do some species have similar body structures and developmental patterns?
Why do scientists think related species have similar body structures and development patterns? The species inherited many of the same genes from a common ancestor. Only traits that are controlled by genes can be acted on by natural selection.
Q. How are analogous structures evidence of evolution?
Similar body parts may be homologous structures or analogous structures. Both provide evidence for evolution. Analogous structures are structures that are similar in unrelated organisms. The structures are similar because they evolved to do the same job, not because they were inherited from a common ancestor.
Q. What is a analogous structure?
Alternative Title: analogous structure. Analogy, in biology, similarity of function and superficial resemblance of structures that have different origins. For example, the wings of a fly, a moth, and a bird are analogous because they developed independently as adaptations to a common function—flying.
Q. What are two homologous structures?
The arm of a human, the wing of a bird or a bat, the leg of a dog and the flipper of a dolphin or whale are homologous structures. They are different and have a different purpose, but they are similar and share common traits. They are considered homologous structures because they have a similar underlying anatomy.
Q. What is an example of vestigial structures?
Structures that have no apparent function and appear to be residual parts from a past ancestor are called vestigial structures. Examples of vestigial structures include the human appendix, the pelvic bone of a snake, and the wings of flightless birds.
Q. How can you tell the difference between homologous and analogous structures?
Homologous structures share a similar embryonic origin. Analogous organs have a similar function. For example, the bones in a whale’s front flipper are homologous to the bones in the human arm. These structures are not analogous.
Q. What explains the existence of analogous structures?
Analogous structures are structures that are similar in unrelated organisms. The structures are similar because they evolved to do the same job, not because they were inherited from a common ancestor. However, wings evolved independently in the two groups of animals.
Q. What is a homologous trait?
A homologous trait is any characteristic which is derived by evolution from a common ancestor. This is contrasted to analogous traits: similarities between organisms that were evolved separately. The term existed before 1859, but got its modern meaning after Darwin established the idea of common descent.
Q. Is DNA a homologous trait?
When considering molecular homologous traits, scientists study organisms’ DNA and RNA to figure out the exact common ancestor. Organisms that are closely related will have similar genetic structures. For instance, humans, bonobos and chimpanzees share almost 99 percent of their DNA.
Q. What are homologous structures give an example is it necessary?
Yes, It is necessary that homologous structures always have a common ancestor. As explained in the above example, the basic structure of arm of human and wing of bat is similar but they modified to perform different function in different vertebrates. Therefore, this shows that they have evolved from a common ancestor.
Q. What are home ologist structure?
Homologous structures are structures having a similar origin, similar development, similar internal structure and basic plan but showing different external form and function. Example – Forelimbs of mammals, birds, reptiles and amphibians.
Q. What are homologous and analogous organs Class 10?
Answer: Homologous organs: These are organs having a similar structural plan, but different functions. Analogous organs: These are organs having different structural plans, but common functions. For example, the wing of a bird and the wing of an insect.
Q. What is the homologous structure found in humans cats whales and bats?
An example of homologous structures are the limbs of humans, cats, whales, and bats. Regardless of whether it is an arm, leg, flipper or wing, these structures are built upon the same bone structure. Homologies are the result of divergent evolution.
Q. Are bat and bird wings homologous?
An example of this is the wings of bats and birds. These structures are homologous in that they are in both cases modifications of the forelimb bone structure of early reptiles. But birds’ wings differ from those of bats in the number of digits and in having feathers for flight while bats have none.
Q. Are humans and apes analogous or homologous?
Homologous (but not analogous) traits can be used to reconstruct the evolutionary relationships between different species. For example, humans, chimpanzees, and gorillas all have thumbs that are very similar anatomically and are homologous.
Q. What is homologous to the wing of a bat?
For example, the bones in the wings of bats and birds have homologous structures. Homologous structures: Bat and bird wings are homologous structures, indicating that bats and birds share a common evolutionary past. Notice it is not simply a single bone, but rather a grouping of several bones arranged in a similar way.
Q. Are bat wings and human arms homologous structures?
A great example of homologous structures are the wings of a bat and the arms of a human. Bats and humans are both mammals, so they share a common ancestry. Both a bat’s wing and a human’s arm share a similar internal bone structure, even though they look very different externally.
Q. Are bats and birds related?
Even though they fly through the air, bats are not birds. Instead, bats are mammals. In fact, bats are the only mammals that can truly fly. A few other mammals, such as the flying squirrel, appear to fly, but they actually glide through the air instead.
Q. How do bats fly differently than birds?
While both birds and bats fly by flapping wings in a down-and-forward way to generate lift, the main difference comes from the bat’s use of additional ‘fingers’. The wings of a bird are comprised of enlongated arms with a single finger on the end. This allows a bat to have a better range of motion in its flying.