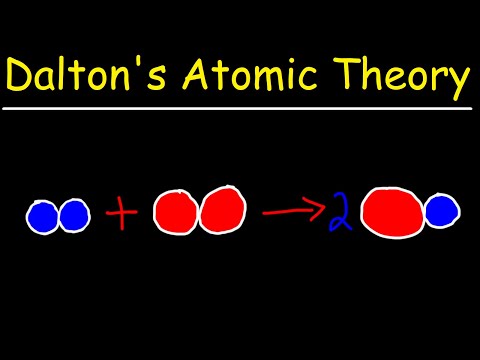
Summary. Dalton’s atomic theory was the first complete attempt to describe all matter in terms of atoms and their properties. The first part of his theory states that all matter is made of atoms, which are indivisible. The second part of the theory says all atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties.
Q. What was the main problem with Democritus idea of the atom?
2,500 years ago, Democritus suggested that all matter in the universe was made up of tiny, indivisible, solid objects he called “atomos.” However, other Greek philosophers disliked Democritus’ “atomos” theory because they felt it was illogical.
Table of Contents
- Q. What was the main problem with Democritus idea of the atom?
- Q. Why did Aristotle reject Democritus idea of the atom?
- Q. What are Democritus four principles of the atom?
- Q. What are the major components of an atom?
- Q. What are the 2 main parts of an atom?
- Q. What two parts make up an atom?
- Q. What are the two components of the core of an atom?
- Q. What is the function of the atom?
- Q. How do atoms behave?
- Q. How do atoms look?
- Q. Can an atom die?
- Q. Can a atom be destroyed?
- Q. Can the atom be seen?
- Q. What is the smallest thing in the world?
- Q. Can you photograph an atom?
- Q. How many atoms are in a human body?
- Q. How did they take a picture of an atom?
- Q. Are humans made of atoms?
- Q. Do atoms die when we die?
- Q. What is the heaviest element in the human body?
- Q. Is there gold in our body?
- Q. What’s the most important part of the body?
- Q. How much gold is there on earth?
- Q. Is silver found in the human body?
Q. Why did Aristotle reject Democritus idea of the atom?
Aristotle: He rejected Democritus atomic theroy and didn’t think atoms move through empty spaces because he didn’t think that empty spaces existed. He believed that all matter consisted of four elements. Earth, Air, Water, and Fire.
Q. What are Democritus four principles of the atom?
The theory of Democritus held that everything is composed of “atoms,” which are physically, but not geometrically, indivisible; that between atoms, there lies empty space; that atoms are indestructible, and have always been and always will be in motion; that there is an infinite number of atoms and of kinds of atoms.
Q. What are the major components of an atom?
Our current model of the atom can be broken down into three constituents parts – protons, neutron, and electrons. Each of these parts has an associated charge, with protons carrying a positive charge, electrons having a negative charge, and neutrons possessing no net charge.
Q. What are the 2 main parts of an atom?
An atom is composed of two regions: the nucleus, which is in the center of the atom and contains protons and neutrons, and the outer region of the atom, which holds its electrons in orbit around the nucleus.
Q. What two parts make up an atom?
Protons and neutrons are the heavy parts of an atom. Their combined weights are called the atomic weight of an element.
Q. What are the two components of the core of an atom?
All atoms have a dense central core called the atomic nucleus. Forming the nucleus are two kinds of particles: protons, which have a positive electrical charge, and neutrons, which have no charge. All atoms have at least one proton in their core, and the number of protons determines which kind of element an atom is.
Q. What is the function of the atom?
Atoms are the basic building blocks of ordinary matter. Atoms can join together to form molecules, which in turn form most of the objects around you.
Q. How do atoms behave?
Electrons are attracted to any positive charge by their electric force; in an atom, electric forces bind the electrons to the nucleus. In some respects, the electrons in an atom behave like particles orbiting the nucleus. In others, the electrons behave like waves frozen in position around the nucleus.
Q. How do atoms look?
The protons and neutrons are packed together into the center of the atom (which is called the nucleus) and the electrons, which are very much smaller, whizz around the outside. When people draw pictures of atoms, they show the electrons like satellites spinning round the Earth in orbits.
Q. Can an atom die?
Since an atom has a finite number of protons and neutrons, it will generally emit particles until it gets to a point where its half-life is so long, it is effectively stable. It undergoes something known as “alpha decay,” and it’s half-life is over a billion times longer than the current estimated age of the universe.
Q. Can a atom be destroyed?
All matter consists of indivisible particles called atoms. Atoms of the same element are similar in shape and mass, but differ from the atoms of other elements. Atoms cannot be created or destroyed. The atom is the smallest unit of matter that can take part in a chemical reaction.
Q. Can the atom be seen?
Atoms are extremely small measuring about 1 x 10-10 meters in diameter. Because of their small size, it’s impossible to view them using a light microscope. While it may not be possible to view an atom using a light microscope, a number of techniques have been developed to observe and study the structure of atoms.
Q. What is the smallest thing in the world?
quarks
Q. Can you photograph an atom?
With enough energized electrons giving off enough light, it’s possible for an ordinary camera to image the atom. Still, that doesn’t mean you’ll be able to see the atom with your naked eye. This image is a long exposure shot, which means even with all that laser light, it’s still too faint to pick up without equipment.
Q. How many atoms are in a human body?
In summary, for a typical human of 70 kg, there are almost 7*1027 atoms (that’s a 7 followed by 27 zeros!) Another way of saying this is “seven billion billion billion.” Of this, almost 2/3 is hydrogen, 1/4 is oxygen, and about 1/10 is carbon. These three atoms add up to 99% of the total!
Q. How did they take a picture of an atom?
The atom is being illuminated by a blue-violet laser. The energy from the laser causes the atom to emit photons which Nadlinger could capture on camera using a long exposure. The whole thing is housed inside an ultra-high vacuum chamber and dramatically cooled to keep the atom still.
Q. Are humans made of atoms?
About 99 percent of your body is made up of atoms of hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen and oxygen. You also contain much smaller amounts of the other elements that are essential for life. Nuclei are around 100,000 times smaller than the atoms they’re housed in.
Q. Do atoms die when we die?
When we die, our atoms will disassemble and move off to finds new uses elsewhere – as part of a leaf or other human being or a drop of dew. Atoms themselves, however go on practically forever.
Q. What is the heaviest element in the human body?
Iodine
Q. Is there gold in our body?
An adult human body weighing 70 kg contains about 0.2 milligrams of gold. It’s been found that the element plays an important health function, helping to maintain our joints, as well as facilitating the transmittal of electrical signals throughout the body.
Q. What’s the most important part of the body?
The brain
Q. How much gold is there on earth?
About 244,000 metric tons of gold has been discovered to date (187,000 metric tons historically produced plus current underground reserves of 57,000 metric tons). Most of that gold has come from just three countries: China, Australia, and South Africa.
Q. Is silver found in the human body?
Silver is a white lustrous transitional metallic element found widely in the human environment. Low concentrations of silver are present in the human body through inhalation of particles in the air and contamination of the diet and drinking water, but silver serves no trace metal value in the human body.