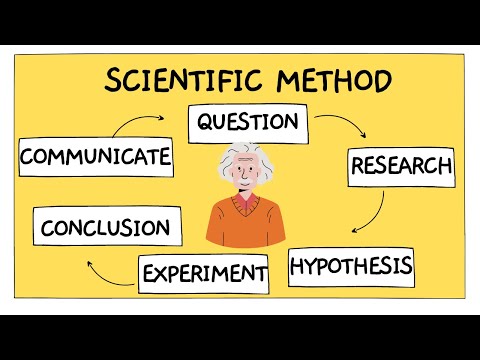
The scientific method
Q. Why is the scientific method important in biology?
When conducting research, scientists use the scientific method to collect measurable, empirical evidence in an experiment related to a hypothesis (often in the form of an if/then statement), the results aiming to support or contradict a theory.
Table of Contents
- Q. Why is the scientific method important in biology?
- Q. How the scientific method is used to develop new knowledge?
- Q. How do I make a flow chart?
- Q. What are three different paths you can take to explore a new topic scientifically?
- Q. What is real process?
- Q. What is the order of experiment?
- Q. How is science a process?
- Q. What is the job of the process owner?
- Q. Who is the process owner Six Sigma?
- Q. What is a process role?
- Q. Who should be the control owner?
- Q. Who is a risk owner?
- Q. What is a control owner?
- Q. What is control gap?
- Q. How do you identify a process gap?
Q. How the scientific method is used to develop new knowledge?
Scientific method is a body of techniques for investigating phenomena, acquiring new knowledge, or correcting and integrating previous knowledge. Scientific researchers propose hypotheses as explanations of phenomena, and design experimental studies to test these hypotheses.
- Make an observation.
- Ask a question.
- Form a hypothesis, or testable explanation.
- Make a prediction based on the hypothesis.
- Test the prediction.
- Iterate: use the results to make new hypotheses or predictions.
Q. How do I make a flow chart?
Create a flowchart
- Click the File tab.
- Click New, click Flowchart, and then under Available Templates, click Basic Flowchart.
- Click Create.
- For each step in the process that you are documenting, drag a flowchart shape onto your drawing.
- Connect the flowchart shapes in either of the following ways.
Q. What are three different paths you can take to explore a new topic scientifically?
Steps in the Scientific Method
- 1 – Make an Observation. You can’t study what you don’t know is there.
- 2 – Ask a Question.
- 3 – Do Background Research.
- 4 – Form a Hypothesis.
- 5 – Conduct an Experiment.
- 6 – Analyze Results and Draw a Conclusion.
- 7 – Report Your Results.
Q. What is real process?
Successive investigations of a topic often lead back to the same question, but at deeper and deeper levels. Real process of science (3 of 3) The process of science is not predetermined.
Q. What is the order of experiment?
The usual steps include observation, hypothesis, experiment, and conclusion. The steps may not always be completed in the same order. Following the four steps, the results of the experiment will either support the hypothesis or will not support the hypothesis.
Q. How is science a process?
Science is a process. Scientific ideas are developed through reasoning. Inferences are logical conclusions based on observable facts. Much of what we know from scientific study is based on inferences from data, whether the object of study is a star or an atom.
Q. What is the job of the process owner?
A process owner is responsible for managing a process from end-to-end. Their responsibility includes implementation, maintenance and improvement of this process. Process owners are most effective when they understand how their process interacts with upstream and downstream processes.
Q. Who is the process owner Six Sigma?
The role of a process owner is enormous in Six Sigma roll out. A Process Owner is a person, who is accountable for the performance of the process and manages the process on a daily basis. Sometimes, he is the leader who commands his team on the deliverables and action items.
Q. What is a process role?
Process roles are names for whoever performs certain tasks in a process. A name like ‘hiring manager’ isn’t a job title; it is just one of many roles that someone performs as part of their job.
Q. Who should be the control owner?
A person or entity with accountability for ensuring that the control activity is in place and is operating effectively. The control owner does not necessarily perform the control activity, however, if not conducting the control, they should have a level of oversight of its performance.
Q. Who is a risk owner?
A risk owner is an accountable point of contact for an enterprise risk at the senior leadership level, who coordinates efforts to mitigate and manage the risk with various individuals who own parts of the risk. The responsibilities of the risk owner are to ensure that: Risks are clearly articulated in risk statements.
Q. What is a control owner?
A control owner is accountable for implementing and maintaining the effectiveness of specific controls as recorded in a risk register, in a position description or in organisational policies and procedures. Control owners may also be responsible for designing or modifying controls to improve their effectiveness.
Q. What is control gap?
A control gap occurs when a control does not exist, does not effectively mitigate a risk or is not operating effectively. Control gaps can relate to the design effectiveness of operating effectiveness of the control.
Q. How do you identify a process gap?
WHAT
- Identify current process gaps and categorize by impact area.
- Combine to eliminate duplicates and move forward with only unique gaps.
- Rate how big an impact closing the gaps will have on your desired state.
- Prioritize the top-rated gaps against your key goals.
- Develop a specific action plan to close the gaps.