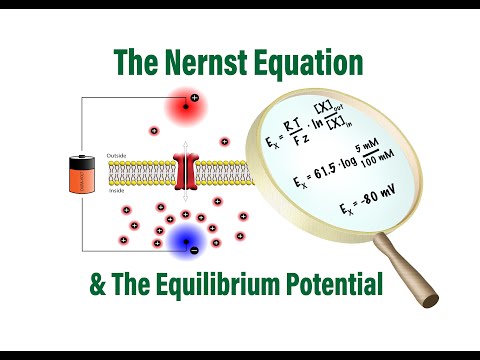
The Nernst Equation enables the determination of cell potential under non-standard conditions. It relates the measured cell potential to the reaction quotient and allows the accurate determination of equilibrium constants (including solubility constants).
Q. What happens when the action potential reaches the end of the axon at the axon terminal?
When the action potential reaches the end of the axon (the axon terminal), it causes neurotransmitter-containing vesicles to fuse with the membrane, releasing neurotransmitter molecules into the synaptic cleft (space between neurons).
Table of Contents
- Q. What happens when the action potential reaches the end of the axon at the axon terminal?
- Q. What is the threshold of action potential?
- Q. What does CL do to membrane potential?
- Q. How do you calculate membrane potential?
- Q. Do all cells have resting membrane potential?
- Q. What is threshold in muscle contraction?
- Q. What is the role of acetylcholine in muscle contraction?
Q. What is the threshold of action potential?
The action potential is an explosion of electrical activity that is created by a depolarizing current. This means that some event (a stimulus) causes the resting potential to move toward 0 mV. When the depolarization reaches about -55 mV a neuron will fire an action potential. This is the threshold.
Q. What does CL do to membrane potential?
Sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl-) are at a high concentration outside of neu- rons. These changes in membrane potential are caused by particular ion channels opening and closing, and thereby changing the conductance of the membrane to the ions.
Q. How do you calculate membrane potential?
How To Calculate A Membrane Potential
- R is the universal gas constant (8.314 J.K-1.
- T is the temperature in Kelvin (°K = °C + 273.15).
- z is the ionic charge for an ion.
- F is the Faraday’s constant (96485 C.
- [X]out is the concentration of the ion outside of the species.
Q. Do all cells have resting membrane potential?
All cells within the body have a characteristic resting membrane potential depending on their cell type. Of primary importance, however, are neurons and the three types of muscle cells: smooth, skeletal, and cardiac.
Q. What is threshold in muscle contraction?
The minimum strength required for stimuli to initiate the response in a muscle ie contraction is called Threshold stimulus in muscle contraction. The stimuli other than nerve threshold stimulus are mechanical stimuli like pressure, electrical stimuli like shock, chemical stimuli.
Q. What is the role of acetylcholine in muscle contraction?
What is the role of acetylcholine in a skeletal muscle contraction? Acetylcholine binds to receptors in the motor end plate, initiating a change in ion permeability that results in the end-plate potential. Relaxation period is at the end of muscle contraction.