(a) What are the values of Vmax and Km in the absence of inhibitor? In its presence? ANSWER: In the absence of inhibitor, Vmax = 47.6 micromol/min and Km = 1.1 x 10-5 . In the presence of inhibitor Vmax is the same and the apparent Km = 3.1 x 10-5.
Q. What is the Vmax in the absence of inhibitor?
(a) In the absence of inhibitor, Vmax is 47.6 μmol minute-1, and KM is 1.1 × 10-5 M. In the presence of inhibitor, Vmax is the same, and the apparent KM is 3.1 × 10-5 M.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the Vmax in the absence of inhibitor?
- Q. How are the kinetics of an enzyme catalyzed reaction affected by a competitive inhibitor?
- Q. What’s km in enzyme kinetics?
- Q. What is a normal Km value?
- Q. What does km value indicate?
- Q. What does a higher Km value mean?
- Q. Is Vmax dependent on substrate concentration?
- Q. What does a high kcat km mean?
- Q. Do inhibitors affect kcat?
- Q. Does kcat affect Vmax?
- Q. How are kcat and KM related?
- Q. What is significance of kcat km parameter?
- Q. How do you find kcat from Km and Vmax?
- Q. Why is lower km better?
- Q. Does km depend on temperature?
- Q. How do you calculate Km and Vmax on a graph?
- Q. What km means?
- Q. What is an example of a kilometer?
- Q. Who uses km?
- Q. How far away is 1 km?
- Q. Is 1 km a long walk?
- Q. How many clicks is a mile?
- Q. How far down is 1000 meters?
- Q. How many football fields is 1000 meters?
- Q. What is a 1000 meter run?
- Q. How many seconds are 1000?
- Q. How many seconds is 700?
- Q. How much is a 1000 minutes?
- Q. How many hours and minutes is 1000 seconds?
Q. How are the kinetics of an enzyme catalyzed reaction affected by a competitive inhibitor?
Competitive inhibitors INCREASE the Km of the enzyme but does not affect Kcat or Vmax (still gets to same Vmax level).
Q. What’s km in enzyme kinetics?
The rate of reaction when the enzyme is saturated with substrate is the maximum rate of reaction, Vmax. This is usually expressed as the Km (Michaelis constant) of the enzyme, an inverse measure of affinity. For practical purposes, Km is the concentration of substrate which permits the enzyme to achieve half Vmax.
Q. What is a normal Km value?
For most enzymes, KM lies between 10^-1 and 10^-7 M. The KM value for an enzyme depends on the particular substrate and on environmental conditions such as pH, temperature, and ionic strength.
Q. What does km value indicate?
It indicates the affinity of an enzyme for a given substrate: the lower the KM value, the higher the affinity of the enzyme for the substrate.
Q. What does a higher Km value mean?
We define Km as the substrate concentration that gives Vmax/2. The higher the Km of an enzyme, the LOWER its affinity for its substrate. This is because a high Km means that it takes a LOT of substrate before the enzyme gets to Vmax/2.
Q. Is Vmax dependent on substrate concentration?
Although enzymes are catalysts, Vmax does depend on the enzyme concentration, because it is just a rate, mol/sec – more enzyme will convert more substrate moles into product.
Q. What does a high kcat km mean?
The higher the Kcat is, the more substrates get turned over in one second. Km is the concentration of substrates when the reaction reaches half of Vmax. A small Km indicates high affinity since it means the reaction can reach half of Vmax in a small number of substrate concentration.
Q. Do inhibitors affect kcat?
Uncompetitive inhibitors bind only to the enzyme–substrate complex, not to the free enzyme, and they decrease both kcat and Km (the decrease in Km stems from the fact that their presence pulls the system away from free enzyme toward the enzyme–substrate complex).
Q. Does kcat affect Vmax?
Kcat is equal to Vmax/[Enzyme]. Because the concentration of enzyme is taken into account in this equation, Kcat does NOT vary with the amount of enzyme used and is therefore a constant for an enzyme. Kcat is equal to the number of molecules of product made per enzyme per unit time.
Q. How are kcat and KM related?
kcat is the turnover number, the number of times each enzyme site converts substrate to product per unit time. Km is the Michaelis-Menten constant, in the same units as X. It is the substrate concentration needed to achieve a half-maximum enzyme velocity. Et is the concentration of enzyme catalytic sites.
Q. What is significance of kcat km parameter?
The ratio between these two parameters, kcat /KM, usually referred. to as the specificity constant, is in turn a useful indicator of the relative efficiency. of an enzyme acting simultaneously on two competing substrates, A and B, whose. KM values equal the Ki for the other reaction.
Q. How do you find kcat from Km and Vmax?
- TURNOVER NUMBER (kcat) – CATALYTIC CONSTANT.
- turnover number = kcat = Vmax/[ET]
- kcat/KM = catalytic efficiency.
