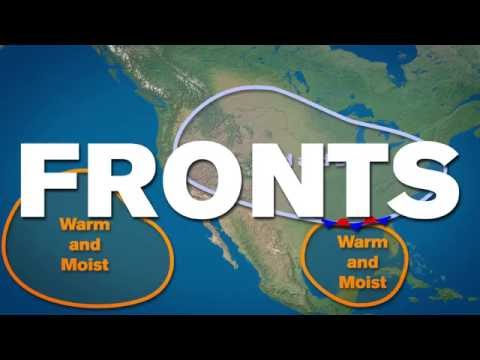
So, when two different air masses meet, a boundary is formed. The boundary between two air masses is called a front. Weather at a front is usually cloudy and stormy. There are four different fronts- Cold, Warm, Stationary, and Occluded.
Q. What are the 4 main types of air masses in the United States?
Four major types of air masses influence the weather in North America:
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the 4 main types of air masses in the United States?
- Q. What are the 4 types of air masses in North America?
- Q. What are the four different types of air masses and where do they originate?
- Q. Where do air masses come from?
- Q. What happens to the air masses during a cold front?
- Q. When neither air mass is advancing it is called a?
- Q. What will happen to the air just above the ground that becomes warmer?
- Q. What type of air mass will cause a cold front?
- Q. Which type of air mass is the least dense?
- Q. Are air masses warm or cold?
- Q. Why do air masses move?
- Q. Do air masses compress as they rise?
- Q. What is the relationship between air masses and storms?
- Q. What does a rising air generally indicate?
- Q. What are characteristics of an unstable air mass?
- Q. What are the four characteristics of stable air?
- Q. When an air mass is stable we can expect?
- Q. What two characteristics determine an air mass?
- Q. What causes an unstable air mass?
- Q. What situation leads to a stable air mass?
- Q. Which would increase the stability of an air mass?
- Q. What two conditions working together make the atmosphere the most unstable?
- Q. Which of the following is the coldest most stable air mass?
- Maritime Tropical (mT)
- Maritime Polar (mP)
- Continental Tropical (cT)
- Continental Polar (cP)
Q. What are the 4 types of air masses in North America?
The air masses in and around North America include the continental arctic (cA), maritime polar (mP), maritime tropical (mT), continental tropical (cT), and continental polar (cP) air masses.
Q. What are the four different types of air masses and where do they originate?
Terms in this set (9)
- CONTINENTAL POLAR. cold and dry air. forms on land.
- CONTINENTAL TROPICAL. hot and dry air. forms on land.
- MARITIME TROPICAL. forms over water. hot moist air.
- MARITIME POLAR. forms over water. cold moist air.
- maritime. = ocean (moist/humid air)
- continental. = land (dry air)
- polar. = cold.
- tropical. = warm/hot.
Q. Where do air masses come from?
An air mass forms whenever the atmosphere remains in contact with a large, relatively uniform land or sea surface for a time sufficiently long to acquire the temperature and moisture properties of that surface. The Earth’s major air masses originate in polar or subtropical latitudes.
Q. What happens to the air masses during a cold front?
A cold front is defined as the transition zone where a cold air mass is replacing a warmer air mass. The air behind a cold front is noticeably colder and drier than the air ahead of it. When a cold front passes through, temperatures can drop more than 15 degrees within the first hour.
Q. When neither air mass is advancing it is called a?
stationary front
Q. What will happen to the air just above the ground that becomes warmer?
Warm air rises, creating a low pressure zone; cool air sinks, creating a high pressure zone. Air that moves horizontally between high and low pressure zones makes wind. When cool air descends, it warms. Since it can then hold more moisture, the descending air will evaporate water on the ground.
Q. What type of air mass will cause a cold front?
Cold fronts form when a cooler air mass moves into an area of warmer air in the wake of a developing extratropical cyclone. The warmer air interacts with the cooler air mass along the boundary, and usually produces precipitation. Cold fronts often follow a warm front or squall line.
Q. Which type of air mass is the least dense?
Moist air
Q. Are air masses warm or cold?
Tropical air masses form in low-latitude areas and are moderately warm. Polar air masses take shape in high-latitude regions and are cold. Equatorial air masses develop near the Equator, and are warm. Air masses are also identified based on whether they form over land or over water.
Q. Why do air masses move?
Winds and air currents cause air masses to move. Moving air masses cause changes in the weather. A front forms at the boundary between two air masses. Types of fronts include cold, warm, occluded, and stationary fronts.
Q. Do air masses compress as they rise?
When cool air descends, it warms. Since it can then hold more moisture, the descending air will evaporate water on the ground. Gases at sea level are also compressed by the weight of the atmosphere above them. At higher altitudes the atmospheric pressure is lower and the air is less dense than at lower altitudes.
Q. What is the relationship between air masses and storms?
Storms arise if the air mass and the region it moves over have different characteristics. For example, when a colder air mass moves over warmer ground, the bottom layer of air is heated. That air rises, forming clouds, rain, and sometimes thunderstorms.
Q. What does a rising air generally indicate?
Rising Air: a key process in the production of clouds and precipitation. Imagine a block of air, or air parcel, rising upward through the atmosphere. The air parcel expands as it rises and this expansion, or work, causes the temperature of the air parcel to decrease.
Q. What are characteristics of an unstable air mass?
What are characteristics of an unstable air mass?
| Unstable Air | Stable Air |
|---|---|
| Cumuliform clouds | Stratiform clouds and fog |
| Showery precipitation | Continuous precipitation |
| Rough air (turbulence) | Smooth air |
| Good visibility, except in blowing obstructions | Fair to poor visibility in haze and smoke |
Q. What are the four characteristics of stable air?
What are the characteristics of stable air? A—Good visibility; steady precipitation; stratus clouds. B—Poor visibility; steady precipitation; stratus clouds. C—Poor visibility; intermittent precipitation; cumulus clouds.
Q. When an air mass is stable we can expect?
Weather is strongly affected by how stable or unstable the atmosphere is. Stable air means that the weather is likely to be calm. It may rain or snow slowly and steadily, it may be sunny, but the weather will not change quickly. Unstable air means that the weather might change quickly with very little warning.
Q. What two characteristics determine an air mass?
Temperature and humidity are two characteristics used to classify air masses.
Q. What causes an unstable air mass?
To be “unstable”, the lowest layers of an air mass must be so warm and/or humid that, if some of the air rises, then that air parcel is warmer than its environment, and so it continues to rise. This condensation releases heat, which warms the air parcel, which can cause the parcel to rise higher still.
Q. What situation leads to a stable air mass?
If the environmental lapse rate is like the blue one on the graph, a bubble of air a degree or two warmer than the surrounding ground will not rise very far before cooling to the same rate as the surrounding air and stopping. This is therefore a stable air mass and will experience no convectional rain.
Q. Which would increase the stability of an air mass?
Indicates stability: stability of the atmosphere is determined by vertical movements of air. Warm air rises when the air above is cooler. Cooling from below: surrounding air is warmer, which would increase the stability of an air mass.
Q. What two conditions working together make the atmosphere the most unstable?
The difference between the cold parcel air and the warmer surroudings gets larger and larger with increasing altitude. Sunlight warms the ground and the air next to it during the day. This steepens the environmental lapse rate and makes the atmosphere more unstable. Cooling air above the ground has the same effect.
Q. Which of the following is the coldest most stable air mass?
The coldest air masses are Arctic air masses. These air masses originate at the poles of the Earth in Greenland and Antarctica.