UNCONFORMITIES ARE THE RECORD OF MAJOR EPISODES OF UPLIFT, EROSION AND SUBSIDENCE DURING THE GROWTH OF THE CONTINENTS AS EARTH HISTORY PROGRESSED. THEY ARE THEREFORE IMPORTANT EVIDENCE FOR CRUSTAL MOBILITY THROUGHOUT EARTH HISTORY.
Q. What are the three different types of unconformities?
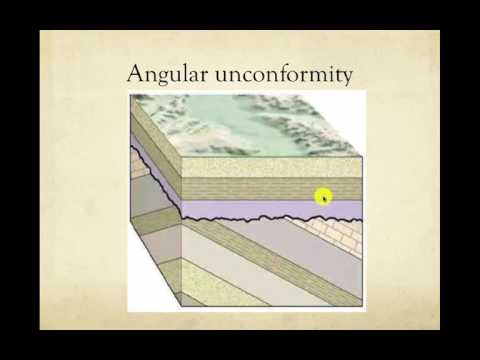
There are three kinds of unconformities: disconformities, nonconformities, and angular unconformities.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the three different types of unconformities?
- Q. What are 2 ways geologists use the geologic column?
- Q. What are different types of unconformity?
- Q. Why do Unconformities occur?
- Q. How do you identify an unconformity?
- Q. What is the difference between an unconformity and a nonconformity?
- Q. How do Unconformities form?
- Q. What is the age relationship between H and O?
- Q. Why are Zion Rocks Red?
- Q. Why are rocks red in Moab?
- Q. How were the rocks in Zion formed?
- Q. Is Zion a color?
- Q. What color represents Zion?
- Q. What color is Sion?
- Q. What Zion means?
- Q. Is Zion the same as heaven?
- Q. Why is it called Zion?
- Q. Does Zion refer to heaven?
- Q. What is Zion in the New Testament?
- Q. What is the difference between Zion and Jerusalem?
- Q. What is Zion to Rastafarians?
- Q. Is Jah and God the same?
- Q. Who is Rastafarians God?
- Q. What can Rastafarians eat?
Q. What are 2 ways geologists use the geologic column?
geologists use the geologic colum to interpret rock sequences and to identify layers in puzzling rock sequences. List 2 ways in which the geologists use the geologic column. geologists use the geologic colum to interpret rock sequences and to identify layers in puzzling rock sequences.
Q. What are different types of unconformity?
Types
- Disconformity.
- Nonconformity.
- Angular unconformity.
- Paraconformity.
- Buttress unconformity.
- Blended unconformity.
Q. Why do Unconformities occur?
Unconformities occur when either erosion wears away rocks, or rock deposits never form. Therefore, a time gap exists between when the rocks below the unconformity formed and when those above it formed. Common to all three, erosion causes them to form, and younger rocks sit on older rocks.
Q. How do you identify an unconformity?
Unconformities are ancient surfaces of erosion and/or non-deposition that indicate a gap or hiatus in the stratigraphic record. An unconformity may be represented on a map by different type of line than that used for other contacts, and in cross-section is shown by a wavy or crenulated line.
Q. What is the difference between an unconformity and a nonconformity?
Unconformities represent periods of non-deposition of sediment or active erosion of strata. Nonconformity: develops where sediments are deposited on top of an eroded surface of igneous or metamorphic rocks. Paraconformity: strata on either side of the unconformity are parallel, there is little apparent erosion.
Q. How do Unconformities form?
Unconformities are gaps in the geologic rock record. They are surfaces of contact between older rocks and younger sedimentary rocks, formed due to erosion or lack of sediment deposition over extended periods of time.
Q. What is the age relationship between H and O?
The rock sequence from oldest to youngest is; O, H, B, L, J, A, F, M, D, G, N, E, I, C, K. The relationship between H and O is that O is older than H.
Q. Why are Zion Rocks Red?
Thin beds of clay and silt mark the end of this formation. The most prominent outcrops of this formation make up the capstone of The West Temple in Zion Canyon. Rain dissolves some of the iron oxide and thus streaks Zion’s cliffs red (the red streak seen on the Altar of Sacrifice is a famous example).
Q. Why are rocks red in Moab?
Upon prolonged exposure, the iron in the nail oxidizes and rust is formed as a coating on the surface of the nail. So basically what we have in red rock country is a lot of rusting sandstones and shales. Entrada sandstone, from the late Jurassic, forms the spectacular red, slickrock around Moab.
Q. How were the rocks in Zion formed?
Zion was a relatively flat basin near sea level 240 million years ago. Nearby mountains eroded sand, gravel, and mud, and streams carried these materials into the basin, where they were deposited in layers. The weight of these layers caused the basin to sink, and the top surface remained near sea level.
Q. Is Zion a color?
ZION is a nature green with a tea undertone. Depending on the light source or time of day, it may appear as a wasabi green on the walls.
Q. What color represents Zion?
Blue is the “Real World” of Zion and represents the Body.
Q. What color is Sion?
Cyan (/ˈsaɪ. ən, ˈsaɪˌæn/) is the color between green and blue on the visible spectrum of light. It is evoked by light with a predominant wavelength between 490 and 520 nm, between the wavelengths of green and blue.
Q. What Zion means?
Zion is a specific, historically important location — the name refers to both a hill in the city of Jerusalem and to the city itself — but it’s also used in a general way to mean “holy place” or “kingdom of heaven.” The root of Zion is the Hebrew Tsiyon, and while the word holds a special importance in the Jewish faith …
Q. Is Zion the same as heaven?
Zion is heaven, a place devoted to God, Jerusalem, or the land of Israel. An example of Zion is a mountain near Jerusalem; Mount Zion.
Q. Why is it called Zion?
The first Anglo-European settlers, Mormon pioneers, arrived in the area in the late 1800s. They named the area Zion, which is ancient Hebrew for sanctuary or refuge. The name was believed to be a Paiute name meaning straight canyon.
Q. Does Zion refer to heaven?
Although the name of Zion is rare in the New Testament, it has been frequently used in Christian literature and hymns as a designation for the heavenly city or for the earthly city of Christian faith and fraternity.
Q. What is Zion in the New Testament?
In the New Testament, Mount Zion is used metaphorically to refer to the heavenly Jerusalem, God’s holy, eternal city.
Q. What is the difference between Zion and Jerusalem?
The Bible has two different ways of speaking about two objects of God’s love: Israel and Zion. Israel is masculine, and Zion/Jerusalem is feminine. The difference between the two is more visible in Hebrew which distinguishes masculine and feminine in the verbs as well as in the adjectives.
Q. What is Zion to Rastafarians?
Rastafari movement In Rastafari, “Zion” stands for a utopian place of unity, peace and freedom, as opposed to “Babylon”, the oppressing and exploiting system of the materialistic modern world and a place of evil.
Q. Is Jah and God the same?
Jah or Yah (Hebrew: יה, Yah) is a short form of Hebrew: יהוה (YHWH), the four letters that form the tetragrammaton, the personal name of God: Yahweh, which the ancient Israelites used. …
Q. Who is Rastafarians God?
Haile Selassie I – God of the Black race Rastafarians regard Haile Selassie I as God because Marcus Garvey’s prophecy – “Look to Africa where a black king shall be crowned, he shall be the Redeemer” – was swiftly followed by the ascension of Haile Selassie as Emperor of Ethiopia.
Q. What can Rastafarians eat?
For Rastas, Eating Pure Food From the Earth is a Sacred Duty. Scotch bonnet peppers, squash, cabbage, pineapples and onions are just a few of the foods Rastafarians use in their cooking.