Once a star has exhausted its supply of hydrogen in its core, leaving nothing but helium, the outward force created by fusion starts to decrease and the star can no longer maintain equilibrium. The force of gravity becomes greater than the force from internal pressure and the star begins to collapse.
Q. What happens to our sun after all fusion stops?
At the very end, the Sun will literally cough itself to death as multiple fuel ignitions and choked-off fusion extinguishments rip through its atmosphere. In four or five huge bursts, spaced roughly 100,000 years apart, the outer layers of the Sun will separate from the core and be completely blown away.
Table of Contents
- Q. What happens to our sun after all fusion stops?
- Q. What would happen if the nuclear reactions in the sun stopped?
- Q. What happens when fusion stops in a star?
- Q. What is the last stage of a star?
- Q. Do low mass stars live longer?
- Q. What is the lowest mass star?
- Q. Do high mass stars die faster?
- Q. What would happen if a black hole hit the sun?
- Q. Could a human survive a black hole?
- Q. Why can’t we escape a black hole?
- Q. What is the scariest thing in the universe?
- Q. What can destroy a black hole?
- Q. Can you travel faster than the speed of light?
- Q. Can time escape a black hole?
- Q. Did anyone die in a black hole?
- Q. Where do you go if you fall into a black hole?
Q. What would happen if the nuclear reactions in the sun stopped?
Since certain fraction mass that was being converted to energy due to these nuclear reactions, stopping the reactions would reduce the rate of loss and mass and therefore mass will be become constant.
Q. What happens when fusion stops in a star?
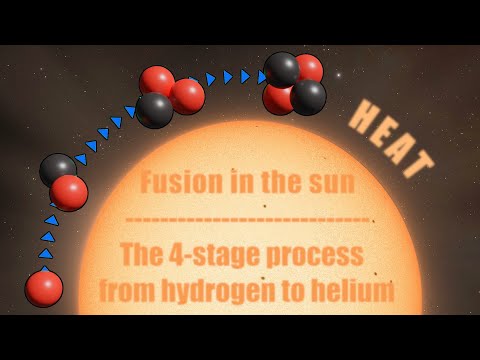
A star remains on the main sequence as long as there is hydrogen in its core that it can fuse into helium. Eventually the hydrogen fuel in the core runs out and fusion stops, shutting off the outward radiation pressure.
Q. What is the last stage of a star?
Hubble Views Final Stages of a Star’s Life A planetary nebula is the final stage of a Sun-like star. As such, planetary nebulas allow us a glimpse into the future of our own solar system. A star like our Sun will, at the end of its life, transform into a red giant.
Q. Do low mass stars live longer?
A smaller star has less fuel, but its rate of fusion is not as fast. Therefore, smaller stars live longer than larger stars because their rate of fuel consumption is not as rapid.
Q. What is the lowest mass star?
the Sun
Q. Do high mass stars die faster?
Massive stars evolve quicker than light stars. Massive stars live shorter lives than the common small stars because even though they have a larger amount of hydrogen for nuclear reactions, their rate of consuming their fuel is very much greater.
Q. What would happen if a black hole hit the sun?
If a black hole under 100 million masses of our Sun entered our Solar System, it wouldn’t swallow the Sun in one go. It would gradually start pulling matter from our star, until all that’s left of it would be a cloud of gas. Our planet could be torn apart by the tidal forces from the black hole consuming our Sun.
Q. Could a human survive a black hole?
Even light, the fastest-moving thing in our universe, cannot escape – hence the term “black hole.” The radial size of the event horizon depends on the mass of the respective black hole and is key for a person to survive falling into one. A person falling into a supermassive black hole would likely survive.
Q. Why can’t we escape a black hole?
This is the reason why light cannot escape a black hole. Another way to look at it is that the escape velocity from the event horizon of a black hole is faster than the speed of light. Since nothing can travel faster than the speed of light, nothing escapes the event horizon of a black hole.
Q. What is the scariest thing in the universe?
Supermassive black holes are strange The biggest black hole discovered so far weighs in at 40 billion times the mass of the Sun, or 20 times the size of the solar system. Whereas the outer planets in our solar system orbit once in 250 years, this much more massive object spins once every three months.
Q. What can destroy a black hole?
Anything that gets too close to the central singularity of a black hole, be it an asteroid, planet, or star, risks being torn apart by its extreme gravitational field.
Q. Can you travel faster than the speed of light?
Albert Einstein’s special theory of relativity famously dictates that no known object can travel faster than the speed of light in vacuum, which is 299,792 km/s. Unlike objects within space–time, space–time itself can bend, expand or warp at any speed.
Q. Can time escape a black hole?
Near a black hole, the slowing of time is extreme. From the viewpoint of an observer outside the black hole, time stops. For example, an object falling into the hole would appear frozen in time at the edge of the hole. No force in the universe can stop this fall, any more than we can stop the flow of time.
Q. Did anyone die in a black hole?
The good news about massive black holes is that you could survive falling into one. Although their gravity is stronger, the stretching force is weaker than it would be with a small black hole and it would not kill you.
Q. Where do you go if you fall into a black hole?
Of course, no matter what type of black hole you fall into, you’re ultimately going to get torn apart by the extreme gravity. No material, especially fleshy human bodies, could survive intact. So once you pass beyond the edge of the event horizon, you’re done. There’s no getting out.