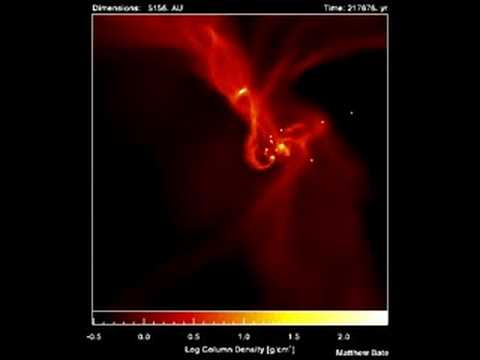
What happens to the rotation of a molecular cloud as it collapses to form a star? The rotation rate increases and results in a disk of material around a protostar.
Q. What likely happened to the other stars in the cluster the Sun was born in?
What likely happened to the other stars in the cluster the Sun was born in? They moved away from the Sun over the past 4.5 billion years. Density variations from place to place grow larger as the cloud collapses.
Table of Contents
- Q. What likely happened to the other stars in the cluster the Sun was born in?
- Q. What happens when a molecular cloud collapses?
- Q. Which of the following is most important in causing a cloud of gas to collapse to form a star and planets?
- Q. Which is known as the biggest star in the universe?
- Q. How are star formed?
- Q. What is a star form called?
- Q. Is a star dying?
Q. What happens when a molecular cloud collapses?
A cloud may start with any size or shape, and different clumps of gas within the cloud may be moving in random directions at random speeds. When the cloud collapses, these different clumps collide and merge, resulting in a flattened rotating disk.
Q. Which of the following is most important in causing a cloud of gas to collapse to form a star and planets?
Gravity causes the cloud to collapse. Once bodies are large enough, gravity pulls them together to make even larger bodies.
Q. Which is known as the biggest star in the universe?
UY Scuti
Q. How are star formed?
A star is born when atoms of light elements are squeezed under enough pressure for their nuclei to undergo fusion. All stars are the result of a balance of forces: the force of gravity compresses atoms in interstellar gas until the fusion reactions begin.
Q. What is a star form called?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as “stellar nurseries” or “star-forming regions”, collapse and form stars.
Q. Is a star dying?
All stars, even our Sun, will someday eventually die. After burning on the main sequence for billions of years, the Sun will expand into a red giant, [+] As the core contracts, it heats up, illuminating the gas in a planetary nebula.