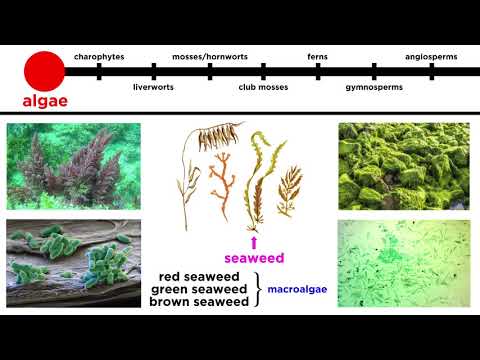
The seedless vascular plants include club mosses, which are the most primitive; whisk ferns, which lost leaves and roots by reductive evolution; and horsetails and ferns.
Q. What are two examples of vascular seedless plants?
Ferns, club mosses, horsetails, and whisk ferns are seedless vascular plants that reproduce with spores and are found in moist environments.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are two examples of vascular seedless plants?
- Q. What are 4 key traits of seedless vascular plants?
- Q. What are the 3 types of vascular plants?
- Q. What makes a plant vascular?
- Q. What is the difference between a vascular plant and a nonvascular plant?
- Q. What are plants that have vascular tissue called?
- Q. What is the main function of vascular tissue in plant?
- Q. Which is the first vascular plant?
- Q. What is the era and period of first vascular land plants?
- Q. What are the first vascular and true land plants?
- Q. Which type of plant is not vascular?
- Q. Which of the following is non vascular?
- Q. Is Cactus a vascular plant?
- Q. Is a grass a vascular plant?
- Q. What is another name for seedless plants?
- Q. Do vascular plants grow close to the ground?
- Q. What traits allowed vascular plants to grow tall?
- Q. What allows a plant’s vascular system to work as a transport system?
- Q. Do Vascular Plants make their own food?
- Q. Why are vascular plants successful?
- Q. What is the main division of non vascular plants?
- Q. Which plants are seedless?
Q. What are 4 key traits of seedless vascular plants?
What are some characteristics about Seedless Vascular Plants? Seedless vascular plants include ferns, whisk ferns, club mosses, and horsetails. The plants do not produce seeds so, like bryophytes, they are dispersed (spread) by windblown spores. The gametophyte and sporophyte are independent.
Q. What are the 3 types of vascular plants?
The ferns, gymnosperms, and flowering plants are all vascular plants.
Q. What makes a plant vascular?
Vascular system, in plants, assemblage of conducting tissues and associated supportive fibres. Xylem tissue transports water and dissolved minerals to the leaves, and phloem tissue conducts food from the leaves to all parts of the plant.
Q. What is the difference between a vascular plant and a nonvascular plant?
The main difference between vascular and nonvascular plants is that a vascular plant has vascular vessels to carry water and food to all the different parts of the plant. Nonvascular plants are most commonly found in moist environments, which ensures they get enough water without relying on roots.
Q. What are plants that have vascular tissue called?
Vascular plants include the clubmosses, horsetails, ferns, gymnosperms (including conifers) and angiosperms (flowering plants). Scientific names for the group include Tracheophyta, Tracheobionta and Equisetopsida sensu lato.
Q. What is the main function of vascular tissue in plant?
The vascular tissues of plants, which are composed of specialized conducting tissues, xylem and phloem, form continuous systems through the plant body and provide transport pathways for water, nutrients, and signaling molecules and support a plant body against mechanical stresses.
Q. Which is the first vascular plant?
Cooksonia
Q. What is the era and period of first vascular land plants?
The first vascular plants appeared in the late Ordovician period of the Paleozoic Era (approximately 440-485 million years ago).
Q. What are the first vascular and true land plants?
The first fossil records of vascular plants, that is, land plants with vascular tissues, appeared in the Silurian period. The earliest known representatives of this group (mostly from the northern hemisphere) are placed in the genus Cooksonia.
Q. Which type of plant is not vascular?
Mosses
Q. Which of the following is non vascular?
muscular tissue is non vascular tissue .
Q. Is Cactus a vascular plant?
Answer. Cactus is an example of a vascular plant. They have xylem and phloem that transports food, water, and minerals from roots to leaves. These plants can propagate to be extremely enormous because nutrients and water are moved on all plant parts.
Q. Is a grass a vascular plant?
Trees, shrubs, grasses, flowering plants, and ferns are all vascular plants; just about everything that is not a moss, algae, lichen, or fungus (nonvascular plants) is vascular. Nonvascular plants absorb water through membranes rather than roots, although a few mosses and liverworts have similar vascular structures.
Q. What is another name for seedless plants?
Plants that lack vascular tissue, which is formed of specialized cells for the transport of water and nutrients, are referred to as non-vascular plants. Liverworts, mosses, and hornworts are seedless, non-vascular plants that likely appeared early in land plant evolution.
Q. Do vascular plants grow close to the ground?
Non-vascular plants grow closer to the ground because they cannot transfer nutrients and water up to other areas of the organism. Whether tap or fibrous, the roots must continue to grow into new regions of soil to provide the plant with water and minerals.
Q. What traits allowed vascular plants to grow tall?
Vascular plants evolved stems made of vascular tissues and lignin. Because of lignin, stems are stiff, so plants can grow high above the ground where they can get more light and air. Because of their vascular tissues, stems keep even tall plants supplied with water so they don’t dry out in the air.
Q. What allows a plant’s vascular system to work as a transport system?
“A plants vascular system is made up of specialized cells that for straw-like tubes” is the one among the following that allows a plant’s vascular system to work as a transport system.
Q. Do Vascular Plants make their own food?
The phloem carries food (in the form of organic molecules) that the leaves and stems have made by photosynthesis (the process by which plants use light energy to make food from simple chemicals) to parts of the plant that are unable to make their own food (such as the roots and stem tip).
Q. Why are vascular plants successful?
Vascular plants are successful due to better transportation for water, nutrients and reproduction. The xylem and phloem of the vascular bundles allow for distribution of water and food to all parts of the body. This structures allow vascular plants to colonize farther inland.
Q. What is the main division of non vascular plants?
There are three divisions of nonvascular plants—mosses (Division Bryophyta), liverworts (Division Hepatophyta, named for the resemblance of some to small livers), and hornworts (Division Anthocerotophyta, named for the horn-like appearance of their reproductive structures).
Q. Which plants are seedless?
These seedless plants include mosses, liverworts, club mosses, ferns, and horsetails. They reproduce by forming spores.