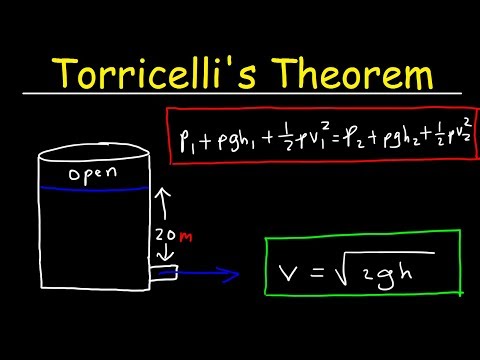
Torricelli’s theorem, also called Torricelli’s law, Torricelli’s principle, or Torricelli’s equation, statement that the speed, v, of a liquid flowing under the force of gravity out of an opening in a tank is proportional jointly to the square root of the vertical distance, h, between the liquid surface and the centre …
Q. What does atmospheric pressure depend on?
An atmosphere is the unit for atmospheric pressure, and sea level is set at 1 atmosphere (atm). The atmospheric pressure at any given point depends on two factors: altitude (the height of a thing in relation to sea level) and temperature (the intensity of heat).
Table of Contents
- Q. What does atmospheric pressure depend on?
- Q. How do you test for Torricelli’s Law?
- Q. What is efflux speed?
- Q. What is Torricelli’s theorem Class 11?
- Q. What is 11th surface tension?
- Q. What do you mean by hydrostatic paradox?
- Q. What do you mean by hydrostatic?
- Q. What is meant by Streamline?
- Q. What creates laminar flow?
- Q. What are the characteristics of laminar flow?
- Q. What are the advantages and disadvantages of laminar flow?
- Q. Why is laminar flow important?
- Q. What is steady flow?
Q. How do you test for Torricelli’s Law?
A simple experiment to test Torricelli’s law can also be performed by a soda bottle by puncturing the bottom with a small hole. As the height in the reservoir decreases, the exit velocity decreases.
Q. What is efflux speed?
The average flow rate of material emitted into the atmosphere from a source such as a smokestack. This is the average speed of gas out of the top of a smokestack.
Q. What is Torricelli’s theorem Class 11?
Torricelli’s law Torricelli law states that the speed of flow of fluid from an orifice is equal to the speed that it would attain if falling freely for a distance equal to the height of the free surface of the liquid above the orifice.
Q. What is 11th surface tension?
Surface tension is the property of any liquid by virtue of which tries to minimize its free surface area. Surface tension of a liquid is measured as the force acting per length on an imaginary line drawn tangentially on the free surface the liquid. Surface tension S = Force/Length = F/l = Work done/Change in area.
Q. What do you mean by hydrostatic paradox?
The hydrostatic paradox states the fact that in different shaped containers, with the same base area, which are filled with a liquid of the same height, the applied force by the liquid on the base of each container is exactly the same.
Q. What do you mean by hydrostatic?
: of or relating to fluids at rest or to the pressures they exert or transmit — compare hydrokinetic.
Q. What is meant by Streamline?
A streamline is a path traced out by a massless particle as it moves with the flow. It is easiest to visualize a streamline if we move along with the body (as opposed to moving with the flow). Since the streamline is traced out by a moving particle, at every point along the path the velocity is tangent to the path.
Q. What creates laminar flow?
Laminar flow occurs when the fluid flows in infinitesimal parallel layers with no disruption between them. In laminar flows, fluid layers slide in parallel, with no eddies, swirls or currents normal to the flow itself. The laminar regime is ruled by momentum diffusion, while the momentum convection is less important.
Q. What are the characteristics of laminar flow?
In laminar flow, the motion of the particles of the fluid is very orderly with particles close to a solid surface moving in straight lines parallel to that surface. Laminar flow is a flow regime characterized by high momentum diffusion and low momentum convection.
Q. What are the advantages and disadvantages of laminar flow?
This is because laminar flow provides a lower heat and mass transfer rates. But in the the turbulent flow phenomenon where the fluid particles are chaotic in nature the flow behaviour reduces the film thickness which in turn decreases the resistance offered for heat and mass transfer.
Q. Why is laminar flow important?
Laminar flow is the opposite of turbulent flow. It is the smooth flow of a fluid over a surface. Though a boundary layer of air “sticks” to a wing, the air overtop should be moving quickly and smoothly to reduce friction drag.
Q. What is steady flow?
A steady flow is the one in which the quantity of liquid flowing per second through any section, is constant. This is the definition for the ideal case. True steady flow is present only in Laminar flow. In turbulent flow, there are continual fluctuations in velocity. Pressure also fluctuate at every point.