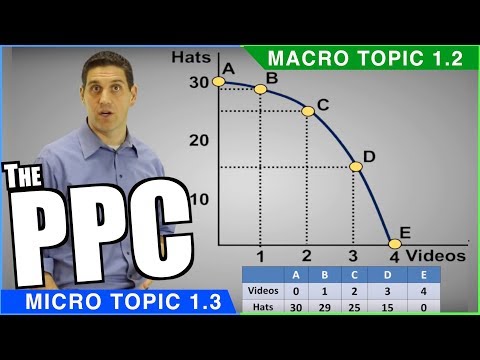
production possibilities frontier (PPF): a diagram that shows the productively efficient combinations of two products that an economy can produce given the resources it has available.
Q. How can an economist Use a production possibilities graph to express?
The Production Possibilities Curve (PPC) is a model used to show the tradeoffs associated with allocating resources between the production of two goods. The PPC can be used to illustrate the concepts of scarcity, opportunity cost, efficiency, inefficiency, economic growth, and contractions.
Table of Contents
- Q. How can an economist Use a production possibilities graph to express?
- Q. How does a production possibilities curve show efficiency?
- Q. What is an example of productive efficiency?
- Q. Where is allocative efficiency on a graph?
- Q. What causes allocative inefficiency?
- Q. How do you find allocative efficiency?
- Q. Where is allocative efficiency on a monopoly graph?
- Q. Is there allocative efficiency in a monopoly?
- Q. What kind of efficiency does a monopoly tend to achieve?
- Q. Are monopolies dynamically efficient?
- Q. Why is monopoly power bad?
- Q. Are all monopolies bad for the economy?
- Q. How do monopolies affect the economy?
- Q. What are the advantages and disadvantages of being monopolistic?
- Q. What are the advantages and disadvantages of monopolistic competition?
- Q. Who benefits from monopolistic competition?
- Q. Which situation is the best example of monopolistic competition?
- Q. What are advantages and disadvantages of perfect competition?
- Q. What are the disadvantages of competitive market?
- Q. What are 3 benefits of competition?
- Q. What are the 5 areas of competitive advantage?
- Q. What are six factors of competitive advantage?
- Q. How do you identify a competitive advantage?
- Q. What are the 6 sources of competitive advantage?
- Q. What is competitive advantage and its sources?
Q. How does a production possibilities curve show efficiency?
Explain how production possibilities curves show efficiency, growth, and cost. Production possibilities curves show efficiency by having inefficiency below the curve. Efficiency is the curve. Growth is anything above the curve.
Q. What is an example of productive efficiency?
Any time a society is producing a combination of goods that falls along the PPF, it is achieving productive efficiency. For example, often a society with a younger population has a preference for production of education, over production of health care.
Q. Where is allocative efficiency on a graph?
In economics, allocative efficiency materializes at the intersection of the supply and demand curves. At this equilibrium point, the price offered for a given supply exactly matches the demand for that supply at that price, and so all products are sold.
Q. What causes allocative inefficiency?
Allocative inefficiency occurs when the consumer does not pay an efficient price. An efficient price is one that just covers the costs of production incurred in supplying the good or service. Allocative efficiency occurs when the firm’s price, P, equals the extra (marginal) cost of supply, MC.
Q. How do you find allocative efficiency?
When a purely competitive industry is in a long-run equilibrium, quantity supplied equals quantity demanded (this is the profit maximizing quantity) AND therefore marginal social cost equals marginal social benefit (MSC = MSB), this is the allocatively efficient quantity.
Q. Where is allocative efficiency on a monopoly graph?
Monopoly sets a price of Pm. This is allocatively inefficient because at this output of Qm, price is greater than MC. Allocative efficiency would occur at the point where the MC cuts the Demand curve so Price = MC. The area of deadweight welfare loss shows the degree of allocative inefficiency in the economy.
Q. Is there allocative efficiency in a monopoly?
The Allocative Inefficiency of Monopoly. Thus, monopolies don’t produce enough output to be allocatively efficient. Thus, consumers will suffer from a monopoly because it will sell a lower quantity in the market, at a higher price, than would have been the case in a perfectly competitive market.
