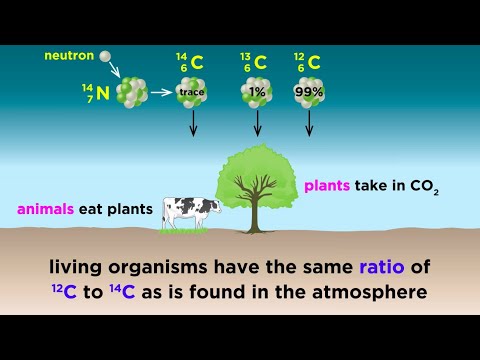
Radiocarbon decays slowly in a living organism, and the amount lost is continually replenished as long as the organism takes in air or food. Once the organism dies, however, it ceases to absorb carbon-14, so that the amount of the radiocarbon in its tissues steadily decreases.
Q. What would carbon-14 dating be primarily used to age?
Carbon-14 dating is a way of determining the age of certain archeological artifacts of a biological origin up to about 50,000 years old. It is used in dating things such as bone, cloth, wood and plant fibers that were created in the relatively recent past by human activities.
Table of Contents
- Q. What would carbon-14 dating be primarily used to age?
- Q. How old is the oldest fossil you could use carbon-14 to date?
- Q. What is the oldest carbon dating?
- Q. Can carbon-14 dating be used to measure the age of a rock?
- Q. How is carbon 14 age determined?
- Q. What is the use of carbon-14?
- Q. Is there any adverse effect in using carbon 14?
- Q. Do all carbon 14s decay at the same time?
- Q. What type of radiation does carbon 14 emit?
- Q. How long would it take for 7/8 of the original amount of carbon-14 in a sample to decay?
- Q. How many years does it take for 100 g of carbon-14 to decay?
Q. How old is the oldest fossil you could use carbon-14 to date?
Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope of carbon. Its has a half-life of about 5,730 years. The short half-life of carbon-14 means its cannot be used to date extremely old fossils.
Q. What is the oldest carbon dating?
Since the 1960s, researchers have mainly done this recalibration with trees, counting annual rings to get calendar dates and matching those with measured radiocarbon dates. The oldest single tree for which this has been done, a bristlecone pine from California, was about 5,000 years old.
Q. Can carbon-14 dating be used to measure the age of a rock?
For older objects, scientists don’t use carbon-14 as a measure of age. Instead, they often look to radioactive isotopes of other elements present in the environment. For the world’s oldest objects, uranium-thorium-lead dating is the most useful method. “We use it to date the Earth,” Higham said.
Q. How is carbon 14 age determined?
Basic principles of carbon 14 dating The percent of carbon-14 remaining after time t is given by N/No . Using the first equation, we can determine λt . The half-life of carbon-14 is 5,730 years, thus, we can calculate λ using the second equation, and then find t .
Q. What is the use of carbon-14?
Carbon-14, which is radioactive, is the isotope used in radiocarbon dating and radiolabeling. … medically important radioactive isotope is carbon-14, which is used in a breath test to detect the ulcer-causing bacteria Heliobacter pylori.
Q. Is there any adverse effect in using carbon 14?
Carbon-14 is a low energy beta emitter and even large amounts of this isotope pose little external dose hazard to persons exposed. The beta radiation barely penetrates the outer protective dead layer of the skin of the body. Some 14 C labelled compounds may migrate through gloves and skin.
Q. Do all carbon 14s decay at the same time?
And scientists know exactly how long it will take for half of any amount of carbon-14 to decay away. Scientists call that time its “half-life.” The amount of carbon-12 stays the same, but the carbon-14 decays away, at a constant rate, making carbon-14 a ticking atomic clock.
Q. What type of radiation does carbon 14 emit?
beta particles
Q. How long would it take for 7/8 of the original amount of carbon-14 in a sample to decay?
Explanation: The half-life of carbon-14 is 5730 years.
Q. How many years does it take for 100 g of carbon-14 to decay?
Decay of carbon-14
| t (years) | m (ng to 4 decimal places) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 100.0000 |
| 100 | 98.7973 |
| 1000 | 88.6034 |
| 2000 | 78.5056 |