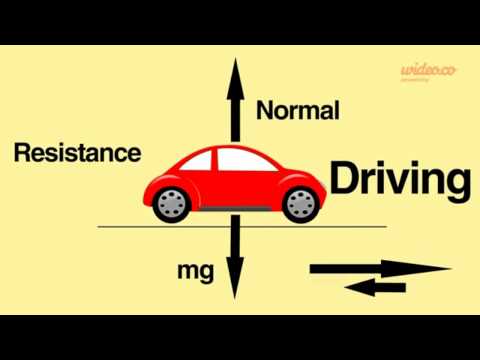
For example, when a car travels at a constant speed, the driving force from the engine is balanced by resistive forces such as air resistance and friction in the car’s moving parts. The resultant force on the car is zero.
Q. Does a car moving at a constant speed in a straight road accelerate?
The acceleration of a car that travels in a straight line at a constant speed of 100 km/h is zero. Average acceleration = (change in velocity)/(time it takes). Since the car’s change in velocity is zero, its acceleration is zero.
Table of Contents
- Q. Does a car moving at a constant speed in a straight road accelerate?
- Q. Is car constant constant or velocity?
- Q. How do you explain constant speed?
- Q. Does constant speed mean acceleration is zero?
- Q. What happens when force is constant?
- Q. What does it mean when force is constant?
- Q. What does constant speed look like on a graph?
- Q. What is the slope of a line on a distance-time graph?
- Q. What does no motion look like on a graph?
- Q. Which formula is used to find an object’s acceleration?
- Q. How do you find acceleration without distance and time?
- Q. How do you find acceleration with distance?
- Q. What is the formula for weight in physics?
Q. Is car constant constant or velocity?
While the speed of the object is constant, its velocity is changing. Velocity, being a vector, has a constant magnitude but a changing direction.
Q. How do you explain constant speed?
Definition: When the speed of an object remains the same – it does not increase or decrease – we say it is moving at a constant speed.
- constant speed.
- Return to Physics Home.
Q. Does constant speed mean acceleration is zero?
At constant speed, acceleration is zero, no doubt. Velocity is a vector quantity that has its magnitude+ direction. The magnitude of instant velocity termed as speed. Speed is a scalar quantity.
Q. What happens when force is constant?
At this point, the students technically already have enough evidence to see that a constant force will mean the object will move with a continuously increasing speed (if the force is in the same direction as the motion of the object).
Q. What does it mean when force is constant?
Constant applied force means constant velocity, thus 0 acceleration, thus 0 net force according to the [math]F=m a[/math] formula.
Q. What does constant speed look like on a graph?
Constant speed is shown by straight lines on a graph. steeper dashed line got there before the other one: A steeper line indicates a larger distance moved in a given time. In other words, higher speed. Both lines are straight, so both speeds are constant.
Q. What is the slope of a line on a distance-time graph?
In a distance-time graph, the slope or gradient of the line is equal to the speed of the object. The steeper the line (and the greater the gradient) the faster the object is moving.
Q. What does no motion look like on a graph?
If an object exhibits non-uniform motion, a position-time graph of the motion will be curved, not straight. If you graph the velocity of the object vs. time, then this graph will tell you how quickly the velocity is changing, a quantity called acceleration.
Q. Which formula is used to find an object’s acceleration?
According to Newton’s second law of motion, the acceleration of an object equals the net force acting on it divided by its mass, or a=Fm. This equation for acceleration can be used to calculate the acceleration of an object when its mass and the net force acting on it are known.
Q. How do you find acceleration without distance and time?
If the acceleration is constant, it is possible to find acceleration without time if we have the initial and final velocity of the object as well as the amount of displacement. The formula v2=u2+2as where v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity, a is the acceleration and s is the displacement is used.
Q. How do you find acceleration with distance?
Calculating acceleration involves dividing velocity by time — or in terms of SI units, dividing the meter per second [m/s] by the second [s]. Dividing distance by time twice is the same as dividing distance by the square of time. Thus the SI unit of acceleration is the meter per second squared .
Q. What is the formula for weight in physics?
The most common definition of weight found in introductory physics textbooks defines weight as the force exerted on a body by gravity. This is often expressed in the formula W = mg, where W is the weight, m the mass of the object, and g gravitational acceleration.