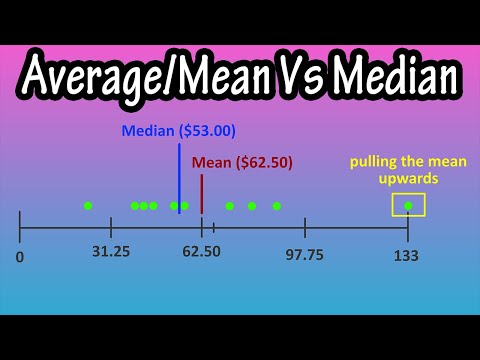
If the mean is greater than the median, the distribution is positively skewed. If the mean is less than the median, the distribution is negatively skewed.
Q. What is the mean between numbers?
The mean is the average of the numbers. It is easy to calculate: add up all the numbers, then divide by how many numbers there are. In other words it is the sum divided by the count.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the mean between numbers?
- Q. What’s the average between two numbers?
- Q. Whats does median mean?
- Q. What does it mean when the mean and median are far apart?
- Q. What does positively skewed mean?
- Q. What is an acceptable level of skewness?
- Q. What kurtosis tells us?
- Q. What is a good kurtosis value?
- Q. Is high kurtosis good or bad?
- Q. What does a high positive kurtosis mean?
- Q. How do you interpret skewness and kurtosis values?
- Q. What is a bad kurtosis?
- Q. What does Mesokurtic mean?
- Q. Is Platykurtic positively skewed?
- Q. What is Platykurtic curve?
- Q. Why kurtosis of normal distribution is 3?
- Q. What is the use of kurtosis?
- Q. How is kurtosis calculated?
- Q. How much skewness and kurtosis is normal?
Q. What’s the average between two numbers?
How to Calculate Average. The average of a set of numbers is simply the sum of the numbers divided by the total number of values in the set. For example, suppose we want the average of 24 , 55 , 17 , 87 and 100 . Simply find the sum of the numbers: 24 + 55 + 17 + 87 + 100 = 283 and divide by 5 to get 56.6 .
Q. Whats does median mean?
Median is the middle number in a sorted list of numbers. The median can be used to determine an approximate average, or mean, but is not to be confused with the actual mean. If there is an odd amount of numbers, the median value is the number that is in the middle, with the same amount of numbers below and above.
Q. What does it mean when the mean and median are far apart?
A good test: calculate the average and the median for a group of values. If they’re close, then the group is probably normally distributed (the familiar bell curve), and the average is useful. If they’re far apart, then the values are not normally distributed and the median is the better representation.
Q. What does positively skewed mean?
In statistics, a positively skewed (or right-skewed) distribution is a type of distribution in which most values are clustered around the left tail of the distribution while the right tail of the distribution is longer.
Q. What is an acceptable level of skewness?
As a general rule of thumb: If skewness is less than -1 or greater than 1, the distribution is highly skewed. If skewness is between -1 and -0.5 or between 0.5 and 1, the distribution is moderately skewed. If skewness is between -0.5 and 0.5, the distribution is approximately symmetric.
Q. What kurtosis tells us?
Kurtosis is a measure of whether the data are heavy-tailed or light-tailed relative to a normal distribution. That is, data sets with high kurtosis tend to have heavy tails, or outliers. Data sets with low kurtosis tend to have light tails, or lack of outliers.
Q. What is a good kurtosis value?
Both skew and kurtosis can be analyzed through descriptive statistics. Acceptable values of skewness fall between − 3 and + 3, and kurtosis is appropriate from a range of − 10 to + 10 when utilizing SEM (Brown, 2006).
Q. Is high kurtosis good or bad?
Kurtosis is only useful when used in conjunction with standard deviation. It is possible that an investment might have a high kurtosis (bad), but the overall standard deviation is low (good). Conversely, one might see an investment with a low kurtosis (good), but the overall standard deviation is high (bad).
Q. What does a high positive kurtosis mean?
For investors, high kurtosis of the return distribution implies the investor will experience occasional extreme returns (either positive or negative), more extreme than the usual + or – three standard deviations from the mean that is predicted by the normal distribution of returns. …
Q. How do you interpret skewness and kurtosis values?
A general guideline for skewness is that if the number is greater than +1 or lower than –1, this is an indication of a substantially skewed distribution. For kurtosis, the general guideline is that if the number is greater than +1, the distribution is too peaked.
Q. What is a bad kurtosis?
A negative kurtosis means that your distribution is flatter than a normal curve with the same mean and standard deviation. The easiest way to visualise this is to plot a histogram with a fitted normal curve.
Q. What does Mesokurtic mean?
Mesokurtic is a statistical term used to describe the outlier characteristic of a probability distribution in which extreme events (or data that are rare) is close to zero. A mesokurtic distribution has a similar extreme value character as a normal distribution.
Q. Is Platykurtic positively skewed?
What Does Platykurtic Mean? The term “platykurtic” refers to a statistical distribution in which the excess kurtosis value is negative. For this reason, a platykurtic distribution will have thinner tails than a normal distribution, resulting in fewer extreme positive or negative events.
Q. What is Platykurtic curve?
Introduction. The word “platykurtic” refers to a statistical distribution where the value of excess kurtosis is negative. A platykurtic distribution would, therefore, have thinner tails than a normal distribution, leading to less extreme positive or negative events.
Q. Why kurtosis of normal distribution is 3?
The standard normal distribution has a kurtosis of 3, so if your values are close to that then your graph’s tails are nearly normal. These distributions are called mesokurtic. Kurtosis is the fourth moment in statistics.
Q. What is the use of kurtosis?
Kurtosis is a statistical measure that defines how heavily the tails of a distribution differ from the tails of a normal distribution. In other words, kurtosis identifies whether the tails of a given distribution contain extreme values.
Q. How is kurtosis calculated?
The kurtosis can also be computed as a4 = the average value of z4, where z is the familiar z-score, z = (x−x̅)/σ.
Q. How much skewness and kurtosis is normal?
(2010) and Bryne (2010) argued that data is considered to be normal if Skewness is between ‐2 to +2 and Kurtosis is between ‐7 to +7. Multi-normality data tests are performed using leveling asymmetry tests (skewness < 3), (Kurtosis between -2 and 2) and Mardia criterion (< 3).