Q. What kind of efficiency does a monopoly tend to achieve?
Productive efficiency
Q. Are monopolies dynamically efficient?
Monopolists can also be dynamically efficient – once protected from competition monopolies may undertake product or process innovation to derive higher profits, and in so doing become dynamically efficient. Because of barriers to entry, a monopolist can protect its inventions and innovations from theft or copying.
Q. Why is monopoly power bad?
Monopolies restrict free trade and prevent the market from setting prices. That creates the following four adverse effects: Price fixing: Since monopolies are lone providers, they can set any price they choose. Declining product quality: Not only can monopolies raise prices, but they also can supply inferior products.
Q. Are all monopolies bad for the economy?
Monopolies over a particular commodity, market or aspect of production are considered good or economically advisable in cases where free-market competition would be economically inefficient, the price to consumers should be regulated, or high risk and high entry costs inhibit initial investment in a necessary sector.
Q. How do monopolies affect the economy?
The monopoly pricing creates a deadweight loss because the firm forgoes transactions with the consumers. Monopolies can become inefficient and less innovative over time because they do not have to compete with other producers in a marketplace. In the case of monopolies, abuse of power can lead to market failure.
Q. What are the advantages and disadvantages of being monopolistic?
Monopolies are generally considered to have several disadvantages (higher price, fewer incentives to be efficient e.t.c). However, monopolies can also give benefits, such as – economies of scale, (lower average costs) and a greater ability to fund research and development.
Q. What are the advantages and disadvantages of monopolistic competition?
Advantages and Disadvantages of Monopolistic Competition
- a few barriers to entry for new companies;
- active business environment;
- customers can obtain a great variety of products and services since the products are differentiated;
- consumers are informed about goods and services available in the market;
Q. Who benefits from monopolistic competition?
Monopolistic competition can bring the following advantages: There are no significant barriers to entry; therefore markets are relatively contestable. Differentiation creates diversity, choice and utility. For example, a typical high street in any town will have a number of different restaurants from which to choose.
Q. Which situation is the best example of monopolistic competition?
The Fast Food companies like the McDonald and Burger King who sells the burger in the market are the most common type of example of monopolistic competition. The two companies mentioned above sell an almost similar type of products but are not the substitute of each other.
Q. What are advantages and disadvantages of perfect competition?
First and foremost advantage of perfect competition is that chances of consumer exploitation are very low in case of this type of market structure because in perfect competition sellers do not have any monopoly pricing power and hence they cannot influence the price of the product or charge higher than the normal price …
Q. What are the disadvantages of competitive market?
Disadvantages for Businesses Competition decreases your market share and shrinks your customer base, especially if demand for your products or services is limited from the start. A competitive market can also force you to lower your prices to stay competitive, decreasing your return on each item you produce and sell.
Q. What are 3 benefits of competition?
6 Reasons competition is good for Business – Benefits of…
- Awareness & Market penetration –
- Higher quality at same prices –
- Consumption increases –
- Differentiation –
- Increases Efficiency –
- Customer service and satisfaction –
Q. What are the 5 areas of competitive advantage?
5 areas to drive competitive advantage
- MARKETING. How can your marketing team make claims about your product and the ability to deliver it without knowing the capabilities of your supply chain?
- FINANCE. Here are two departments which ought to be so close their husbands and wives start to get jealous.
- HUMAN RESOURCES.
- LEGAL.
- CUSTOMER SERVICE.
Q. What are six factors of competitive advantage?
The six factors of competitive advantage are quality, price, location, selection, service and speed/turnaround.
Q. How do you identify a competitive advantage?
5 Practical Tips To Find Your Competitive Advantage
- Perform a competitive audit – both with marketing and the actual product. The marketing audit tracks the marketing tactics your competitors use.
- Talk to your existing customers.
- Talk to prospective customers.
- Now, assess your opportunities to improve or develop your competitive advantage.
- Communicate it!
Q. What are the 6 sources of competitive advantage?
There are 6 sources of competitive advantage.
- People. People are the driving force behind most competitive advantage.
- Organizational Culture & Structure.
- Processes & Practices.
- Products & Intellectual Property.
- Capital & Natural Resources.
- Technology.
Q. What is competitive advantage and its sources?
A competitive advantage may include access to natural resources, such as high-grade ores or a low-cost power source, highly skilled labor, geographic location, high entry barriers, and access to new technology.