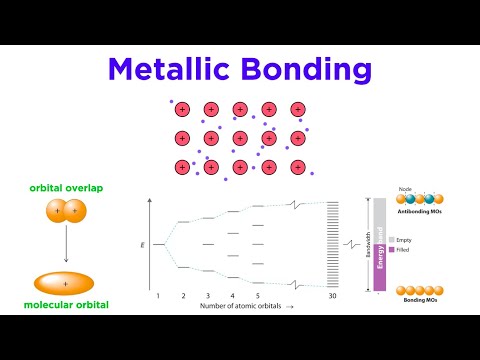
Metallic bonds can occur between different elements to form an alloy. In contrast to electrons that participate in both ionic and covalent bonds, electrons that participate in metallic bonds delocalize, forming a sea of electrons around the positive nuclei of metals.
Q. What subatomic particles are involved in bonding?
Answer and Explanation: The subatomic particle involved in chemical bonding is the electron.
Table of Contents
- Q. What subatomic particles are involved in bonding?
- Q. What is most important when forming bonds?
- Q. Which electrons are most important for bonding?
- Q. Which particle in the atom is involved in bonding?
- Q. What are two unique properties of metallic bonds?
- Q. Why can metals be harmed without breaking?
- Q. What is the basis of metallic bonding?
- Q. How is a metallic bond different from an ionic or covalent bond?
- Q. Why is a covalent bond stronger than a metallic bond?
- Q. What type of bond is called Electrovalent bond?
- Q. How many types of Electrovalent bonds are there?
- Q. What are the characteristics of Electrovalent bond?
- Q. What are the four main properties of covalent bonds?
Q. What is most important when forming bonds?
There are a number of types of chemical bonds, as you’ll learn, but all bonds between atoms form for the same essential reason: the opportunity for the atoms involved to complete their outermost electron shells, or valence shells.
Q. Which electrons are most important for bonding?
Explanation: Understanding valence electrons is key to understanding chemical bonding. Valence electrons are the electrons that are shared between atoms which are covalently bonded to each other. Valence electrons are the electrons which are transferred when ionic bonds are formed.
Q. Which particle in the atom is involved in bonding?
electrons
Q. What are two unique properties of metallic bonds?
Metals have several qualities that are unique, such as the ability to conduct electricity and heat, a low ionization energy, and a low electronegativity (so they will give up electrons easily to form cations). Their physical properties include a lustrous (shiny) appearance, and they are malleable and ductile.
Q. Why can metals be harmed without breaking?
Metals are malleable because it is a property that allows a certain material to be hammered and flattened without breaking. In each case, we are changing the shape of the metal without cracking or breaking it. This is possible because the metallic bonds are strong but not directed between particular ions.
Q. What is the basis of metallic bonding?
Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that arises from the electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons (in the form of an electron cloud of delocalized electrons) and positively charged metal ions.
Q. How is a metallic bond different from an ionic or covalent bond?
While metallic bonds have the strong electrostatic force of attractions between the cation or atoms and the delocalized electrons in the geometrical arrangement of the two metals. Covalent bonds occur between two non-metals, metallic bonds is between two metals, while ionic is observed between non-metal and metal.
Q. Why is a covalent bond stronger than a metallic bond?
Strength of a bond depends upon the extent of overlapping of two electron clouds. Covalent bond means overlapping of two electron clouds. So, in metallic bond there is actually no overlapping between any two atoms. So,we can conclude that a covalent bond is more stronger than a metallic bond.
Q. What type of bond is called Electrovalent bond?
Ionic bond
Q. How many types of Electrovalent bonds are there?
There are primarily three ways in which two atoms combine to lose energy and to become stable. One of the ways is by donating or accepting electrons to complete their octet configuration. The bond formed by this kind of combination is known as an ionic bond or electrovalent bond.
Q. What are the characteristics of Electrovalent bond?
The general characteristics of electrovalent compounds are:
- (i) Electrovalent compounds are mostly crystalline in nature.
- (ii) Electrovalent compounds form hard crystals.
- (iii) Electrovalent compounds have high density with high melting and boiling points.
- (iv) Electrovalent compounds are soluble in polar solvents.
Q. What are the four main properties of covalent bonds?
Properties of Covalent Molecular Compounds.
- Low melting points and boiling points.
- Low enthalpies of fusion and vaporization These properties are usually one or two orders of magnitude smaller than they are for ionic compounds.
- Soft or brittle solid forms.
- Poor electrical and thermal conductivity.