Q. Why is lower km better?
Km turns out to be the concentration of substrate required to get an enzymatic reaction to half maximum velocity. Km provides a measure of an enzyme’s “affinity” for its substrate. An enzyme with a high Km has a low affinity for its substrate. An enzyme with a low Km has a high affinity for its substrate.
Q. Does km depend on temperature?
Abstract. A number of enzymes that are used in clinical analysis have been studied in relation to the effect of temperature on their activity. In most cases, Km did not increase as fast as Vmax, consequently the enzyme efficiency, Vmax/Km, also increased slightly with temperature.
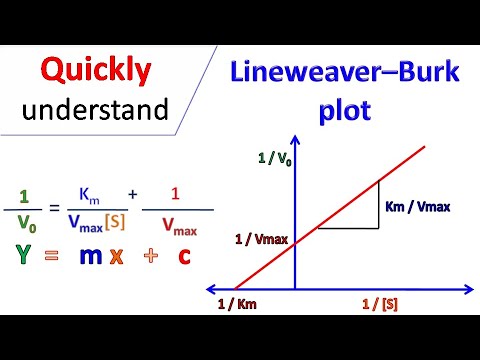
Q. How do you calculate Km and Vmax on a graph?
From the graph find the maximum velocity and half it i.e. Vmax/2. Draw a horizontal line from this point till you find the point on the graph that corresponds to it and read off the substrate concentration at that point. This will give the value of Km.
Q. What km means?
The kilometre (SI symbol: km; /ˈkɪləmiːtər/ or /kɪˈlɒmɪtər/), spelt kilometer in American English, is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to one thousand metres (kilo- being the SI prefix for 1000). A slang term for the kilometre in the US and UK militaries is klick.
Q. What is an example of a kilometer?
The definition of a kilometer is a unit of measurement equal to 1,000 meters or . 6214 miles. An example of a kilometer is how far a person will run if she wants to run for just over 1/2 of a mile. A unit of length in the metric system equal to 1,000 meters (0.62 mile).
Q. Who uses km?
Despite the UK having officially converted to the metric system, they still use mph as well. Japan is one of the countries that uses kph as a unit of measure, as well as Australia, China, India, the UAE, and rest of 81% of the world.
Q. How far away is 1 km?
Kilometers to Miles table
| Kilometers | Miles |
|---|---|
| 1 km | 0.62 mi |
| 2 km | 1.24 mi |
| 3 km | 1.86 mi |
| 4 km | 2.49 mi |
Q. Is 1 km a long walk?
Kilometer: A kilometer is 0.62 miles, which is also 3281.5 feet, or 1000 meters. It takes 10 to 12 minutes to walk at a moderate pace. Mile: A mile is 1.61 kilometers or 5280 feet. It takes 15 to 20 minutes to walk 1 mile at a moderate pace.
Q. How many clicks is a mile?
1.609344
Q. How far down is 1000 meters?
How far is 1,000 meters in miles? 1,000 m to mi conversion. A meter, or metre, is the fundamental unit of length in the metric system, from which all other length units are based. It is equal to 100 centimeters, 1/1000th of a kilometer, or about 39.37 inches….Convert 1,000 Meters to Miles.
| m | mi |
|---|---|
| 1,000 | 0.62137 |
| 1,010 | 0.62758 |
| 1,020 | 0.63380 |
| 1,030 | 0.64001 |
Q. How many football fields is 1000 meters?
AREA Units Conversion square-meters to football-fields
| Square Meters | to Football Fields (table conversion) |
|---|---|
| 800 m2, sq m | = 0.ff |
| 900 m2, sq m | = 0.ff |
| 1000 m2, sq m | = 0.ff |
| 2000 m2, sq m | = 0.ff |
Q. What is a 1000 meter run?
The 1000 metres is an uncommon middle-distance running event in track and field competitions. The 1000 yards, an imperial alternative, was sometimes also contested.
Q. How many seconds are 1000?
Convert 1,000 Hours to Seconds
| hr | s |
|---|---|
| 1,000 | 3,600,000 |
| 1,010 | 3,636,000 |
| 1,020 | 3,672,000 |
| 1,030 | 3,708,000 |
Q. How many seconds is 700?
This conversion of 700 seconds to minutes has been calculated by multiplying 700 seconds by 0.0166 and the result is 11.6666 minutes.
Q. How much is a 1000 minutes?
Convert 1,000 Minutes to Hours
| min | hr |
|---|---|
| 1,000 | 16.667 |
| 1,010 | 16.833 |
| 1,020 | 17 |
| 1,030 | 17.167 |
Q. How many hours and minutes is 1000 seconds?
This conversion of 1,000 seconds to hours has been calculated by multiplying 1,000 seconds by 0.0002 and the result is 0.2777 hours.