Hydroelectric power, also called hydropower, electricity produced from generators driven by turbines that convert the potential energy of falling or fast-flowing water into mechanical energy.
Q. Which word are related to hydroelectric power plants?
other words for hydroelectric plant
Table of Contents
- Q. Which word are related to hydroelectric power plants?
- Q. What are the parts of a hydroelectric power plant?
- Q. Who regulates hydropower?
- Q. Is hydroelectric power illegal?
- Q. When was the Federal Power Act passed?
- Q. What does the Federal Power Act do?
- Q. What did the Federal Power Act do?
- Q. Is purpa part of the Federal Power Act?
- Q. What did the purpa 1978 law state?
- Q. What is a FERC 203 filing?
- Q. Is the Public Utility Holding Company Act still around today?
- Q. When was electricity regulated?
- Q. What is an electric holding company?
- Q. Why are electric utilities regulated?
- Q. Who determines a utility’s authorized return on equity?
- Q. Does the government control electricity?
- Q. What is the difference between regulated and unregulated utilities?
- Q. What is unregulated electricity?
- Q. How do Regulated utilities make money?
- Q. What is the largest energy company in the US?
- Q. Who are the big 5 energy companies?
- Q. What are the top 5 energy companies?
- power station.
- station.
- atomic power plant.
- generating station.
- hydroelectric scheme.
- nuclear power plant.
- power source.
- powerhouse.
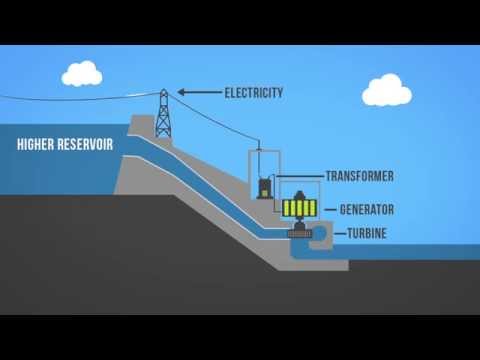
Q. What are the parts of a hydroelectric power plant?
A typical hydroelectric plant is a system with three parts: a power plant where the electricity is produced, a dam that can be opened or closed to control water flow, and a reservoir where water is stored. The water behind the dam flows through an intake and pushes against blades in a turbine, causing them to turn.
Q. Who regulates hydropower?
FERC regulates only 56 percent of the hydroelectric projects in the U.S. The remaining projects have been built by the federal government. They are operated by the U.S. Department of the Interior (Bureau of Reclamation), the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and the Tennessee Valley Authority.
Q. Is hydroelectric power illegal?
It’s not necessarily “illegal” as it is heavily regulated. Among the issues that will be problems are: You don’t own the water – Simply because you purchased property with a flowing body of water running through it (as opposed to a pond or a small lake) doesn’t mean that you control that water.
Q. When was the Federal Power Act passed?
1920
Q. What does the Federal Power Act do?
Overview. The act created the Federal Power Commission (FPC) (now the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission) as the licensing authority for these plants. The FPC regulated the interstate activities of the electric power and natural gas industries, and coordinated national hydroelectric power activities.
Q. What did the Federal Power Act do?
By 1920, as 40% of the power produced in the United States was hydroelectric, the Federal Power Act was enacted into law. The Act created the Federal Power Commission whose main purpose was to regulate hydroelectric power plants on federal land and water.
Q. Is purpa part of the Federal Power Act?
The Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act (PURPA, Pub. L. 95–617, 92 Stat. 3117, enacted November 9, 1978) is a United States Act passed as part of the National Energy Act….Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act.
| Citations | |
|---|---|
| U.S.C. sections created | 16 U.S.C. ch. 46 § 2601 et seq. |
| Legislative history | |
Q. What did the purpa 1978 law state?
The Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act of 1978 (PURPA) was enacted following the energy crisis of the 1970s to encourage cogeneration and renewable resources and promote competition for electric generation. It also sought to encourage electricity conservation.
Q. What is a FERC 203 filing?
Under Section 203 of the Federal Power Act (FPA), FERC approval is required if “a public utility seeks to sell, lease, or otherwise dispose of jurisdictional facilities.” FERC has interpreted this authority broadly, requiring Section 203 approval for a wide variety of transactions.
Q. Is the Public Utility Holding Company Act still around today?
The Public Utility Holding Company Act of 1935 (PUHCA 1935) was repealed in the Energy Policy Act of 2005. The burden of oversight of the financial transactions of public utility companies, including mergers and acquisitions, now falls more heavily on the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC).
Q. When was electricity regulated?
1935
Q. What is an electric holding company?
In general, a parent company that directly or indirectly owns a majority or all the voting securities (such as common stock) of one or more electric utility companies located in the region.
Q. Why are electric utilities regulated?
Electric utilities are monopolies, so they have to be carefully regulated in order to protect the interests of their captive customers. The allowed rate of return (return on assets) drives a utility’s profitability. Expenses are simply passed through, including fuel in cases where regulated utilities own power plants.
Q. Who determines a utility’s authorized return on equity?
the authorized rate of return on equity, which is set by the utility regulator, typically in the range of 9 to 11% in the U.S. the amount of equity invested in buying capital assets (less depreciation taken over time), called equity rate base.
Q. Does the government control electricity?
A: The Federal government, through the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, regulates interstate power sales and service. State governments, through their public utility commissions or equivalent, regulate retail electric service as well as facility planning and siting.
Q. What is the difference between regulated and unregulated utilities?
In a regulated electricity market, vertically integrated monopoly utilities cover the entire value chain with oversight from a public regulator. In a deregulated electricity market, market participants other than utility companies own power plants and transmission lines.
Q. What is unregulated electricity?
Unregulated energy is building energy consumption resulting from a system or process that is not ‘controlled’, ie energy consumption from systems in the building on which the Building Regulations do not impose a requirement. Some buildings can have unregulated energy accounting for 50% of total energy use.
Q. How do Regulated utilities make money?
In part, because the way utilities are regulated and paid has hardly changed in a hundred years. Here’s the basic idea behind this century-year-old utility business model: utilities make profit by investing in the infrastructure, like pipes and wires, that provide energy services to customers.
Q. What is the largest energy company in the US?
Pacific Gas & Electric
Q. Who are the big 5 energy companies?
The large energy suppliers (often also called the ‘Big Six’) are the companies that hold supply licences and supply most of the energy to domestic households in the GB market. They are: Centrica plc (parent company of British Gas), E. ON UK, Scottish and Southern Energy (SSE), RWE npower, EDF Energy and ScottishPower.
Q. What are the top 5 energy companies?
Who are the big six?
- British Gas. British Gas is the UK’s largest energy company and is the greenest supplier of the big six.
- EDF Energy. EDF Energy is the UK arm of the French energy giant and supplies more than 5.5 million customers.
- E.ON. E.
- npower.
- Scottish Power.
- SSE.