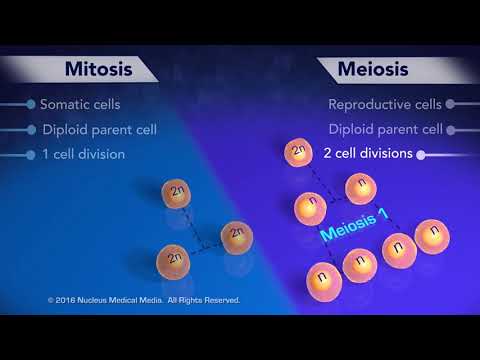
Mitosis consists of one stage whereas meiosis consists of two stages. Mitosis produces diploid cells (46 chromosomes) whereas meiosis produces haploid cells (23 chromosomes). Mitosis produces two identical daughter cells whereas meiosis produces four genetically different daughter cells.
Q. What are the 2 main differences between prophase 1 of meiosis and prophase of mitosis?
Search for: What is the difference between prophase 1 and prophase?
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the 2 main differences between prophase 1 of meiosis and prophase of mitosis?
- Q. What distinguishes prophase 1 of meiosis from prophase of mitosis?
- Q. What happens during prophase of mitosis?
- Q. What 3 things happen during prophase?
- Q. What is the purpose of prophase?
- Q. What are all the parts of cell division?
- Q. What type of cell is meiosis?
- Q. What are the two parts of mitosis?
- Q. What is mitosis explain with diagram?
- Q. What type of cell does mitosis create?
- Q. What are the 3 main parts of cell division?
- Q. What are the four functions of mitosis?
- Q. What are the main two functions of mitosis?
- Q. What are the three main functions of mitosis?
- Q. Which is not function of mitosis *?
- Q. What are the three important functions of meiosis?
Q. What distinguishes prophase 1 of meiosis from prophase of mitosis?
Search for: What two things happen during prophase 1?
Q. What happens during prophase of mitosis?
Prophase is the first phase of mitosis, the process that separates the duplicated genetic material carried in the nucleus of a parent cell into two identical daughter cells. During prophase, the complex of DNA and proteins contained in the nucleus, known as chromatin, condenses.
Q. What 3 things happen during prophase?
Mitotic prophase These copies are referred to as sister chromatids and are attached by DNA element called the centromere. The main events of prophase are: the condensation of chromosomes, the movement of the centrosomes, the formation of the mitotic spindle, and the beginning of nucleoli break down.
Q. What is the purpose of prophase?
Q. What are all the parts of cell division?
These phases are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Cytokinesis is the final physical cell division that follows telophase, and is therefore sometimes considered a sixth phase of mitosis.
Q. What type of cell is meiosis?
Meiosis is the form of eukaryotic cell division that produces haploid sex cells or gametes (which contain a single copy of each chromosome) from diploid cells (which contain two copies of each chromosome).
Q. What are the two parts of mitosis?
Flemming divided mitosis into two broad parts: a progressive phase, during which the chromosomes condensed and aligned at the center of the spindle, and a regressive phase, during which the sister chromatids separated.
Q. What is mitosis explain with diagram?
Mitosis is the phase of the cell cycle where the nucleus of a cell is divided into two nuclei with an equal amount of genetic material in both the daughter nuclei. It succeeds the G2 phase and is succeeded by cytoplasmic division after the separation of the nucleus.
Q. What type of cell does mitosis create?
During mitosis, a eukaryotic cell undergoes a carefully coordinated nuclear division that results in the formation of two genetically identical daughter cells. Mitosis itself consists of five active steps, or phases: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Q. What are the 3 main parts of cell division?
One “turn” or cycle of the cell cycle consists of three general phases: interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis.
Q. What are the four functions of mitosis?
There are four key reasons why a cell may be required to divide mitotically:
- Tissue repair / replacement.
- Organismal growth.
- Asexual reproduction.
- Development (of embryos)
Q. What are the main two functions of mitosis?
The main functions of mitosis are growth and repair. Some cells once fully formed do not undergo cell division, such as nerve cells and muscle cells.
Q. What are the three main functions of mitosis?
Mitosis is important for three main reasons: development and growth cell replacement and asexual reproduction.
Q. Which is not function of mitosis *?
C. This is not one of the functions of mitosis. The production of gametes from diploid cells is one of the functions of meiosis.
Q. What are the three important functions of meiosis?
Meiosis is important for three main reasons: it allows sexual reproduction of diploid organisms, it enables genetic diversity, and it aids the repair of genetic defects.